This topic describes how to integrate the Anti-Bot SDK into Android apps. In this topic, Anti-Bot SDK is referred to as SDK. Before you can enable the app protection feature for your Android apps, you must integrate the SDK into your Android apps.
Limits
Your Android apps must use Android 16 or later. If the API version is earlier than 16, the SDK cannot work as expected.
Prerequisites
The app protection feature is purchased and enabled.
For more information, see Procedure to enable app protection.
The SDK for Android apps is obtained.
After you purchase the app protection feature, you can contact technical support in the DingTalk service group to obtain the SDK. You can also submit a New Ticket page to obtain the SDK.
The SDK for Android apps contains an AAR file, which is named in the following format: AliTigerTally_X.Y.Z.aar. X.Y.Z indicates the version number of the file.
The SDK authentication key, namely the
app key, is obtained.To obtain the app key, log on to the Web Application Firewall console and choose . On the Bot Management tab of the Website Protection page, turn on App Protection and click Obtain and Copy Appkey. The SDK authentication key is used to send SDK initialization requests. The key must be included in the integration code.
NoteEach Alibaba Cloud account has a unique
app key, which can be used for all the domain names in your WAF instance. You can use theapp key, regardless of whether you integrate the SDK into Android apps or iOS apps.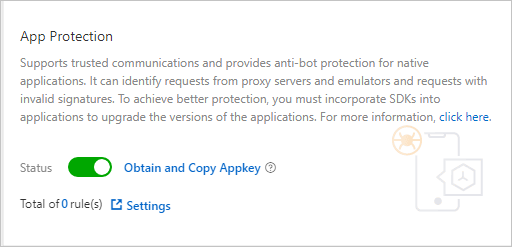
Authentication key example:
****OpKLvM6zliu6KopyHIhmneb_****u4ekci2W8i6F9vrgpEezqAzEzj2ANrVUhvAXMwYzgY_****vc51aEQlRovkRoUhRlVsf4IzO9dZp6nN_****Wz8pk2TDLuMo4pVIQvGaxH3vrsnSQiK****
Background information
The SDK is used to sign requests that are sent by apps. Web Application Firewall (WAF) verifies the signatures in the requests to identify risks in app services and block malicious requests.
(Optional) Create a test Android project
You can integrate the SDK into a real Android project. You can also integrate the SDK into a test Android project to familiarize yourself with the integration operations before you integrate the SDK into a real Android project.
In this example, use Android Studio to create a test Android project.
The following figure shows a test project named TigerTally_sdk_test.  Before you integrate the SDK into apps, make sure that the test project runs as expected.
Before you integrate the SDK into apps, make sure that the test project runs as expected. 
Procedure
Use Android Studio to open the test project and enter the file directory.
Reference the AAR file.
Copy the AliTigerTally.aar file to the libs directory. You can also drag the file to the directory.

Open the build.gradle file and modify the configurations based on the following descriptions:
Add the libs directory as a source of dependencies.
repositories{ flatDir { dirs 'libs' } }Add a compilation dependency.
ImportantYou must replace the version number (X.Y.Z) in the following code with the version number of the AAR file that you obtain.
dependencies { compile(name: 'AliTigerTally_X.Y.Z', ext: 'aar') }
Click Sync Now to synchronize the modifications to the project.
Reference an SO file.
If an SO file is included in the project, skip this step. Otherwise, add the following configuration to the build.gradle file:
android { defaultConfig { ndk { abiFilters 'arm64-v8a', 'x86', "armeabi-v7a" //abiFilters "armeabi-v7a" } } }Apply for the following permissions for apps.
Permission
Required
Description
android.permission.INTERNET
Yes
Connects to the Internet.
android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE
No
Obtains the network status of a device.
android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE
No
Obtains the Wi-Fi connection status of a device.
android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE
No
Reads the status and identity of a device.
ImportantYou must dynamically apply for this permission for Android 6.0 or later apps.
android.permission.BLUETOOTH
No
Obtains the Bluetooth permissions of a device.
android.permission. READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
No
Reads the external storage of a device.
