After you add a website to Web Application Firewall (WAF), HTTP flood protection is enabled by default and protects your website against HTTP flood attacks. When HTTP flood attacks are blocked, the 405 Method Not Allowed error code is returned. You can adjust HTTP flood protection policies as needed.
Prerequisite
A WAF instance is purchased.
Your website is added to WAF. For more information, see Tutorial.
Procedure
Log on to the WAF console.
In the top navigation bar, select the resource group and the region in which the WAF instance is deployed. You can select Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the upper part of the Website Protection page, select the domain name for which you want to configure protection from the Switch Domain Name drop-down list.
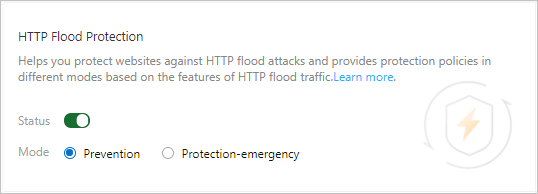
On the Access Control/Throttling tab, find the HTTP Flood Protection section and configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Status
Enable or disable HTTP flood protection. By default, HTTP flood protection is enabled after you add a website to WAF.
NoteAfter HTTP flood protection is enabled, all requests destined for your website are checked by this function. You can configure a Access Control/Throttling rule so that requests that match the rule bypass the check. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for Access Control/Throttling.
Mode
The protection mode. Valid values:
Prevention: This mode blocks only suspicious requests and maintains a low false positive rate. We recommend that you apply this mode when no abnormal traffic is detected on the website to avoid false positives.
Protection-emergency: This mode effectively blocks HTTP flood attacks but maintains a high false positive rate. You can apply this mode if the Protection mode fails to block HTTP flood attacks, the website responds slowly, and indicators such as traffic, CPU, and memory are abnormal.
NoteThe Protection-emergency mode is applicable to web pages and HTML5 pages. This mode is not suitable for APIs or native applications because a large number of false positives may occur. We recommend that you create custom protection policies for API and native applications scenarios. For more information, see Create a custom protection policy.
References
If you find that the Protection-emergency mode cannot block a large number of attacks, we recommend that you check whether the attacks come from back-to-origin IP addresses of WAF. If the origin server is directly attacked, you can change the settings to allow only requests from the back-to-origin IP addresses of WAF. For more information, see Configure protection for an origin server.
If you need to reinforce protection and maintain a low false positive rate, we recommend that you use the custom protection policy. For more information, see Create a custom protection policy.