本文將為您介紹Aggregator的執行機制、相關API,並以Kmeans Clustering為例說明Aggregator的具體用法。
Aggregator是MaxCompute Graph作業中常用的特徵,特別適用於解決機器學習問題。MaxCompute Graph中,Aggregator用於匯總並處理全域資訊。
Aggregator機制
Aggregator的邏輯分為兩部分:
一部分在所有Worker上執行,即分布式執行。
一部分只在Aggregator Owner所在的Worker上執行,即單點執行。
其中,在所有Worker上執行的操作包括建立初始值及局部彙總,然後將局部彙總結果發送給Aggregator Owner所在的Worker上。Aggregator Owner所在的Worker上彙總普通Worker發送過來的局部彙總對象,得到全域彙總結果,然後判斷迭代是否結束。全域彙總的結果會在下一輪超步(迭代)分發給所有Worker,供下一輪迭代使用。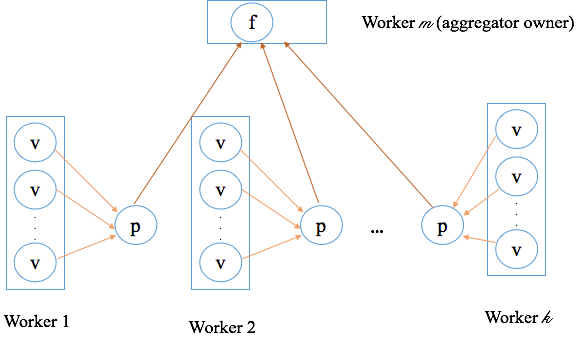
Aggregator的基本流程如下:
每個Worker啟動時執行createStartupValue用於建立AggregatorValue。
每輪迭代開始前,每個Worker執行createInitialValue來初始化本輪的AggregatorValue。
一輪迭代中每個點通過
context.aggregate()來執行aggregate()實現Worker內的局部迭代。每個Worker將局部迭代結果發送給AggregatorOwner所在的Worker。
AggregatorOwner所在Worker執行多次
merge,實現全域彙總。AggregatorOwner所在Worker執行
terminate用於處理全域彙總結果,並決定是否結束迭代。
Aggregator的API
Aggregator共提供了5個API供您實現。API的調用時機及常規用途如下:
createStartupValue(context)
該API在所有Worker上執行一次,調用時機是所有超步開始之前,通常用於初始化
AggregatorValue。在第0輪超步中,調用WorkerContext.getLastAggregatedValue()或ComputeContext.getLastAggregatedValue()可以擷取該API初始化的AggregatorValue對象。createInitialValue(context)
該API在所有Worker上每輪超步開始時調用一次,用於初始化本輪迭代所用的
AggregatorValue。通常操作是通過WorkerContext.getLastAggregatedValue()得到上一輪迭代的結果,然後執行部分初始化操作。aggregate(value, item)
該API同樣在所有Worker上執行,與上述API不同的是,該API由使用者顯示調用
ComputeContext#aggregate(item)來觸發,而上述兩個API由架構自動調用。該API用於執行局部彙總操作,其中第一個參數value是本Worker在該輪超步已經彙總的結果(初始值是createInitialValue返回的對象),第二個參數是您的代碼調用ComputeContext#aggregate(item)傳入的參數。該API中通常用item來更新value實現彙總。所有aggregate執行完後,得到的value就是該Worker的局部彙總結果,然後由架構發送給Aggregator Owner所在的Worker。merge(value, partial)
該API執行於Aggregator Owner所在Worker,用於合并各Worker局部彙總的結果,達到全域彙總對象。與
aggregate類似,value是已經彙總的結果,而partial待彙總的對象,同樣用partial更新value。假設有3個Worker,分別是w0、w1、w2,其局部彙總結果是p0、p1、p2。例如,發送到Aggregator Owner所在Worker的順序為p1、p0、p2,則
merge執行次序為:首先執行
merge(p1, p0),這樣p1和p0就彙總為p1。然後執行
merge(p1, p2),p1和p2彙總為p1,而p1即為本輪超步全域彙總的結果。
由上述樣本可見,當只有一個Worker時,不需要執行
merge方法,即merge()不會被調用。terminate(context, value)
當Aggregator Owner所在Worker執行完
merge()後,架構會調用terminate(context, value)執行最後的處理。其中第二個參數value,即為merge()最後得到全域彙總,在該方法中可以對全域彙總繼續修改。執行完terminate()後,架構會將全域彙總對象分發給所有Worker,供下一輪超步使用。terminate()方法的一個特殊之處在於,如果返回True,則整個作業就結束迭代,否則繼續執行。在機器學習情境中,通常判斷收斂後返回True以結束作業。
Kmeans Clustering樣本
下面以典型的Kmeans Clustering為例,為您介紹Aggregator的具體用法。
完整代碼請參見Kmeans,此處為解析代碼。
GraphLoader部分
GraphLoader部分用於載入輸入表,並轉換為圖的點或邊。這裡我們輸入表的每行資料為一個樣本,一個樣本構造一個點,並用Vertex的Value來存放樣本。
首先定義一個Writable類
KmeansValue作為Vertex的value類型。public static class KmeansValue implements Writable { DenseVector sample; public KmeansValue() { } public KmeansValue(DenseVector v) { this.sample = v; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { wirteForDenseVector(out, sample); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { sample = readFieldsForDenseVector(in); } }KmeansValue中封裝一個DenseVector對象來存放一個樣本,這裡DenseVector類型來自matrix-toolkits-java,而wirteForDenseVector()及readFieldsForDenseVector()用於實現序列化及還原序列化。自訂的
