サンドボックス型コンテナーランタイムは、アプリケーションとその依存関係を軽量仮想マシン内で実行します。これにより、アプリケーション Pod に独立したカーネルまたは詳細な分離レイヤーが提供されます。これは、コンテナー内の悪意のある攻撃や脆弱性がホストや他のコンテナーに影響を与えるのを防ぐのに役立ちます。このトピックでは、サンドボックス型コンテナーのアーキテクチャ、主な利点、および一般的なシナリオについて説明します。
背景情報
サンドボックス型コンテナーは、信頼できないアプリケーションの隔離、障害分離、パフォーマンス分離、複数ユーザー間のワークロードの隔離などのシナリオに最適です。これらは、パフォーマンスへの影響を最小限に抑えながらセキュリティを強化し、ロギング、モニタリング、エラスティック スケーリングなどの機能において Docker コンテナーと同じユーザーエクスペリエンスを提供します。
コミュニティソリューションである Kata Containers と比較して、サンドボックス型コンテナーはストレージ、ネットワーク、安定性の面で最適化と改善を提供します。

アーキテクチャ

主な利点
サンドボックス型コンテナー V2 は、Alibaba Cloud の次世代セキュアなコンテナーランタイムであり、軽量仮想マシン技術に基づいています。V1 と比較して、強力な隔離を維持しつつ、オーバーヘッドを 90% 削減し、起動速度を 3 倍に向上させ、単一マシン密度を 10 倍に改善しています。主な利点は次のとおりです。
軽量仮想マシンに基づくサンドボックス間の強力な隔離を提供します。
従来の runC コンテナーとのアプリケーション互換性を提供します。
アプリケーション全体の高いパフォーマンスを提供し、runc コンテナーアプリケーションのパフォーマンスの最大 90% に達します。
virtiofs を使用して、サンドボックスモードで NAS、クラウドディスク、および OSS ボリュームのマウントと共有をサポートします。NAS はサンドボックスモードでの直接アタッチもサポートします。
モニタリング、ロギング、ストレージに関して runC と一貫したユーザーエクスペリエンスを提供します。
RuntimeClass (runC および runV) をサポートします。詳細については、「RuntimeClass」をご参照ください。
使いやすく、広範な技術的な専門知識は必要ありません。
コミュニティの Kata Containers と比較して、より高い安定性を提供します。Kata Containers の詳細については、「Kata Containers」をご参照ください。
ACK サンドボックス型コンテナーとコミュニティ Kata Containers の比較
パフォーマンス | パフォーマンスカテゴリ | ACK サンドボックス型コンテナー V2 | コミュニティ Kata Containers |
サンドボックスの起動速度 | 約 150 ms | 約 500 ms | |
追加のサンドボックスオーバーヘッド | 低い | 高い | |
コンテナー RootFS | virtio-fs、パフォーマンス: ☆☆☆☆ |
| |
コンテナー永続ボリューム | HostPath/EmptyDir | virtio-fs、パフォーマンス: ☆☆☆☆ | |
クラウドディスクブロックストレージ | virtio-fs、パフォーマンス: ☆☆☆☆ オンラインスケーリング (リサイズ)、コンテナー I/O モニタリング、ブロック/RAW デバイス、クラウドディスクキュー設定などの機能はサポートしていません。 | ||
NAS ファイルストレージ |
Samba のマウントとアンマウント、ゴミ箱、クォータ容量制御、容量/I/O モニタリング、オンラインスケーリングなどの機能はサポートしていません。 | ||
OSS オブジェクトストレージ | virtio-fs、パフォーマンス: ☆☆☆☆ | ||
