如果您需要將自建Elasticsearch中的全量或增量資料移轉至Elasticsearch,可通過在ECS中自建Logstash,並通過Logstash的管道配置功能實現。本文在ECS上部署自建Elasticsearch和自建Logstash,並通過Logstash將自建Elasticsearch中的資料全量遷移至Elasticsearch。
注意事項
自建Logstash所在的ECS需要與Elasticsearch叢集在同一專用網路下,同時該Logstash需要能夠同時訪問源Elasticsearch叢集(自建)和目標Elasticsearch叢集(阿里雲)。
資料移轉可以全量遷移或增量遷移。如果業務側時刻存在寫入更新,首次遷移時,需先全量遷移,再通過時間識別欄位(或其他可識別值增量的欄位)進行增量遷移,否則遷移後新資料極易被舊資料覆蓋。如果已有全量資料,可以只通過識別欄位實現增量資料移轉。
操作流程
開通Elasticsearch服務,在ECS伺服器部署自建Elasticsearch、準備待遷移資料和部署自建Logstash。
在ECS伺服器運行Python指令碼遷移索引中繼資料。
通過Logstash管道配置功能,將自建Elasticsearch中的全量資料移轉至Elasticsearch中。
步驟一:準備環境與執行個體
建立Elasticsearch執行個體。
具體操作請參見建立Elasticsearch執行個體。本文使用的測試環境如下。
環境項
環境資訊
地區
華東1(杭州)。
版本
通用商業版7.10.0。
執行個體規格配置
3個可用性區域、3個資料節點、單節點4核CPU、16 GB記憶體、100 GB ESSD雲端硬碟。
建立ECS執行個體,用於部署自建Elasticsearch、自建Kibana和自建Logstash。
具體操作請參見自訂購買執行個體。本文使用的測試環境如下。
環境項
環境資訊
地區
華東1(杭州)。
執行個體規格
4 vCPU 16 GiB記憶體。
鏡像
公用鏡像、CentOS 7.9 64位。
儲存
系統硬碟、ESSD雲端硬碟、100 GiB。
網路
與Elasticsearch相同的專用網路,選中分配公網IPv4地址,並按使用流量計費,頻寬峰值為100 Mbps。
安全性群組
入方向添加5601連接埠(即Kibana連接埠),在授權對象中添加您用戶端的IP地址。
重要如果您的用戶端處在家用網路或公司區域網路中,您需要在授權對象中添加區域網路的公網出口IP地址,而非用戶端機器的IP地址。建議您通過瀏覽器訪問cip.cc查詢。
您也可以在授權對象中添加0.0.0.0/0,表示允許所有IPv4地址訪問ECS執行個體。此配置會導致ECS執行個體完全暴露在公網中,增加安全風險,生產環境盡量避免。
部署自建Elasticsearch。
本文使用的自建Elasticsearch版本為7.6.2,1個資料節點,具體操作步驟如下:
串連ECS伺服器。
具體操作,請參見通過密碼或密鑰認證登入Linux執行個體。
使用root使用者權限建立elastic使用者。
useradd elastic設定elastic使用者的密碼。
passwd elastic系統將提示您輸入和確認elastic使用者的密碼。
將root使用者切換為elastic使用者。
su -l elastic下載Elasticsearch軟體安裝包並解壓縮。
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.6.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zvxf elasticsearch-7.6.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz啟動Elasticsearch。
進入Elasticsearch的安裝目錄下,啟動服務。
cd elasticsearch-7.6.2 ./bin/elasticsearch -d驗證Elasticsearch服務是否正常運行。
cd ~ curl localhost:9200正常情況下,返回結果中會顯示Elasticsearch版本號碼和
"You Know, for Search"。
部署自建Kibana,並準備測試資料。
本文使用的自建Kibana版本為7.6.2,1個資料節點,具體操作步驟如下:
串連ECS伺服器。
具體操作請參見通過密碼或密鑰認證登入Linux執行個體。
說明本文檔以普通使用者權限為例。
下載Kibana軟體安裝包並解壓縮。
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.6.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zvxf kibana-7.6.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz修改Kibana設定檔config/kibana.yml,增加
server.host: "0.0.0.0"配置,允許通過公網IP訪問Kibana。進入Kibana安裝目錄,修改kibana.yml。
cd kibana-7.6.2-linux-x86_64 vi config/kibana.yml
使用非root使用者啟用Kibana。
sudo nohup ./bin/kibana &登入Kibana控制台,添加樣本資料。
通過公網IP地址登入Kibana控制台。
公網IP地址為:http://<ECS伺服器的公網IP地址>:5601/app/kibana#/home。
在Kibana控制台首頁,單擊Try our sample data。
在Sample data頁簽,單擊日誌樣本資料模組下的Add data,添加對應資料。
部署自建Logstash。
