VPN Gateway is integrated with Network Intelligence Service (NIS) to provide the path analysis feature. You can use this feature to diagnose network connectivity for resources connected through a VPN gateway.
Background information
When you use path analysis, you must specify a source resource and a destination resource. The system builds a network configuration model between the two resources and analyzes the model to determine whether the network connection is working correctly. If the resources cannot connect, the system provides a reason for the failure, which you can use to troubleshoot the issue. The analysis process does not send real data packets and does not affect your current services.
For example, you can specify an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance in your Alibaba Cloud account as the source resource and another ECS instance in the same account as the destination resource. Then, you can set the destination port to 22 and the protocol to TCP. Path analysis can then verify whether the source ECS instance can connect to the destination ECS instance over the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. For more information about path analysis, see Use path analysis.
This topic describes how to use the path analysis feature to diagnose network connectivity for an IPsec-VPN connection in the following scenarios.
Prerequisites
Before you use the path analysis feature to diagnose the network connectivity of an IPsec-VPN connection, you must ensure that the connection is established. If the IPsec-VPN connection fails to establish, you must first troubleshoot the negotiation issue. You can use the error code displayed in the VPN Gateway console, the log information of the IPsec-VPN connection, or the instance diagnosis feature of VPN Gateway. For more information, see Troubleshoot IPsec-VPN connection issues and Diagnose a VPN gateway.
Scenario 1: Use an IPsec-VPN connection to connect a data center to a VPC
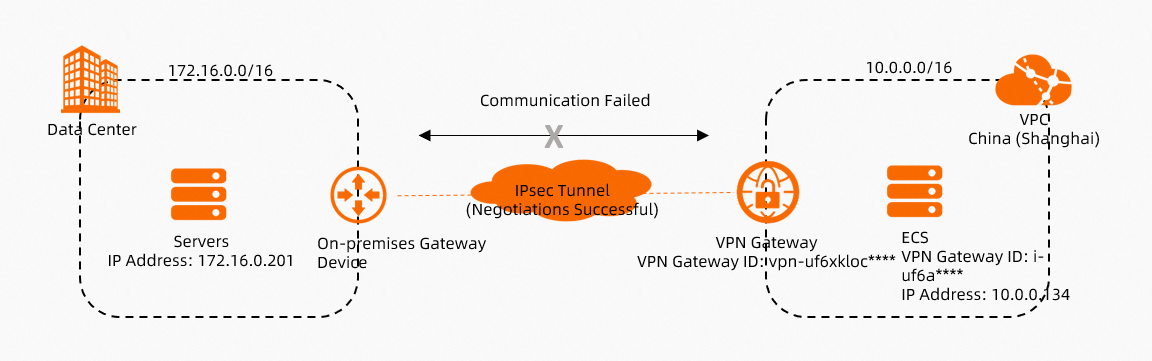
As shown in the preceding figure, an IPsec-VPN connection is used to connect a data center to an Alibaba Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). If the IPsec-VPN connection is established but the IDC and the VPC cannot access each other, you can use the path analysis feature to diagnose the network connectivity issue.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top menu bar, select the region where the VPN gateway is deployed.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the target VPN gateway, and in the Diagnose column, choose .
In the Reachability Analyzer panel, configure the following parameters and click Start Analyzing.
The following information describes how to create a path analysis for traffic in each direction.
Traffic from a data center to the VPC
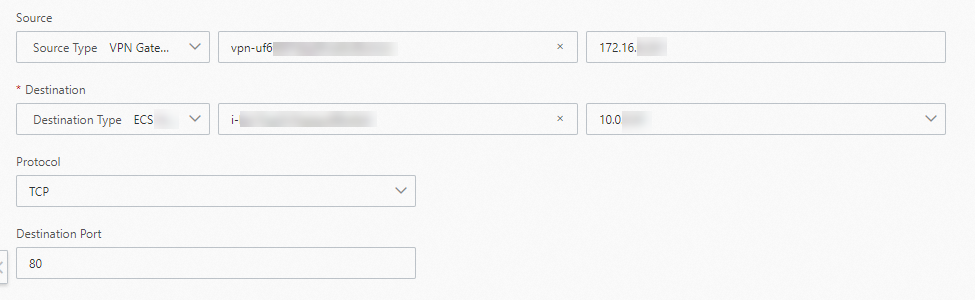
Parameter
Description
Source
Select a Source Type.
In this topic, VPN Gateway is selected. Then, select the VPN gateway vpn-uf6xkloc**** that establishes an IPsec-VPN connection with the data center, and enter the private IP address 172.16.0.201 of the server in the data center.
Destination
Select a Destination Type.
In this topic, ECS Instance ID is selected. Then, select the ECS instance i-uf6a**** in the VPC that communicates with the data center.
Protocol
Select the protocol type for the test.
