This topic describes how to synchronize data between a data center and a database in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You can perform the synchronization by using Data Transmission Service (DTS) over a public VPN gateway.
Scenarios
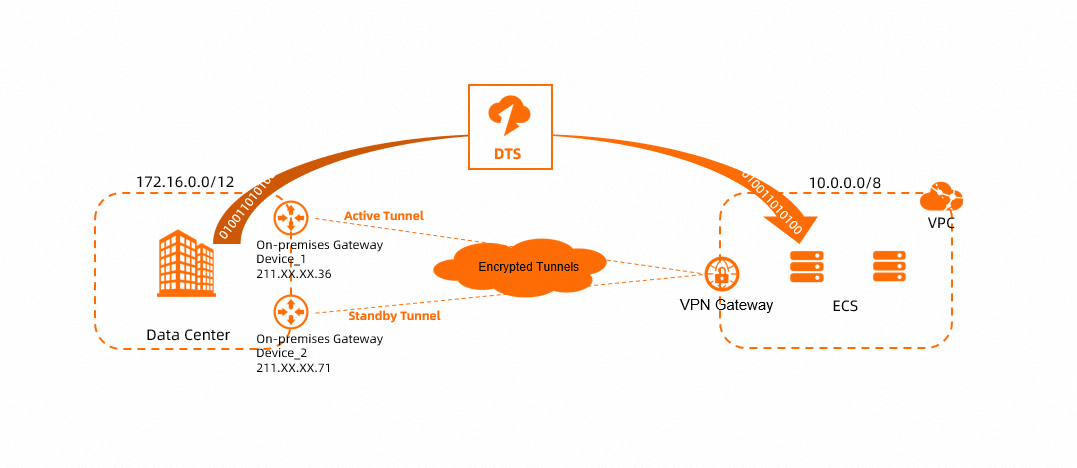
The following scenario is used in this topic: An enterprise has a VPC in the China (Hohhot) region and a data center in Hohhot. The enterprise has created databases in both the data center and the VPC. The enterprise wants to synchronize data from its data center to a database in the VPC.
The enterprise can use a public VPN gateway to create IPsec-VPN connections between the data center and the VPC. This helps implement encrypted communication between the two ends. Then, the enterprise can use DTS to automatically synchronize data from the data center to the database in the VPC.
Prerequisites
A VPC is created in the China (Hohhot) region. A database is deployed on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) in the VPC. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
The following table describes the network configurations of the data center and the VPC.
You can specify the CIDR block of the VPC. Make sure that the CIDR block of the VPC does not overlap with that of the data center.
Resource | CIDR block | IP address | Database account |
Data center | 172.16.0.0/12 |
|
|
VPC | 10.0.0.0/8 | IP address of the ECS instance on which the database runs: 10.0.0.252 |
|
Procedure
Step 1: Create a VPN gateway
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the VPN gateway.
The region of the VPN gateway must be the same as that of the VPC to be associated.
On the VPN Gateway page, click Create VPN Gateway.
On the buy page, configure the following parameters, click Buy Now, and then complete the payment.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the VPN gateway.
In this example, VPNGW is used.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the VPN gateway belongs.
If you leave this parameter empty, the VPN gateway belongs to the default resource group.
In this example, this parameter is left empty.
Region
Select the region in which you want to create the VPN gateway.
In this example, China (Hohhot) is selected.
Gateway Type
Select a gateway type.
In this example, Standard is selected.
Network Type
Select a network type for the VPN gateway.
Public: The VPN gateway can be used to establish VPN connections over the Internet.
Private: The VPN gateway can be used to establish VPN connections over private networks.
In this example, Public is selected.
Tunnels
Select a tunnel mode. Valid values:
Dual-tunnel
Single-tunnel
For more information about the single-tunnel mode and dual-tunnel mode, see [Upgrade notice] IPsec-VPN connections support the dual-tunnel mode.
In this example, the default value Dual-tunnel is used.
VPC
Select the VPC that you want to associate with the VPN gateway.
In this example, the VPC deployed in the China (Hohhot) region is selected.
VSwitch
Select a vSwitch from the selected VPC.