KmeansReader代碼,如下所示。public static class KmeansReader extends GraphLoader<LongWritable, KmeansValue, NullWritable, NullWritable> { @Override public void load( LongWritable recordNum, WritableRecord record, MutationContext<LongWritable, KmeansValue, NullWritable, NullWritable> context) throws IOException { KmeansVertex v = new KmeansVertex(); v.setId(recordNum); int n = record.size(); DenseVector dv = new DenseVector(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { dv.set(i, ((DoubleWritable)record.get(i)).get()); } v.setValue(new KmeansValue(dv)); context.addVertexRequest(v); } }KmeansReader中,每讀入一行資料建立一個點,這裡用recordNum作為點的ID,將record內容轉換成DenseVector對象並封裝進VertexValue中。Vertex部分
自訂的
KmeansVertex代碼如下。邏輯非常簡單,每輪迭代要做的事情就是將自己維護的樣本執行局部彙總。具體邏輯參見下面Aggregator的實現。public static class KmeansVertex extends Vertex<LongWritable, KmeansValue, NullWritable, NullWritable> { @Override public void compute( ComputeContext<LongWritable, KmeansValue, NullWritable, NullWritable> context, Iterable<NullWritable> messages) throws IOException { context.aggregate(getValue()); } }Aggregator部分
整個Kmeans的主要邏輯集中在Aggregator中。首先是自訂的
KmeansAggrValue,用於維護要彙總及分發的內容。public static class KmeansAggrValue implements Writable { DenseMatrix centroids; DenseMatrix sums; // used to recalculate new centroids DenseVector counts; // used to recalculate new centroids @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { wirteForDenseDenseMatrix(out, centroids); wirteForDenseDenseMatrix(out, sums); wirteForDenseVector(out, counts); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { centroids = readFieldsForDenseMatrix(in); sums = readFieldsForDenseMatrix(in); counts = readFieldsForDenseVector(in); } }KmeansAggrValue維護了3個對象:centroids是當前的K個中心點。如果樣本是m維,centroids就是一個K*m的矩陣。sums是和centroids大小一樣的矩陣,每個元素記錄了到特定中心點最近的樣本特定維之和。例如sums(i,j)是到第i個中心點最近的樣本的第j維度之和。counts是個K維的向量,記錄到每個中心點距離最短的樣本個數。sums和counts一起用於計算新的中心點,也是要彙總的主要內容。
接下來是自訂的Aggregator實作類別
KmeansAggregator,按照上述API的順序分析其實現。createStartupValue()的實現。public static class KmeansAggregator extends Aggregator<KmeansAggrValue> { public KmeansAggrValue createStartupValue(WorkerContext context) throws IOException { KmeansAggrValue av = new KmeansAggrValue(); byte[] centers = context.readCacheFile("centers"); String lines[] = new String(centers).split("\n"); int rows = lines.length; int cols = lines[0].split(",").length; // assumption rows >= 1 av.centroids = new DenseMatrix(rows, cols); av.sums = new DenseMatrix(rows, cols); av.sums.zero(); av.counts = new DenseVector(rows); av.counts.zero(); for (int i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) { String[] ss = lines[i].split(","); for (int j = 0; j < ss.length; j++) { av.centroids.set(i, j, Double.valueOf(ss[j])); } } return av; } }在該方法中初始化一個
KmeansAggrValue對象,然後從資源檔centers中讀取初始中心點,並賦值給centroids。而sums和counts初始化為0。createInitialValue()的實現。@Override public KmeansAggrValue createInitialValue(WorkerContext context) throws IOException { KmeansAggrValue av = (KmeansAggrValue)context.getLastAggregatedValue(0); // reset for next iteration av.sums.zero(); av.counts.zero(); return av; }該方法首先擷取上一輪迭代的