This topic uses the default value, TCP.
NoteSelect a protocol and destination port based on your network environment.
Destination Port
Enter the port number of the destination resource.
This topic uses the default value, 80.
Name
Define a name for the path.
After you start a path analysis, the path is automatically saved. This lets you run the analysis again. Go to the Network Intelligence Service console to view the list of saved paths.
Traffic from the VPC to the data center
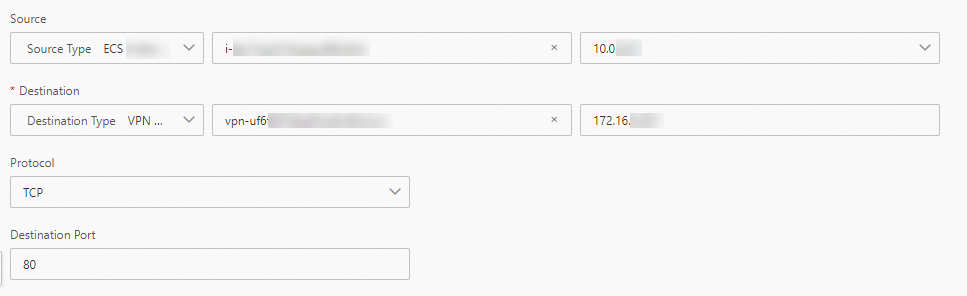
Parameter
Description
Source
Select a Source Type.
In this topic, ECS Instance ID is selected. Then, select the ECS instance i-uf6a**** in the VPC that communicates with the data center.
Destination
Select a Destination Type.
In this topic, VPN Gateway is selected. Then, select the VPN gateway vpn-uf6xkloc**** that establishes an IPsec-VPN connection with the IDC, and enter the private IP address 172.16.0.201 of the server in the data center.
Protocol
Select the protocol type for the test.
This topic uses the default value, TCP.
NoteSelect a protocol and destination port based on your network environment.
Destination Port
Enter the port number of the destination resource.
This topic uses the default value, 80.
Name
Define a name for the path.
After you start a path analysis, the path is automatically saved. This lets you run the analysis again. Go to the Network Intelligence Service console to view the list of saved paths.
In the Reachability Analyzer panel, you can view the path analysis results.
Troubleshoot the issue based on the path analysis results. Then, run the path analysis again to verify that the path is reachable.
If the system indicates that the path is reachable, the IDC and the VPC should be able to communicate with each other. You can try to initiate access between the data center and the VPC.
If the data center and the VPC still cannot communicate, troubleshoot the issue by referring to the IPsec-VPN connection FAQ. For more information, see IPsec-VPN connection FAQ.
Scenario 2: Use an IPsec-VPN connection to connect VPCs across regions within the same account
To create a path analysis for an IPsec-VPN connection between VPCs that belong to different accounts across regions, see Scenario 1.
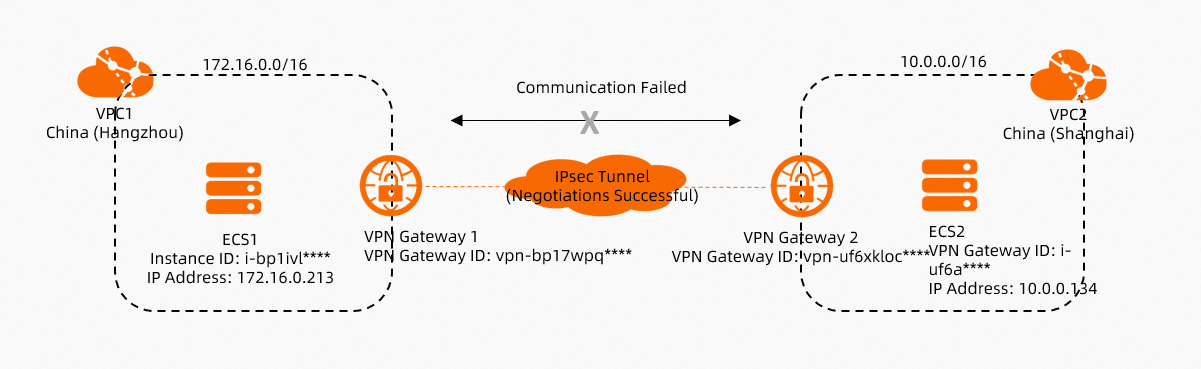
As shown in the preceding figure, an IPsec-VPN connection is used to connect VPCs across regions within the same Alibaba Cloud account. If the IPsec-VPN connection is established but the ECS instances in the two VPCs cannot access each other, you can use the path analysis feature to diagnose the network connectivity issue.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top menu bar, select the region where the VPN gateway is deployed.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the target VPN gateway, and in the Diagnose column, choose .