ネットワークプラグイン |
| Flannel | |
モニタリングとアラート |
| サンドボックス型コンテナー Pod のディスクおよびネットワークモニタリングメトリックが不足しています。 | |
安定性 | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | |
ACK サンドボックス型コンテナーのシナリオ

シナリオ 1: サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) を使用した強力な分離による信頼できないアプリケーションの隔離
runC コンテナーのセキュリティリスク
名前空間と cgroup テクノロジーを使用して隔離を行うコンテナーは、広い攻撃対象領域を持ちます。
ノード上のすべてのコンテナーはホストカーネルを共有します。カーネルの脆弱性が悪用された場合、悪意のあるコードがホストにエスケープする可能性があります。これにより、コードはバックエンドのプライベートネットワークに侵入し、特権コードを実行し、システムサービスや他のアプリケーションを妨害し、重要なデータを盗むことができます。
アプリケーション自体の脆弱性も、攻撃者がプライベートネットワークに侵入することを可能にします。
runC コンテナーのセキュリティリスクは、次の対策を講じることで軽減できます。
Seccomp: システムコールをフィルタリングします。
SELinux: コンテナープロセス、ファイル、およびユーザーの権限を制限します。
Capability: コンテナープロセスの機能を制限します。
ルートレスモード: ユーザーがコンテナーランタイムとコンテナーを root ユーザーとして実行するのを防ぎます。
これらの対策は runC コンテナーのセキュリティを強化できますが、ホストカーネルの脆弱性を悪用するコンテナーエスケープを防ぐことはできません。
サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) を使用して潜在的なセキュリティリスクを隔離
潜在的なセキュリティリスクを持つアプリケーションを軽量仮想マシンサンドボックスに配置すると、アプリケーションは独立したゲスト OS カーネル上で実行されます。ゲスト OS カーネルでセキュリティ脆弱性が発生した場合でも、影響は単一のサンドボックスに限定され、ホストカーネルや他のコンテナーには影響しません。サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) と Terway NetworkPolicy 機能を組み合わせることで、Pod のネットワークアクセスポリシーを柔軟に構成できます。この組み合わせにより、真のシステム、データ、ネットワークの隔離が実現されます。
シナリオ 2: 障害増幅、リソース競合、パフォーマンス干渉など、runC コンテナーの問題に対処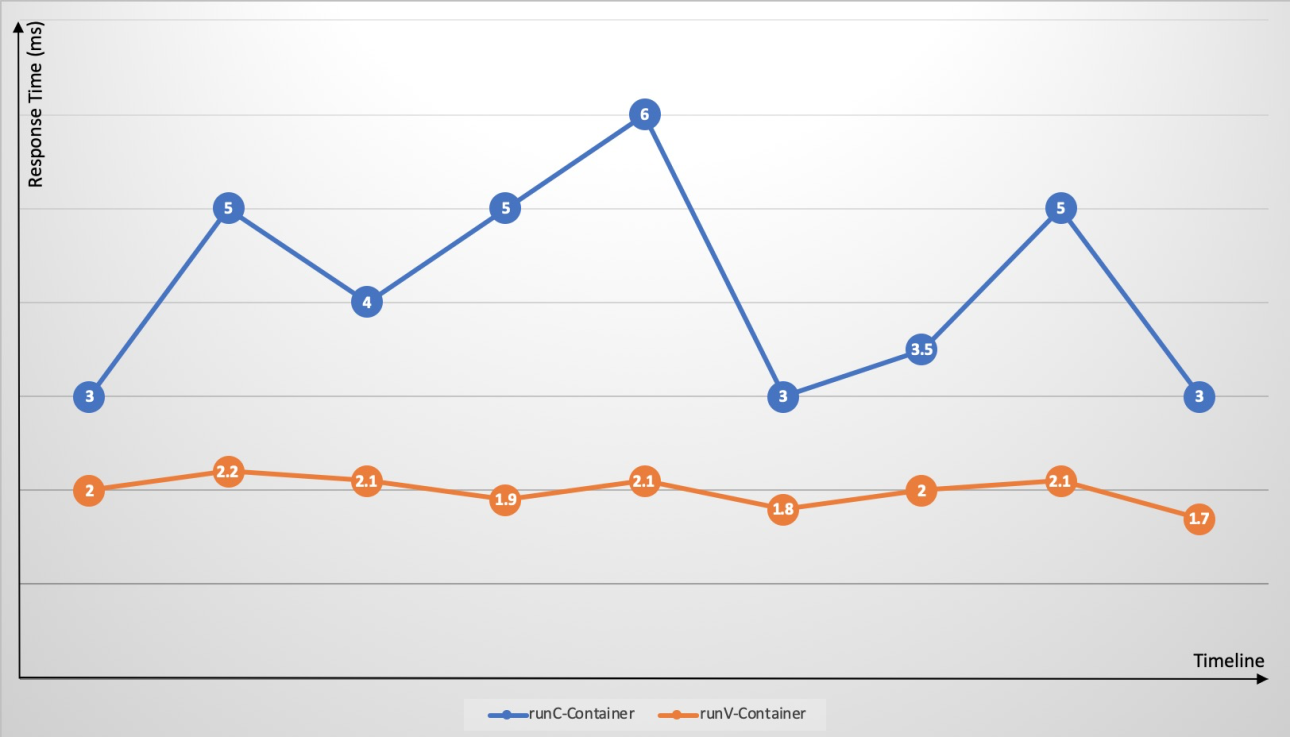
Kubernetes を使用すると、異なるアプリケーションコンテナーを同じノードに簡単にデプロイできます。しかし、cgroups はリソース競合を効果的に解決しないため、同じノード上の CPU 集約型や I/O 集約型などのリソース集約型アプリケーションはリソースを競合します。この競合は、アプリケーション応答時間の大幅な変動を引き起こし、全体的な応答時間を増加させます。ノード上のアプリケーションでメモリリークや頻繁なコアダンプなどの問題が発生すると、ノード全体の負荷が増加します。ホストカーネルのバグをトリガーする単一のコンテナーがシステムダウンを引き起こす可能性があります。単一アプリケーションの障害がノード全体に広がり、クラスター全体が応答不能になることさえあります。サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) は、独立したゲスト OS カーネルとハイパーバイザーを使用して、runC コンテナーに見られる障害増幅、リソース競合、パフォーマンス干渉の問題に効果的に対処します。