本文使用的Logstash版本為7.10.0,1個節點,具體操作步驟如下:
串連ECS伺服器。
具體操作請參見通過密碼或密鑰認證登入Linux執行個體。
說明本文檔以普通使用者權限為例。
回到根目錄,下載Logstash軟體安裝包並解壓縮。
cd ~ wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-7.10.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zvxf logstash-7.10.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz修改Logstash的堆記憶體使用量。
Logstash預設的堆記憶體為1 GB,您需要根據ECS規格配置合適的記憶體大小,加快叢集資料的遷移效率。
進入Logstash的安裝目錄下,修改Logstash設定檔config/jvm.options,增加-Xms8g和-Xmx8g。
cd logstash-7.10.0 sudo vi config/jvm.options
修改Logstash批量寫入記錄條數。
每批量寫入5~15 MB資料,可以加快叢集資料的遷移效率。
修改Logstash設定檔config/pipelines.yml,將每批量寫入記錄條數pipeline.batch.size從125改為5000。
vi config/pipelines.yml
驗證Logstash功能。
通過控制台輸入輸出收集資料。
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { stdout {} }'在控制台中輸入"Hello world!"。
正常情況下,控制台會輸出"Hello world!"。

(可選)步驟二:遷移索引中繼資料(設定和映射)
在進行資料移轉時,Logstash會協助您自動建立索引,但是自動建立的索引可能與您待遷移的索引存在差異,導致遷移前後資料的格式不一致。因此建議您在資料移轉前,在Elasticsearch中手動建立目標索引,確保遷移前後索引資料完全一致。
您可以通過Python指令碼建立目標索引,具體操作步驟如下:
串連ECS伺服器。
具體操作請參見通過密碼或密鑰認證登入Linux執行個體。
說明本文檔以普通使用者權限為例。
建立並開啟Python指令檔(本文以indiceCreate.py為例)。
sudo vi indiceCreate.py修改Python指令檔,拷貝以下代碼(注意修改叢集的串連地址、使用者名稱和密碼)。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 檔案名稱:indiceCreate.py import sys import base64 import time import httplib import json ## 源叢集host。 oldClusterHost = "localhost:9200" ## 源叢集使用者名稱,可為空白。 oldClusterUserName = "elastic" ## 源叢集密碼,可為空白。 oldClusterPassword = "xxxxxx" ## 目的地組群host,可在Elasticsearch執行個體的基本資料頁面擷取。 newClusterHost = "es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200" ## 目的地組群使用者名稱。 newClusterUser = "elastic" ## 目的地組群密碼。 newClusterPassword = "xxxxxx" DEFAULT_REPLICAS = 0 def httpRequest(method, host, endpoint, params="", username="", password=""): conn = httplib.HTTPConnection(host) headers = {} if (username != "") : 'Hello {name}, your age is {age} !'.format(name = 'Tom', age = '20') base64string = base64.encodestring('{username}:{password}'.format(username = username, password = password)).replace('\n', '') headers["Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % base64string; if "GET" == method: headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, headers=headers) else : headers["Content-Type"] = "application/json" conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, body=params, headers=headers) response = conn.getresponse() res = response.read() return res def httpGet(host, endpoint, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("GET", host, endpoint, "", username, password) def