當您的某個微服務應用有安全要求,不希望其它所有應用都能調用時,可以對調用該應用的其它應用進行鑒權,僅允許匹配鑒權規則的應用調用。
背景資訊
下面以一個樣本介紹服務鑒權的使用情境。
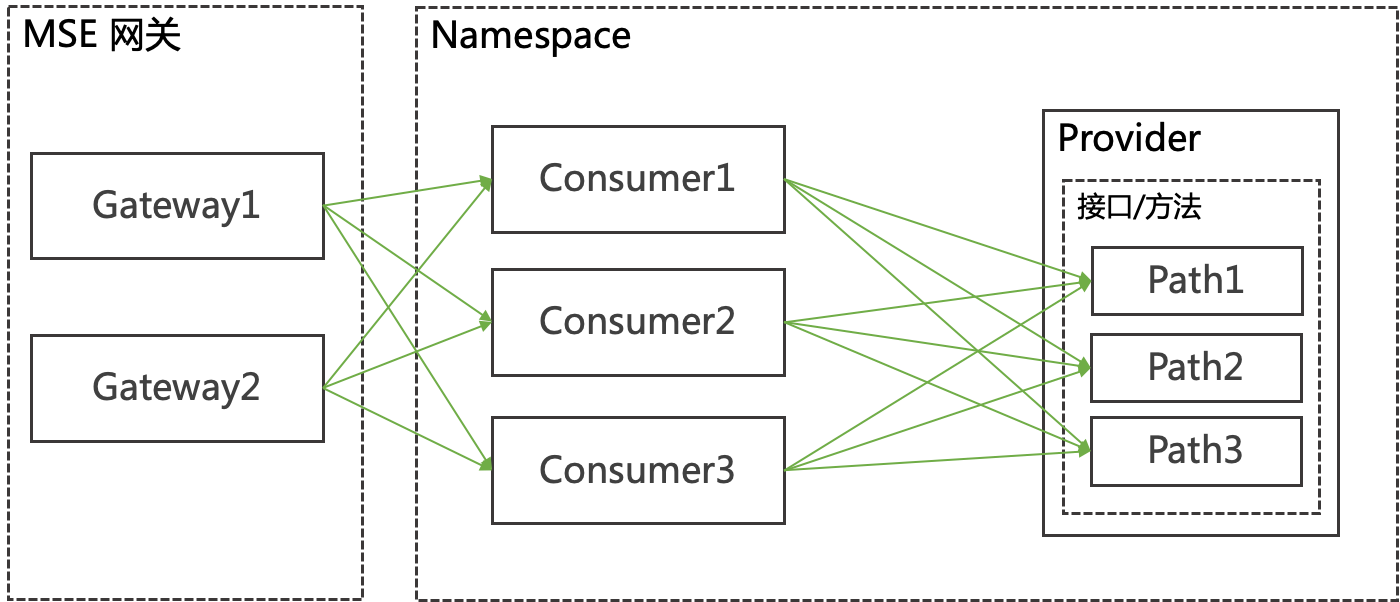
- 未佈建服務鑒權
Consumer 1、2、3和Provider在同一個命名空間內,Consumer 1、2和3預設可以調用Provider的所有Path(Path 1、2和3)。
- 佈建服務鑒權
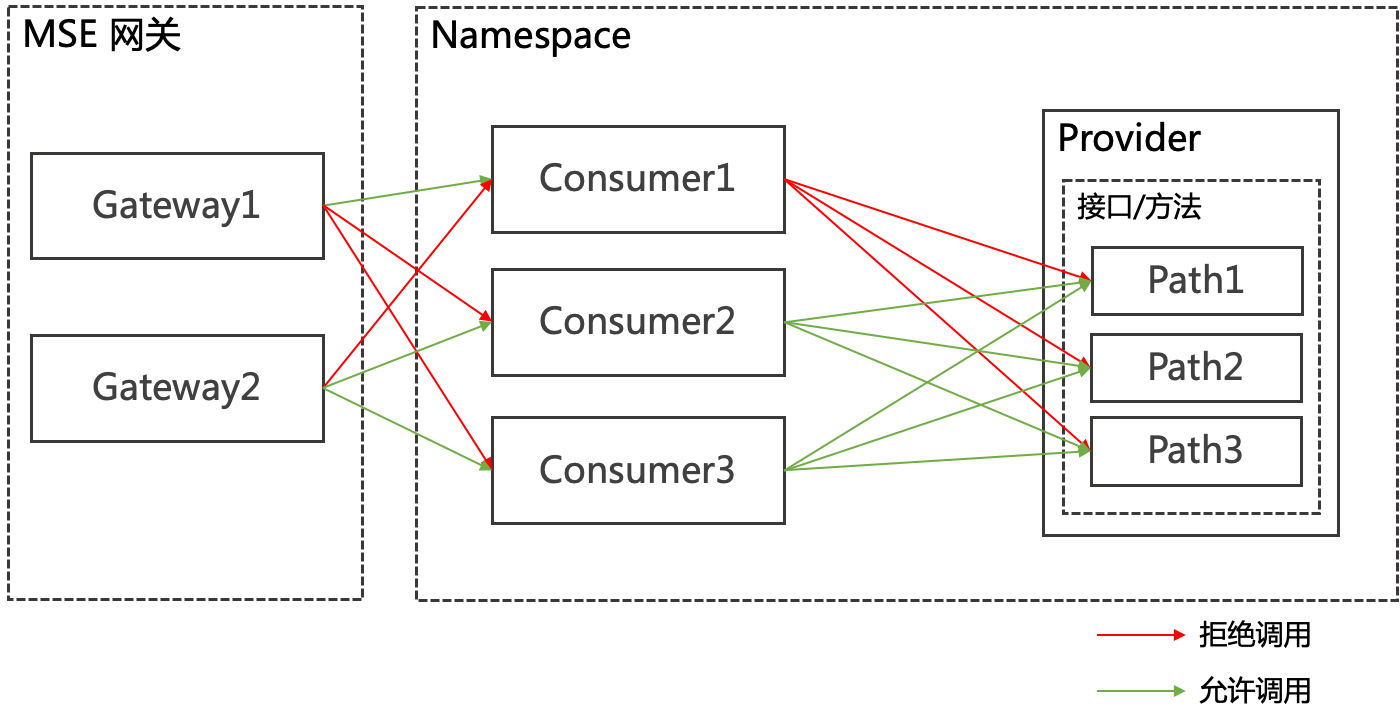
- 設定所有Path的鑒權
可以對Provider的所有Path設定鑒權規則,例如Provider所有Path對Consumer 1的鑒權方式設定為黑名單(拒絕調用),則Consumer 2、3的鑒權方式為白名單(允許調用)。
- 設定指定Path的鑒權