On the Reachability Analyzer panel, configure the following parameters and click Start Analyzing.
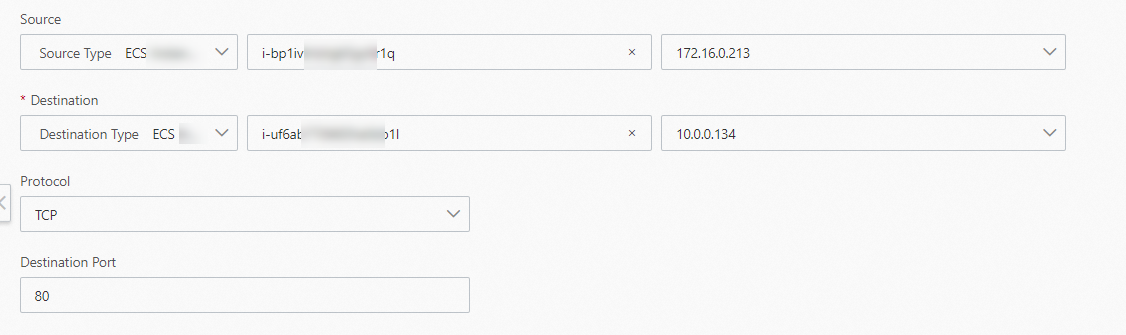
Parameter
Description
Source
Select a Source Type.
In this topic, ECS Instance ID is selected. Then, select ECS1.
Destination
Select a Destination Type.
In this topic, ECS Instance ID is selected. Then, select ECS2.
Protocol
Select the protocol type for the test.
This topic uses the default value, TCP.
NoteSelect a protocol and destination port based on your network environment.
Destination Port
Enter the port number of the destination resource.
This topic uses the default value, 80.
Name
Define a name for the path.
After you start a path analysis, the path is automatically saved. This lets you run the analysis again. Go to the Network Intelligence Service console to view the list of saved paths.
In the Reachability Analyzer panel, you can view the path analysis results.
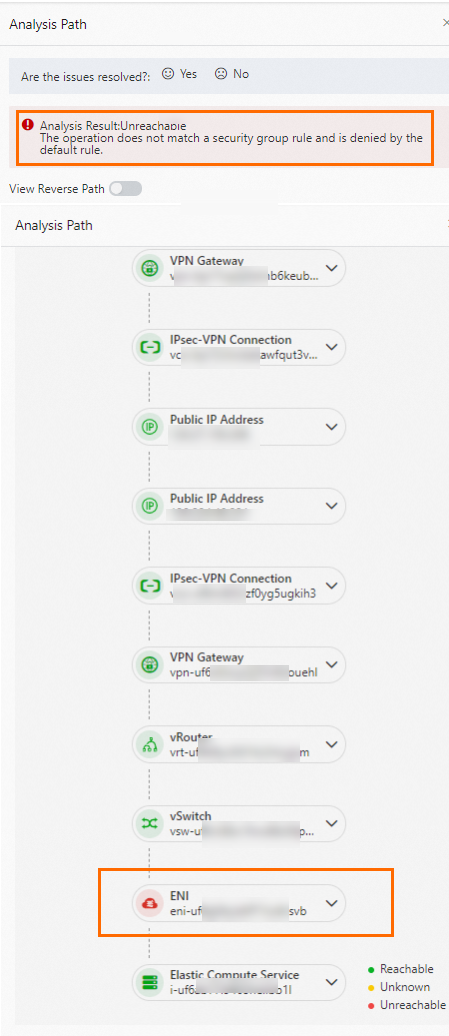
As shown in the preceding figure, ECS1 and ECS2 cannot communicate because the security group rule of ECS2 denies access from ECS1. Check the security group rule applied to ECS2. Then, run the path analysis again to verify that the path is reachable.
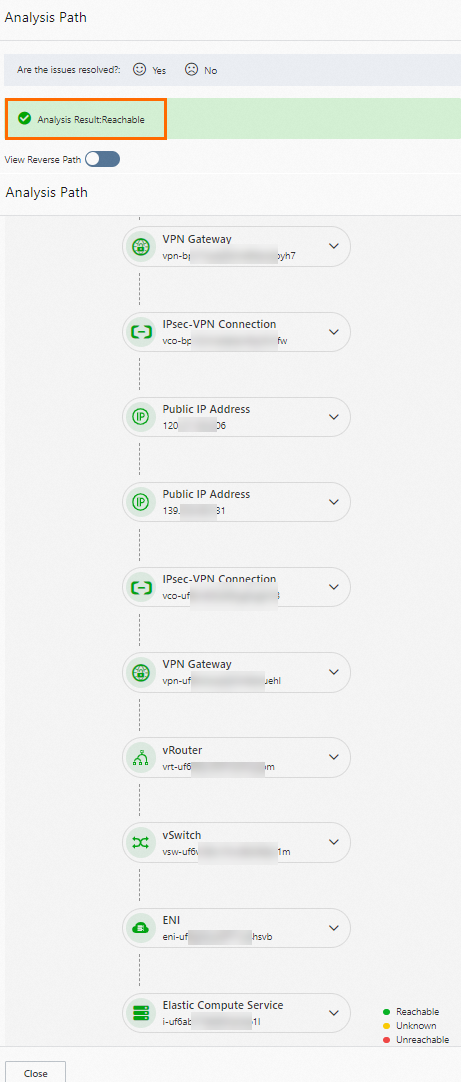
If the system indicates that the path is reachable, the ECS instances in the VPCs should be able to communicate with each other. You can try to initiate access between the VPCs.