ImportantYou must dynamically apply for this permission for Android 6.0 or later apps.
android.permission.CHANGE_NETWORK_STATE
No
Changes the network status of a device.
Add the integration code.
Specify a user ID.
Function:
int setAccount(String account);Description: specifies a user ID in requests. This way, you can configure WAF protection policies in a more efficient manner.
Parameter: <account>, which specifies the user ID. Data type: string. We recommend that you enter a masked user ID.
Return value: a value that indicates whether the setting is successful. Data type: int. The value 0 indicates that the setting is successful. The value -1 indicates that the setting failed.
Sample code:
final String account="account"; TigerTallyAPI.setAccount(account); // If the logon user is a guest, you do not need to call this function. You can directly call the initialization function.Initialize the SDK.
Function:
int init(Context context, String appkey, int type);Description: initializes the SDK and performs one-time information collection. One-time information collection allows you to collect terminal information for one time. If you want to collect terminal information again, call the
initfunction.One-time information collection supports two modes: full data collection and collection of data excluding sensitive fields. The sensitive fields include imei, imsi, simSerial, wifiMac, wifiList, and bluetoothMac of a user. To collect the sensitive fields, you must obtain permissions.
NoteBefore a user agrees on the privacy policy of the apps, we recommend that you use the second mode. After a user agrees on the privacy policy of the apps, we recommend that you use the first mode. Full data collection helps identify risks.
Parameters:
<context>: specifies the context that is passed to the apps.
<appkey>: specifies the SDK authentication key. Data type: string.
<type>: specifies the collection mode. Data type: CollectType. Valid values:
DEFAULT: full data collection.
NO_GRANTED: collection of data excluding sensitive fields.
Return value: a value that indicates whether the initialization is successful. Data type: int. The value 0 indicates that the initialization is successful. The value -1 indicates that the initialization failed.
Sample code:
final String appkey="your_appkey"; // Collect full data. int ret = TigerTallyAPI.init(this.getApplicationContext(), appkey, TigerTallyAPI.CollectType.DEFAULT); // Collect data excluding sensitive fields. int ret = TigerTallyAPI.init(this.getApplicationContext(), appkey, TigerTallyAPI.CollectType.NOT_GRANTED); Log.d("AliSDK", "ret:" + ret);Sign request data.
Function:
String vmpSign(int signType, byte[] input);Description: signs the input data and returns the signature string.
Parameters:
<signType>: specifies the signature algorithm. Data type: int. Set the value to 1, which indicates that the default signature algorithm is used.
<input>: specifies the data to be signed. Data type: byte[].
In most cases, the data to be signed is the entire body of a request. If the POST request body is empty or a GET request body is used, enter
nullor a byte[] array that is converted from an empty string. Example:"".getBytes("UTF-8").
Return value: the signature string. Data type: string.
Sample code:
NoteIn the following sample code, the signature string is defined as wToken.
String request_body = "i am the request body, encrypted or not!"; String wToken = null; try { wToken = TigerTallyAPI.vmpSign(1, request_body.getBytes("UTF-8")); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Log.d("AliSDK", "wToken:" + wToken);Add the signature string to the HTTP header.
For example, if your project uses the
HttpURLConnectionclass, you can add the content of the signature string wToken to the objects of theHttpURLConnectionclass.Sample code:
String request_body = "i am the request body, encrypted or not!"; new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { URL url = new URL("https://www.aliyundoc.com"); HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); conn.setReadTimeout(5000); conn.setRequestMethod("POST"); // set wToken info to header conn.setRequestProperty("wToken", wToken); OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream(); // set request body info byte[] requestBody = request_body.getBytes("UTF-8"); os.write(requestBody); os.flush(); os.close(); int code = conn.getResponseCode(); Log.d("respCode", Integer.toString(code)); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ProtocolException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }; }).start();Send requests that use the new HTTP header to the server of apps.
WAF receives requests that are destined for the server, parses the signature string wToken to identify and block malicious requests, and then forwards normal requests to the server.
Obfuscate code
If you use ProGuard to obfuscate code, you can use -keep to configure the functions of the SDK. This helps prevent the functions of the SDK from being removed.
Sample code:
-keep class com.aliyun.TigerTally.* {*;}