Kubernetesネイティブサービスのバックエンドエンドポイントは、ノード間でランダムに分散されます。 その結果、サービス要求がノードグループ間でノードに分散されると、これらの要求はノードに到達しないか、または迅速に応答されないことがある。 エッジノード上のアプリケーションを現在のノードまたは同じエッジノードプール内のノードにのみ公開するようにサービストポロジを構成できます。 このトピックでは、サービストポロジの仕組みとサービストポロジの構成方法について説明します。
背景情報
エッジコンピューティングでは、エッジノードは、ゾーン、領域、またはCPUアーキテクチャ、インターネットサービスプロバイダ (ISP) 、またはクラウドサービスプロバイダなどの他の論理属性によってグループに分類される。 異なるグループのノードは、何らかの方法で互いに分離されています。 例えば、これらのノードは、切断されてもよく、同じリソースを共有しなくてもよく、異種リソースを有してもよく、または独立して配備されるアプリケーションを実行してもよい。
サービストポロジのしくみ
上記の問題を解決するために、Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) Edgeには、Kubernetesネイティブサービスのエンドポイントのトポロジを管理する機能があります。 たとえば、エッジノード上のアプリケーションを現在のノードまたは同じエッジノードプール内のノードにのみ公開するようにサービストポロジを構成できます。 次の図は、サービストポロジの動作を示しています。
サービス1は、ポッド2およびポッド3に関連付けられる。
アノテーション: "openyurt.io/topologyKeys: kubernetes.io/zone"は、サービス1へのアクセスを許可されているノードプールを指定します。ポッド2はノード2に配置され、ポッド3はノード4に配置される。 ノード2はノードプールAに属し、ノード4はノードプールBに属する。
ポッド3とポッド1は同じノードプールに属していません。 その結果、ポッド1がサービス1にアクセスすると、トラフィックはポッド2にのみ転送されます。 トラフィックはポッド3に転送されません。
使用上の注意
v1.26.3より前のバージョン-aliyun.1: サービスを作成するときに、サービスにサービストポロジ注釈を追加する必要があります。 サービスの作成後にアノテーションを追加すると、サービストポロジは有効になりません。 この場合、サービスを削除して再作成する必要があります。
v1.26.3-aliyun.1以降の場合: サービスの作成後に、サービストポロジ注釈を追加または変更できます。 Serviceトポロジは、注釈を追加または変更した直後に有効になります。
注釈
Kubernetesネイティブサービスにサービストポロジアノテーションを追加して、サービストポロジを設定できます。 次の表に、サービストポロジの構成に使用できるアノテーションを示します。
注釈キー | アノテーション値 | 説明 |
openyurt.io/topologyKeys | kubernetes.io /ホスト名 | サービスがデプロイされているノードのみがサービスにアクセスできるように指定します。 |
openyurt.io/topologyKeys | kubernetes.io/zoneまたはopenyurt.io/nodepool | サービスがデプロイされているノードプール内のノードのみがサービスにアクセスできるように指定します。 ACK Edgeクラスターのバージョンが1.18以降の場合は、openyurt.io/nodepoolを使用することを推奨します。 |
- | - | サービスへのアクセスが制限されないことを指定します。 |
サービストポロジの設定
ACKコンソールまたはCLIを使用して、サービストポロジを設定できます。
方法1: ACKコンソールでのサービストポロジの設定
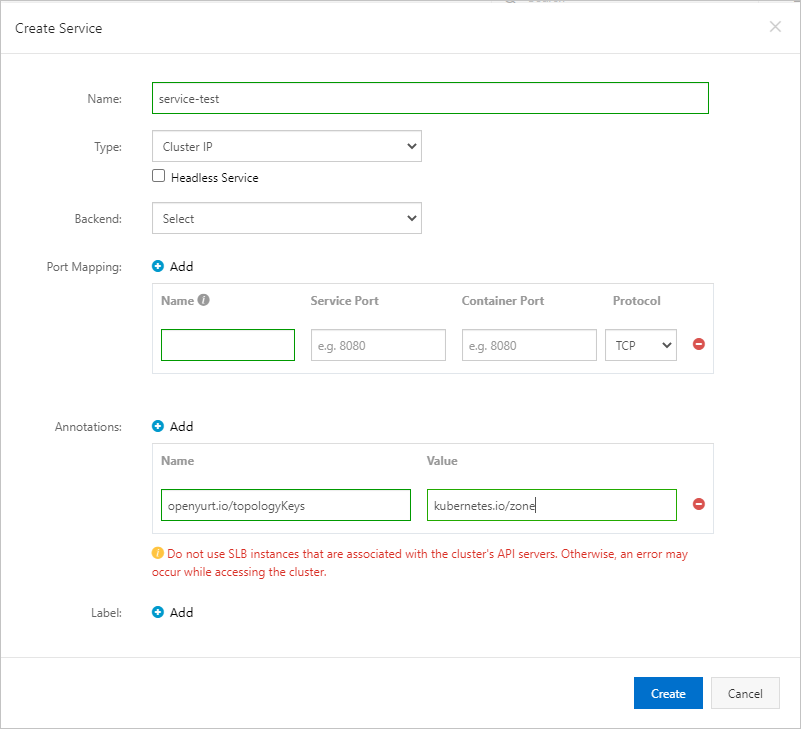
サービスがデプロイされているノードプール内のノードのみがアクセスできるサービスを作成するには、サービスに注釈を追加するだけです。 たとえば、Nameをopenyurt.io/topologyKeysに設定し、Valueをkubernetes.io/zoneに設定できます。 サービスの作成方法の詳細については、「はじめに」をご参照ください。
方法2: CLIを使用してサービストポロジを構成する
特定のノードプールのトポロジカルドメインを使用するサービスを作成します。 次のコードブロックは、YAMLテンプレートの例です。
apiVersion: v1
種類: サービス
メタデータ:
アノテーション:
openyurt.io/topologyKeys: kubernetes.io/zone
名前: my-service-nodepool
namespace: デフォルト
spec:
ポート:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
セレクタ:
アプリ:nginx
sessionAffinity: None
タイプ: ClusterIP