KmeansAggrValue,然後將sums和counts清零,只保留了上一輪迭代出的centroids。aggregate()的實現。@Override public void aggregate(KmeansAggrValue value, Object item) throws IOException { DenseVector sample = ((KmeansValue)item).sample; // find the nearest centroid int min = findNearestCentroid(value.centroids, sample); // update sum and count for (int i = 0; i < sample.size(); i ++) { value.sums.add(min, i, sample.get(i)); } value.counts.add(min, 1.0d); }該方法中調用
findNearestCentroid()找到樣本item距離最近的中心點索引,然後將其各個維度加到sums上,最後counts計數加1。
以上3個方法執行於所有Worker上,實現局部彙總。在Aggregator Owner所在Worker執行的全域彙總相關操作如下:
merge()的實現。@Override public void merge(KmeansAggrValue value, KmeansAggrValue partial) throws IOException { value.sums.add(partial.sums); value.counts.add(partial.counts); }merge的實現邏輯很簡單,就是把各個Worker彙總出的sums和counts相加即可。terminate()的實現。@Override public boolean terminate(WorkerContext context, KmeansAggrValue value) throws IOException { // Calculate the new means to be the centroids (original sums) DenseMatrix newCentriods = calculateNewCentroids(value.sums, value.counts, value.centroids); // print old centroids and new centroids for debugging System.out.println("\nsuperstep: " + context.getSuperstep() + "\nold centriod:\n" + value.centroids + " new centriod:\n" + newCentriods); boolean converged = isConverged(newCentriods, value.centroids, 0.05d); System.out.println("superstep: " + context.getSuperstep() + "/" + (context.getMaxIteration() - 1) + " converged: " + converged); if (converged || context.getSuperstep() == context.getMaxIteration() - 1) { // converged or reach max iteration, output centriods for (int i = 0; i < newCentriods.numRows(); i++) { Writable[] centriod = new Writable[newCentriods.numColumns()]; for (int j = 0; j < newCentriods.numColumns(); j++) { centriod[j] = new DoubleWritable(newCentriods.get(i, j)); } context.write(centriod); } // true means to terminate iteration return true; } // update centriods value.centroids.set(newCentriods); // false means to continue iteration return false; }teminate()中首先根據sums和counts調用calculateNewCentroids()求平均計算出新的中心點。然後調用isConverged()根據新老中心點歐拉距離判斷是否已經收斂。如果收斂或迭代次數達到最大數,則將新的中心點輸出並返回True,以結束迭代。否則更新中心點並返回False以繼續迭代。
main方法main方法用於構造GraphJob,然後設定相應配置,並提交作業。public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { if (args.length < 2) printUsage(); GraphJob job = new GraphJob(); job.setGraphLoaderClass(KmeansReader.class); job.setRuntimePartitioning(false); job.setVertexClass(KmeansVertex.class); job.setAggregatorClass(KmeansAggregator.class); job.addInput(TableInfo.builder().tableName(args[0]).build()); job.addOutput(TableInfo.builder().tableName(args[1]).build()); // default max iteration is 30 job.setMaxIteration(30); if (args.length >= 3) job.setMaxIteration(Integer.parseInt(args[2])); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); job.run(); System.out.println("Job Finished in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000.0 + " seconds"); }說明job.setRuntimePartitioning(false)設定為False後,各個Worker載入的資料不再根據Partitioner重新分區,即誰載入的資料誰維護。