Managed Service for Prometheus allows you to create ServiceMonitors based on custom resource definitions (CRDs) to specify the Services that need to be discovered and monitored. When you create a ServiceMonitor, you can define the namespaces of pods to be discovered and set the matchLabel parameter to specify the Services to be monitored. This topic describes how to create a ServiceMonitor based on the Spring Boot framework to discover and monitor Services.
Demo
You can download the demo to try the features of ServiceMonitors.
Step 1: Add dependencies
Create a Maven project and add the following dependencies to the pom.xml file:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.micrometer</groupId> <artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId> <version>1.6.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>Add the following configuration to the src/resources/applications.properties file of the project:
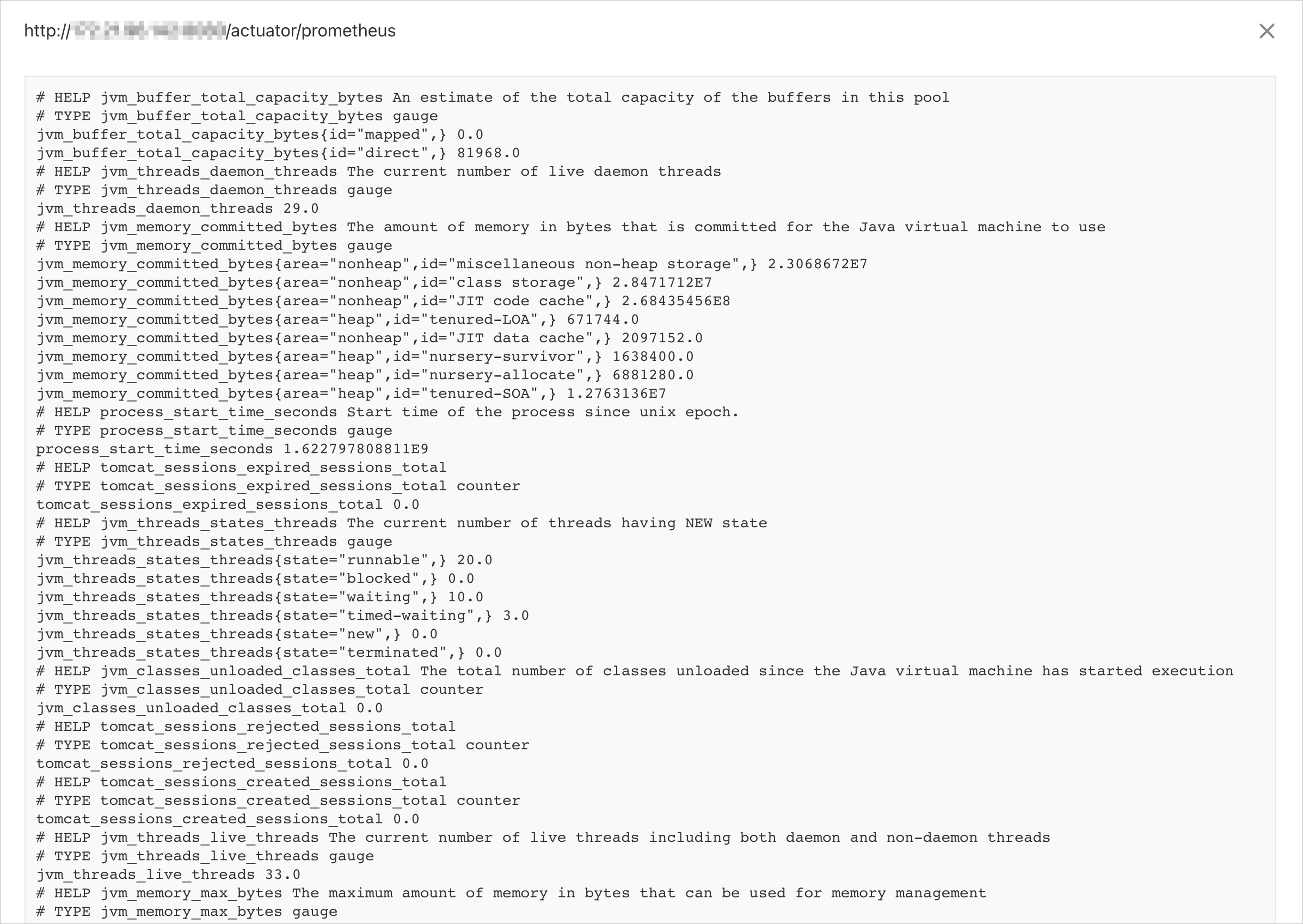
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=prometheusStart the project and visit
http://{host}:{port}/actuator/prometheusby using a browser.The information about Java Virtual Machine (JVM) monitoring is returned, as shown in the following figure.
Step 2: Deploy a Kubernetes cluster
Build an image and upload the Dockerfile of the image to the image repository. For more information, see Bind a source code hosting platform.