httpPost(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("POST", host, endpoint, params, username, password) def httpPut(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("PUT", host, endpoint, params, username, password) def getIndices(host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/_cat/indices" indicesResult = httpGet(oldClusterHost, endpoint, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) indicesList = indicesResult.split("\n") indexList = [] for indices in indicesList: if (indices.find("open") > 0): indexList.append(indices.split()[2]) return indexList def getSettings(index, host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/" + index + "/_settings" indexSettings = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password) print (index + " 原始settings如下:\n" + indexSettings) settingsDict = json.loads(indexSettings) ## 分區數預設和源叢集索引保持一致。 number_of_shards = settingsDict[index]["settings"]["index"]["number_of_shards"] ## 副本數預設為0。 number_of_replicas = DEFAULT_REPLICAS newSetting = "\"settings\": {\"number_of_shards\": %s, \"number_of_replicas\": %s}" % (number_of_shards, number_of_replicas) return newSetting def getMapping(index, host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/" + index + "/_mapping" indexMapping = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password) print (index + " 原始mapping如下:\n" + indexMapping) mappingDict = json.loads(indexMapping) mappings = json.dumps(mappingDict[index]["mappings"]) newMapping = "\"mappings\" : " + mappings return newMapping def createIndexStatement(oldIndexName): settingStr = getSettings(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) mappingStr = getMapping(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) createstatement = "{\n" + str(settingStr) + ",\n" + str(mappingStr) + "\n}" return createstatement def createIndex(oldIndexName, newIndexName=""): if (newIndexName == "") : newIndexName = oldIndexName createstatement = createIndexStatement(oldIndexName) print ("新索引 " + newIndexName + " 的setting和mapping如下:\n" + createstatement) endpoint = "/" + newIndexName createResult = httpPut(newClusterHost, endpoint, createstatement, newClusterUser, newClusterPassword) print ("新索引 " + newIndexName + " 建立結果:" + createResult) ## main indexList = getIndices(oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) systemIndex = [] for index in indexList: if (index.startswith(".")): systemIndex.append(index) else : createIndex(index, index) if (len(systemIndex) > 0) : for index in systemIndex: print (index + " 或許是系統索引,不會重新建立,如有需要,請單獨處理~")執行Python指令碼,建立目標索引。