If you select Single-tunnel, you need to specify only one vSwitch.
If you select Dual-tunnel, you need to specify two vSwitches.
After the IPsec-VPN feature is enabled, the system creates an elastic network interface (ENI) for each of the two vSwitches as an interface to communicate with the VPC over an IPsec-VPN connection. Each ENI occupies one IP address in the vSwitch.
NoteThe system selects a vSwitch by default. You can change or use the default vSwitch.
After a VPN gateway is created, you cannot modify the vSwitch associated with the VPN gateway. You can view the vSwitch associated with the VPN gateway, the zone to which the vSwitch belongs, and the ENI in the vSwitch on the details page of the VPN gateway.
In this example, a vSwitch in the VPC is selected.
vSwitch 2
Select another vSwitch from the selected VPC.
Specify two vSwitches in different zones in the associated VPC to implement disaster recovery across zones for IPsec-VPN connections.
For a region that supports only one zone, disaster recovery across zones is not supported. We recommend that you specify two vSwitches in the zone to implement high availability of IPsec-VPN connections. You can also select the same vSwitch as the first one.
NoteIf only one vSwitch is deployed in the VPC, create a vSwitch. For more information, see Create and manage a vSwitch.
In this example, another vSwitch in the VPC is selected.
Peak Bandwidth
Select a maximum bandwidth value for the VPN gateway. Unit: Mbit/s.
In this example, the default value is used.
Traffic
Select a metering method for the VPN gateway. Default value: Pay-by-data-transfer.
For more information, see Billing.
In this example, the default value is used.
IPsec-VPN
Specify whether to enable IPsec-VPN. Default value: Enable.
In this example, Enable is selected.
SSL-VPN
Specify whether to enable SSL-VPN. Default value: Disable.
In this example, Disable is selected.
Duration
Select a billing cycle for the VPN gateway. Default value: By Hour.
In this example, the default value is used.
Service-linked Role
Click Create Service-linked Role. The system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
The VPN gateway assumes this role to access other cloud resources.
If Created is displayed, the service-linked role is created and you do not need to create it again.
Configure this parameter based on actual conditions.
Return to the VPN Gateways page to view the VPN gateway.
After you create a VPN gateway, it is in the Preparing state. After 1 to 5 minutes, the VPN gateway changes to the Normal state. The Normal state indicates that the VPN gateway has been initialized and can be used.
Two public IP addresses are assigned to the public VPN gateway for establishing two encrypted tunnels. The following table describes the public IP addresses that are assigned to the VPN gateway.
VPN gateway name
VPN gateway ID
Public IP address
VPNGW
vpn-bp1ox1xu1jo8m1ph0****
47.XX.XX.3
47.XX.XX.169
Step 2: Create a customer gateway
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which you want to create the customer gateway.
Make sure that the customer gateway and the VPN gateway to be connected are deployed in the same region.
On the Customer Gateways page, click Create Customer Gateway.
In the Create Customer Gateway panel, configure the following parameters and click OK.
You must create two customer gateways in order to create two encrypted tunnels. The following table describes only the parameters that are relevant to this topic. You can use the default values for other parameters or leave them empty. For more information, see Create and manage a customer gateway.
Parameter
Description
Customer Gateway 1
Customer Gateway 2
Name
Enter a name for the customer gateway.
For Customer Gateway 1, CustomerGW1 is used.
For Customer Gateway 2, CustomerGW2 is used.
IP Address
Enter the public IP address of the gateway device in the data center.
For Customer Gateway 1, 211.XX.XX.36 is used.
For Customer Gateway 2, 211.XX.XX.71 is used.
Step 3: Create IPsec-VPN connections
After the VPN gateway and customer gateways are created, you need to create an IPsec connection over the VPN gateway to establish encrypted VPN tunnels. The procedure varies based on the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) version used for the IPsec-VPN connection.
Procedure if IKEv2 is used
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which you want to create the IPsec-VPN connection.
Make sure that the IPsec-VPN connection and the VPN gateway are in the same region.
On the IPsec Connections page, click Create IPsec-VPN Connection.
On the Create IPsec-VPN Connection page, configure parameters and click OK. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, IPsec-Connection is used.