Create a Deployment based on the following sample code:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: micrometer-prometheus namespace: default labels: app: demo-prometheus spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: demo-prometheus template: metadata: labels: app: demo-prometheus spec: containers: - name: micrometer-prometheus image: manjusakalza/micrometer-prometheus:latest ports: - containerPort: 8080Create a Service based on the following sample code:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prometheus-metrics-demo namespace: default labels: micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true' spec: selector: app: demo-prometheus ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 name: metrics
Step 3: Create a ServiceMonitor
The following sample YAML file is used to create a ServiceMonitor:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: micrometer-demo
namespace: default
spec:
endpoints:
- interval: 15s
path: /actuator/prometheus
port: metrics #Specify a port name instead of a port number.
namespaceSelector:
any: true
selector:
matchLabels:
micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true'The sample YAML file contains the following parameters:
The
nameandnamespaceparameters inmetadataspecify the key metadata required by the ServiceMonitor.The
endpointsparameter inspecspecifies the endpoints that Managed Service for Prometheus uses to collect metrics. The value of theendpointsparameter is an array. Each element in the array is an endpoint. You can specify multipleendpoints. Eachendpointcontains the following parameters:interval: the intervals at which Managed Service for Prometheus collects metrics by using the currentendpoint. Unit: seconds. In this example, Managed Service for Prometheus collects metrics at intervals of 15 seconds (15s).path: the path that stores the metric data collected by Managed Service for Prometheus. In this example, the path is set to/actuator/prometheus.port: the port that is used to collect metrics. Set this parameter to the value of thenameparameter specified for the Service that you created in Step 2. In this example, the port is set tometrics.ImportantSpecify a port name instead of a port number.
The
namespaceSelectorparameter inspecspecifies the namespaces of Services to be discovered. ThenamespaceSelectorsection contains the following two mutually exclusive parameters:any: The value of this parameter is fixed totrue. If this parameter is specified, all Services that meet the filter conditions specified in the selector section are monitored.matchNames: an array that specifies thenamespacesof the Services to be monitored. For example, if you want to monitor only the Services in the default and arms-prom namespaces, use the followingmatchNamessettings:namespaceSelector: matchNames: - default - arms-prom
The
selectorsection inspecspecifies the conditions used to filter Services.In this example, the label of the Service that you created is micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true'. Therefore, the following
selectorsettings are used:selector: matchLabels: micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true'
Managed Service for Prometheus allows you to create a ServiceMonitor by using the following two methods.
Use the console to create a ServiceMonitor
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the name of the Prometheus instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Service Discovery and click the Configure tab.
On the Configure tab, click the ServiceMonitor tab and click Add ServiceMonitor.
In the Add ServiceMonitor dialog box, enter the YAML content and click OK.
Use the CLI to create a ServiceMonitor
Save the YAML file to your computer.
Run the following command to apply the YAML file:
kubectl apply -f {Path of the YAML file}
Step 4: Verify the ServiceMonitor
Perform the following operations to check whether Managed Service for Prometheus can discover Services:
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the name of the Prometheus instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Service Discovery. Then, click the Targets tab.
On the Targets tab, check whether a Service whose name is in the {namespace}/{serviceMonitorName}/x format exists.
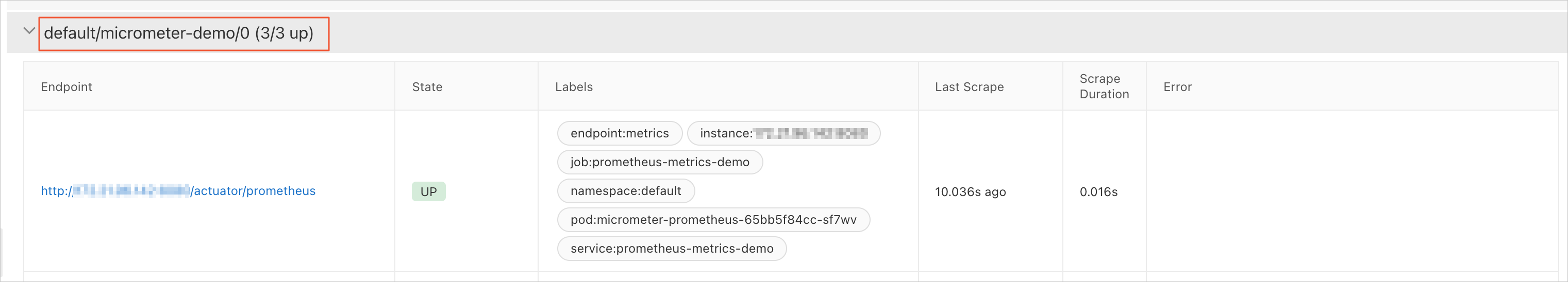
Click the Show icon to the left of the Service name. Then, click the link in the Endpoint column of the table below the Service name.
Check whether the metrics are collected as expected.