シナリオ 3: マルチテナントサービス
通常、企業には複数の事業部門 (LOB) または部門があり、それぞれ独自のアプリケーションをデプロイします。これらの異なる事業部門または部門 (複数のテナント) には、強力な隔離要件があります。たとえば、金融関連ビジネスでは、物理環境で他のセキュリティに機密性のないアプリケーションを実行したくない場合があります。従来の runC コンテナーは、信頼できないアプリケーションによってもたらされる潜在的なセキュリティリスクを効果的に防ぐことはできません。この場合、通常、次のいずれかのオプションを選択します。
複数のシングルテナントクラスター: たとえば、金融ビジネスのクラスターを他のセキュリティに機密性のないビジネスのクラスターから分離できます。
単一のマルチテナントクラスター: 異なる事業部門のアプリケーションを異なる名前空間に分離できます。各ノードは特定の事業部門によって排他的に使用できます。マルチテナント隔離は、リソースクォータ、ネットワークポリシー、およびその他の機能を使用して実現されます。複数のシングルテナントクラスターを使用する場合と比較して、このアプローチはコントロールプレーンが少なく、管理コストも低くなります。ただし、一部のテナントによるリソース使用率の低さから生じる無駄なノードリソースの問題は解決されません。
サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) を使用すると、コンテナーエスケープによるセキュリティリスクを懸念することなく、仮想マシンサンドボックスを使用してクラスター内の信頼できないアプリケーションを隔離できます。これにより、すべてのノードで異なるアプリケーションコンテナーを混在して実行できます。利点は次のとおりです。
リソーススケジューリングの複雑さを軽減します。
ノードは単一のビジネスによって排他的に使用されなくなります。これにより、リソース断片化が軽減され、ノードリソース使用率が向上し、クラスター全体のリソースコストが節約されます。
サンドボックス型コンテナー (runV) は軽量仮想マシンを使用し、runC コンテナーに匹敵するパフォーマンスを提供します。

制限事項
クラスターのバージョン: 対応しているのは、バージョン 1.16~1.34 の ACK マネージドクラスター および ACK 専用クラスターのみです。クラスターをスペックアップするには、「クラスターを手動でスペックアップする」をご参照ください。
オペレーティングシステム: サンドボックス型コンテナーノードプールは、カスタムイメージをサポートしていません。
バージョン 1.30 より前のバージョンを実行するクラスターでは、Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 と Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 (メンテナンスは停止済み) のみがサポートされています。
バージョン 1.30 以降のバージョンを実行するクラスターでは、Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 のみがサポートされています。
インスタンスタイプ: ECS ベアメタルインスタンスタイプのみがサポートされています。
ネットワークプラグイン: サンドボックス型コンテナーノードプールは、Flannel ネットワークプラグインと、一部のモードでの Terway ネットワークプラグインのみをサポートします。Terway ネットワークプラグインを使用する場合、専用 ENI モードはサポートされず、DataPath v2 機能は有効にできません。