sudo /usr/bin/python indiceCreate.py參見登入Kibana控制台,登入目的地組群的Kibana控制台,查看已建立的索引。
GET /_cat/indices?v
步驟三:遷移全量資料
串連ECS伺服器。
具體操作請參見通過密碼或密鑰認證登入Linux執行個體。
在config目錄下,建立並開啟Logstash設定檔。
cd logstash-7.10.0/config vi es2es_all.conf參考以下配置,修改Logstash設定檔。
說明8.5版本Logstash的配置參數有所調整,本文同時列出了7.10.0版本和8.5.1版本Logstash的配置樣本。
為了保證遷移資料的準確性,建議您建立多個Logstash管道設定檔,分批次遷移資料,每個Logstash遷移部分資料。
7.10.0版本
input{ elasticsearch{ # 源端ES地址。 hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼。 user => "xxxxxx" password => "xxxxxx" # 需要遷移的索引列表,多個索引以英文以逗號(,)分隔。 index => "kibana_sample_data_*" # 以下三項保持預設即可,包含線程數和遷移資料大小和Logstash JVM配置相關。 docinfo=>true slices => 5 size => 5000 } } filter { # 去掉一些Logstash自己加的欄位。 mutate { remove_field => ["@timestamp", "@version"] } } output{ elasticsearch{ # 目標端ES地址,可在Elasticsearch執行個體的基本資料頁面擷取。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼。 user => "elastic" password => "xxxxxx" # 目標端索引名稱,以下配置表示索引與源端保持一致。 index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}" # 目標端索引type,以下配置表示索引類型與源端保持一致。 document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}" # 目標端資料的id,如果不需要保留原id,可以刪除以下這行,刪除後效能會更好。 document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}" ilm_enabled => false manage_template => false } }8.5.1版本
input{ elasticsearch{ # 源端ES地址。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-uqm3811160002***.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼。 user => "elastic" password => "" # 需要遷移的索引列表,多個索引以英文以逗號(,)分隔。 index => "test_ecommerce" # 以下三項保持預設即可,包含線程數和遷移資料大小和Logstash JVM配置相關。 docinfo => true size => 10000 docinfo_target => "[@metadata]" } } filter { # 去掉一些Logstash自己加的欄位。 mutate { remove_field => ["@timestamp","@version"] } } output{ elasticsearch{ # 目標端ES地址,可在Elasticsearch執行個體的基本資料頁面擷取。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-nwy38aixp0001****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼。 user => "elastic" password => "" # 目標端索引名稱,以下配置表示索引與源端保持一致。 index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}" # 目標端資料的id,如果不需要保留原id,可以刪除以下這行,刪除後效能會更好。 document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}" ilm_enabled => false manage_template => false } }Elasticsearch input外掛程式可以根據配置的查詢語句,從Elasticsearch叢集讀取文檔資料,適用於大量匯入測試日誌等操作。預設讀取完資料後,同步動作會自動關閉,而阿里雲Logstash需保證進程一直運行,關閉後將會重新啟動進程,導致某些單一任務情境(如logstash input es)存在重複寫資料的情況。設定長時間範圍的定時任務可繞過寫重複的情況,如每年3月5日13點20分觸發任務執行,執行完第一次任務後停止管道運行,可避免重複寫情況。可以通過cron文法配合schedule參數實現,詳情請參見Logstash官網Scheduling介紹。
例如,設定3月5日13點20分執行任務:
schedule => "20 13 5 3 *"進入Logstash目錄。
cd ~/logstash-7.10.0啟動Logstash全量遷移任務。