If the ECS instances in the VPCs still cannot communicate, troubleshoot the issue by referring to the IPsec-VPN connection FAQ. For more information, see IPsec-VPN connection FAQ.
Scenario 3: Use an IPsec-VPN connection to enable communication between multiple sites
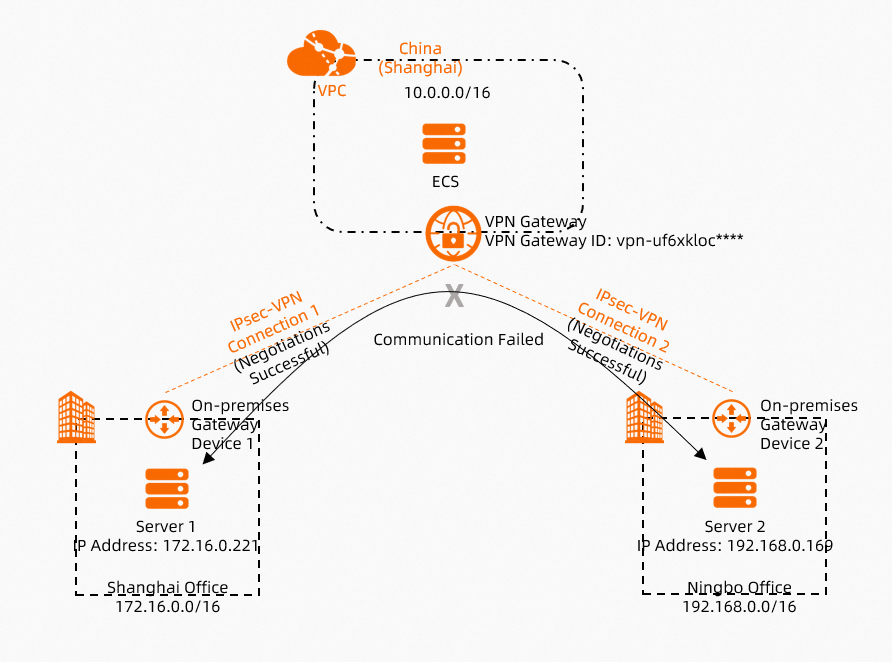
As shown in the preceding figure, an IPsec-VPN connection is used to enable communication between multiple sites. If all IPsec-VPN connections are established but the sites cannot access each other, you can use the path analysis feature to diagnose the network connectivity issue.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top menu bar, select the region where the VPN gateway is deployed.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the target VPN gateway, and in the Diagnose column, choose .
In the Reachability Analyzer panel, set the following parameters and click Start Analyzing.
Parameter
Description
Source
Select a Source Type.
In this topic, VPN Gateway is selected. Then, select the VPN gateway vpn-uf6xkloc**** that establishes an IPsec-VPN connection with the Shanghai office. Enter the private IP address 172.16.0.221 of Server 1 in the Shanghai office.
Destination
Select a Destination Type.
In this topic, VPN Gateway is selected. Then, select the VPN gateway vpn-uf6xkloc**** that establishes an IPsec-VPN connection with the Ningbo office. Enter the private IP address 192.168.0.169 of Server 2 in the Ningbo office.
Protocol
Select the protocol type for the test.
This topic uses the default value, TCP.
NoteSelect a protocol and destination port based on your network environment.
Destination Port
Enter the port number of the destination resource.
This topic uses the default value, 80.
Name
Define a name for the path.
After you start a path analysis, the path is automatically saved. This lets you run the analysis again. Go to the Network Intelligence Service console to view the list of saved paths.
In the Reachability Analyzer panel, you can view the path analysis results.
Troubleshoot the issue based on the path analysis results. Then, run the path analysis again to verify that the path is reachable.
If the system indicates that the path is reachable, the sites should be able to communicate with each other. You can try to initiate access between the sites.
If the sites still cannot communicate, troubleshoot the issue by referring to the IPsec-VPN connection FAQ. For more information, see IPsec-VPN connection FAQ.