在設定所有Path的鑒權基礎上,還可以設定Consumer指定Path的鑒權規則,例如按所有Path的鑒權方式,Consumer 2、3可以訪問Provider的所有Path,但Provider的Path 2涉及一些核心業務或資料,不希望Consumer 2調用,可以將Path 2對Consumer 2的鑒權方式設定為黑名單(拒絕調用),則Consumer 2隻能訪問Provider的Path 1和Path 3。
設定完鑒權規則的調用示意如下圖所示。
- 設定所有Path的鑒權
建立服務鑒權規則
登入EDAS控制台。
- 在左側導覽列,選擇。
- 在Spring Cloud左側導覽列單擊服務鑒權。
- 在服務鑒權頁面單擊建立規則。
- 在建立規則面板設定服務鑒權參數,然後單擊確定。
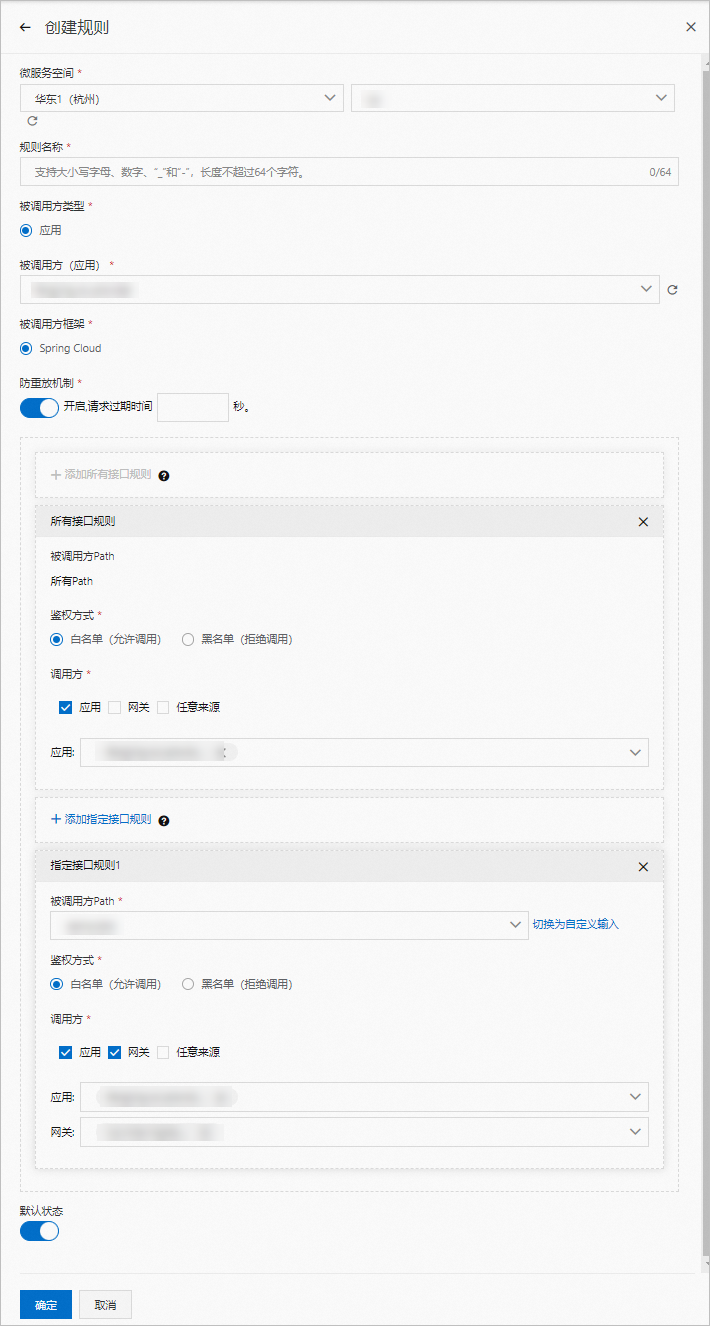
服務鑒權規則參數說明:
參數 說明 微服务空间 服務所在的地區和微服務空間。 規則名稱 鑒權規則名稱,支援大小寫字母、數字、底線(_)和短劃線(-),長度不超過64個字元。 被呼叫者 被調用的應用。 被呼叫者架構 被調用的應用所使用的架構,選擇Spring Cloud。 添加所有介面規則 重要 所有介面的通用規則僅支援添加一次。被呼叫者介面 預設為所有Path,且該參數值不可修改。 鑒權方式 服務鑒權的方式,包含白名單(允許調用)和黑名單(拒絕調用),請根據實際鑒權需求選擇。 調用方 需要鑒權的調用方應用,可以單擊添加調用方設定多個需要鑒權的調用方應用。 添加指定介面規則 重要 指定介面添加的規則不是追加,而是覆蓋針對所有介面的通用規則,請謹慎配置。被呼叫者Path 指定被調用應用的Path。 鑒權方式 服務鑒權的方式,包含白名單(允許調用)和黑名單(拒絕調用),請根據實際鑒權需求選擇。 調用方 需要鑒權的調用方應用,可以單擊添加調用方設定多個需要鑒權的調用方應用。 預設狀態 規則的啟用開關。 - 開啟:建立後即啟用,預設開啟。
- 關閉:建立後不啟用,需要在服務鑒權頁面規則的操作列單擊開啟規則。
結果驗證
服務鑒權規則配置完成且開啟後,請根據實際業務驗證服務鑒權規則是否生效。