このトピックでは、DTSコンソールでデータ移行タスクの進行状況を表示する方法について説明します。 DTSには、スキーマ移行、フルデータ移行、増分データ移行の移行タイプがあります。
前提条件
データ移行タスクが開始されます。
手順
DTSコンソールにログインします。
左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、データ移行をクリックします。
移行タスクページの上部で、データ移行インスタンスが存在するリージョンを選択します。
移行タスクページで、データ移行インスタンスのIDをクリックします。
移行タイプに基づいて操作を実行します。
説明タスクの設定時に移行タイプを選択しない場合、または移行タイプがサポートされていない場合、この移行タイプは左側のナビゲーションウィンドウに表示されません。
スキーマ移行の詳細を表示します。
左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、 を選択します。
スキーマオブジェクトの種類を示すタブをクリックして、移行の詳細を表示します。 たとえば、[テーブル] をクリックして、テーブルの移行の詳細を表示します。 オブジェクト名を指定することで、特定のオブジェクトの移行の詳細を検索できます。
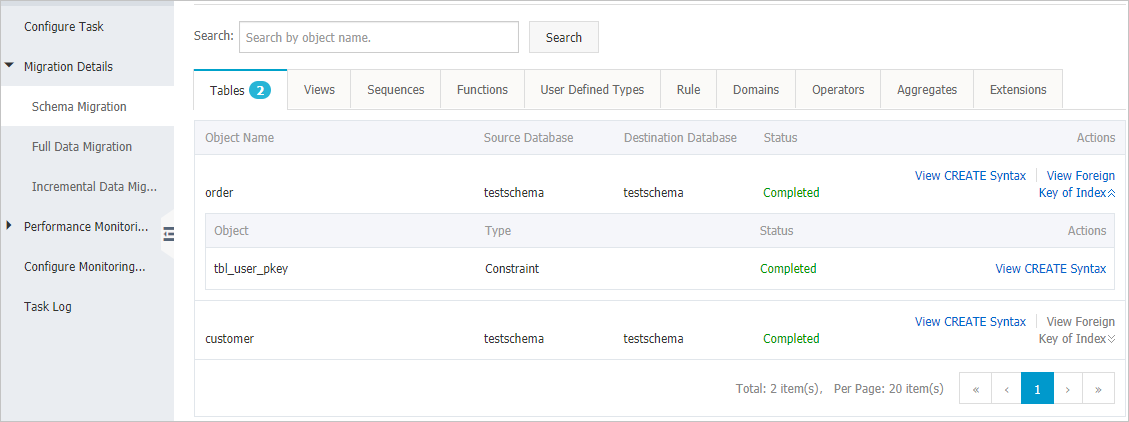 説明
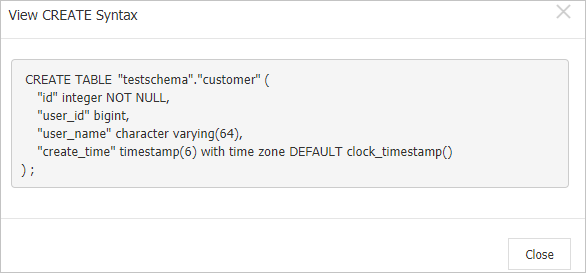
説明オブジェクトの [操作] 列で、[作成構文の表示] をクリックするか、 を選択します。 表示される [作成構文の表示] メッセージで、オブジェクトの作成構文を表示できます。
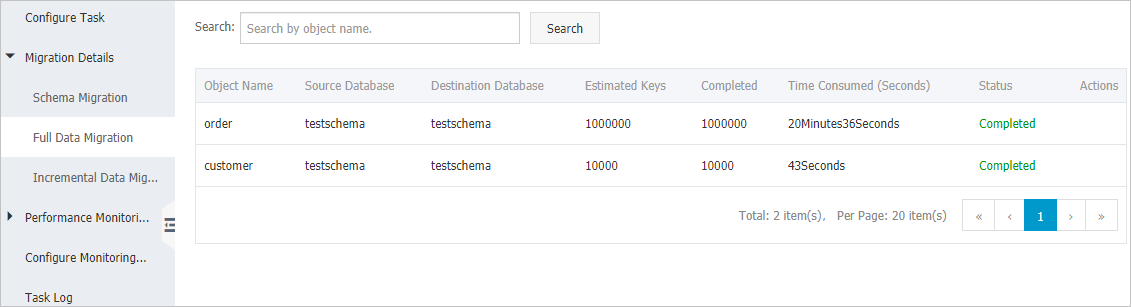
フルデータ移行の詳細を表示する
左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、 を選択します。
各オブジェクトの移行の詳細を表示するか、オブジェクト名を指定して特定のオブジェクトの移行の詳細を検索します。
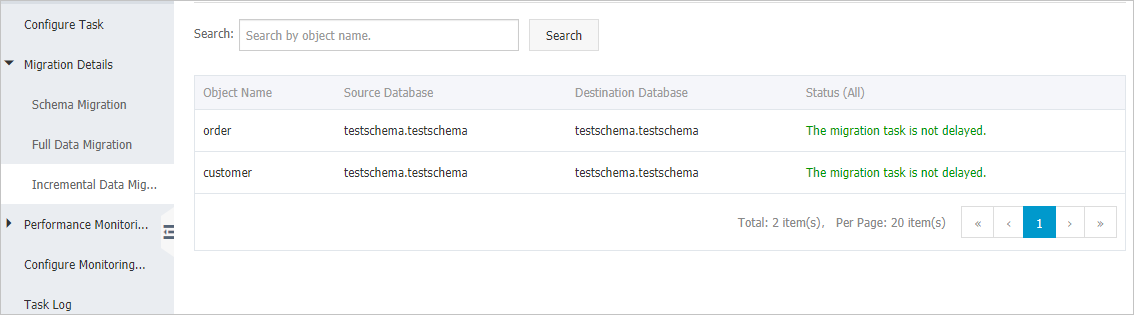
増分データ移行の詳細を表示する
左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、 を選択します。
各オブジェクトの移行の詳細を表示するか、オブジェクト名を指定して特定のオブジェクトの移行の詳細を検索します。
関連ドキュメント
フルデータ移行の接続状態とパフォーマンスの表示: 帯域幅、1秒あたりのレコード数 (RPS) 、読み取り /書き込み応答時間、およびネットワーク遅延を表示します。
増分データ移行の接続ステータスとパフォーマンスの表示: 移行された行数、帯域幅、および移行パフォーマンスの表示。