nohup bin/logstash -f config/es2es_all.conf >/dev/null 2>&1 &
步驟四:遷移增量資料
串連ECS伺服器,在config目錄下,建立並開啟Logstash增量設定檔。
cd config vi es2es_kibana_sample_data_logs.conf說明本文檔以普通使用者權限為例。
參考以下配置,修改Logstash設定檔。
7.10.0版本配置樣本如下。
說明8.5版本Logstash的配置參數有所調整,需要去掉
document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}"。按如下指令碼修改Logstash設定檔後,開啟Logstash定時任務即可觸發增量遷移。
input{ elasticsearch{ # 源端ES地址。 hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼。 user => "xxxxxx" password => "xxxxxx" # 需要遷移的索引列表,多個索引使用英文逗號(,)分隔。 index => "kibana_sample_data_logs" # 按時間範圍查詢增量資料,以下配置表示查詢最近5分鐘的資料。 query => '{"query":{"range":{"@timestamp":{"gte":"now-5m","lte":"now/m"}}}}' # 定時任務,以下配置表示每分鐘執行一次。 schedule => "* * * * *" scroll => "5m" docinfo=>true size => 5000 } } filter { # 去掉一些Logstash自己加的欄位. mutate { remove_field => ["@timestamp", "@version"] } } output{ elasticsearch{ # 目標端ES地址,可在Elasticsearch執行個體的基本資料頁面擷取。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全叢集配置登入使用者名稱密碼. user => "elastic" password => "xxxxxx" # 目標端索引名稱,以下配置表示索引與源端保持一致。 index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}" # 目標端索引type,以下配置表示索引類型與源端保持一致。 document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}" # 目標端資料的id,如果不需要保留原id,可以刪除以下這行,刪除後效能會更好。 document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}" ilm_enabled => false manage_template => false } }重要Logstash記錄的時間戳記為UTC時間,如果您的本地時間為北京時間(東八區),那麼兩者會存在8個小時的時區差,此時將UTC時間轉化為北京時間,可使用公式:UTC+時區差=北京時間。例如,以上樣本中通過源端索引中的@timestamp欄位進行range範圍過濾查詢擷取增量資料,並在對應的時間上+8h轉換為北京時間。
通過Logstash控制時間欄位實現增量資料的同步,需確保原索引中有可控制的時間欄位,如果原索引中沒有時間欄位資料,可使用ingest pipeline指定_ingest.timestamp擷取中繼資料值,從而引入@timestamp時間欄位。
進入Logstash目錄。
cd ~/logstash-7.10.0啟動Logstash增量遷移任務。
sudo nohup bin/logstash -f config/es2es_kibana_sample_data_logs.conf >/dev/null 2>&1 &在目標端Elasticsearch叢集的Kibana中,查詢最新動向的記錄,驗證增量資料是否同步。
以下樣本的查詢條件為:索引名稱為kibana_sample_data_logs、最近時間範圍為5分鐘。
GET kibana_sample_data_logs/_search { "query": { "range": { "@timestamp": { "gte": "now-5m", "lte": "now/m" } } }, "sort": [ { "@timestamp": { "order": "desc" } } ] }
步驟五:查看資料移轉結果
查看是否完成全量遷移。
查看自建Elasticsearch叢集的索引和資料量資訊。
GET _cat/indices?v結果如下。

全量遷移前,查看Elasticsearch叢集的索引和資料量資訊。
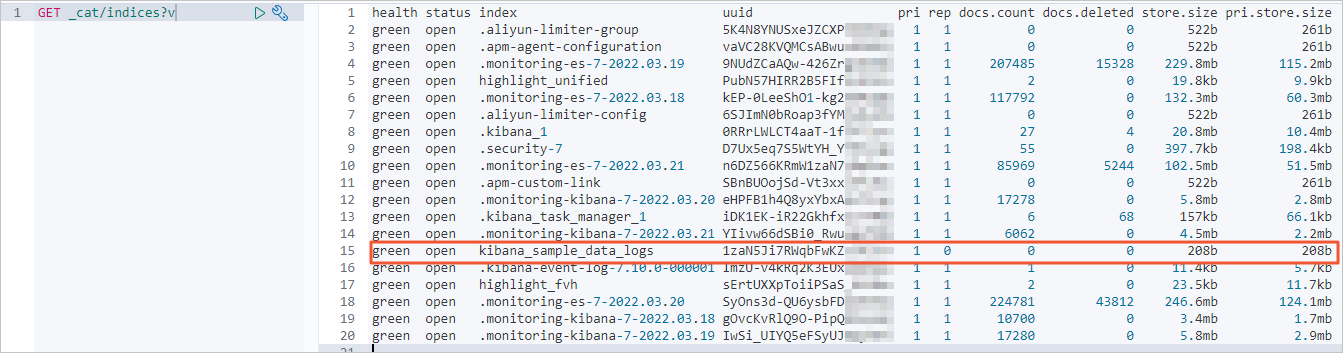
全量遷移後,查看Elasticsearch叢集索引和資料量資訊。
正常情況下,返回的記錄條數應該與自建Elasticsearch叢集一致。

查看是否完成增量遷移。
查看自建Elasticsearch叢集的最新動向記錄。
GET kibana_sample_data_logs/_search { "query": { "range": { "@timestamp": { "gte": "now-5m", "lte": "now/m" } } }, "sort": [ { "@timestamp": { "order": "desc" } } ] }返回結果如下。

增量遷移完成後,使用同樣命令查看Elasticsearch叢集最近的更新記錄。正常情況下,Elasticsearch叢集的更新記錄會與自建叢集一致。