Associate Resource
Select the type of network resource to be associated with the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, VPN Gateway is selected.
VPN Gateway
Select the VPN gateway that you want to associate with the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, the VPN gateway VPNGW is selected.
Routing Mode
Select a routing mode.
Destination Routing Mode: Traffic is forwarded based on the destination IP address.
Protected Data Flows: forwards traffic based on the source and destination IP addresses.
In this example, Protected Data Flows is selected.
Local Network
Enter the CIDR block of the VPC with which the VPN gateway instance is associated.
In this example, enter the following two CIDR blocks:
CIDR block of the VPC: 10.0.0.0/8
CIDR block of the DTS server: 100.104.0.0/16
ImportantYou must add the CIDR block of the DTS server to the Local Network section. This helps DTS access the database of the peer end over the VPN gateway.
For more information about the CIDR blocks used by DTS, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
Remote Network
Enter the CIDR block of the data center.
In this example, 172.16.0.0/12 is used.
Effective Immediately
Specifies whether the configuration immediately takes effect. Valid value:
Yes: starts negotiations after the configuration is complete.
No: starts negotiations when inbound traffic is detected.
In this example, Yes is selected.
BGP Configuration
If you want the IPsec-VPN connection to use the BGP protocol, turn on BGP. BGP is disabled by default.
In this example, the default value is used. BGP is disabled.
Tunnel 1
Configure VPN parameters for the active tunnel.
By default, Tunnel 1 serves as the active tunnel and Tunnel 2 serves as the standby tunnel. You cannot modify this configuration.
Customer Gateway
Select the customer gateway that you want to associate with the active tunnel.
In this example, CustomerGW1 is selected.
Pre-Shared Key
The pre-shared key of the active tunnel that is used to verify identities.
The pre-shared key must be 1 to 100 characters in length, and can contain digits, letters, and the following characters:
~ ` ! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) _ - + = { } [ ] \ | ; : ' , . < > / ?If you do not specify a pre-shared key, the system randomly generates a 16-character string as the pre-shared key.
ImportantThe IPsec-VPN connection and the peer gateway devices must use the same pre-shared key. Otherwise, the system cannot establish an IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, fddsFF123**** is used.
Encryption Configuration
Configure the parameters for the IKE, IPsec, dead peer detection (DPD), and NAT traversal features.
In this example, the default encryption settings are used. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
Tunnel 2
Configure VPN parameters for the standby tunnel.
Customer Gateway
Select the customer gateway that you want to associate with the standby tunnel.
In this example, CustomerGW2 is selected.
Pre-Shared Key
Enter a pre-shared key for the standby tunnel to verify identities.
In this example, fddsFF456**** is used.
Encryption Configuration
Configure the parameters for the IKE, IPsec, dead peer detection (DPD), and NAT traversal features.
In this example, the default encryption settings are used. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
In the Established dialog box, click OK.
On the IPsec Connections page, find the IPsec-VPN connection that you create and click Generate Peer Configuration in the Actions column.
The configurations of the IPsec peer refer to the VPN configurations that you need to add when you create the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, you need to add the VPN configurations to the gateway device of the data center.
In the IPsec-VPN Connection Configuration dialog box, copy and save the configurations to an on-premises machine. The configurations are required when you configure the gateway device of the data center.
Procedure if IKEv1 is used
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which you want to create the IPsec-VPN connection.
Make sure that the IPsec-VPN connection and the VPN gateway are in the same region.
On the IPsec Connections page, click Create IPsec-VPN Connection.
On the Create IPsec-VPN Connection page, configure parameters and click OK. The following table describes the parameters.
If you use IKEv1, you cannot add multiple CIDR blocks in the Local Network section. In this case, you must create two IPsec-VPN connections to transmit traffic for DTS and the VPC.
Parameter
Description
IPsec-VPN connection 1
IPsec-VPN connection 2
Name
The name of the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, IPsec-Connection1 is used.
In this example, IPsec-Connection2 is used.
Associate Resource
Select the type of network resource to be associated with the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, VPN Gateway is selected.
In this example, VPN Gateway is selected.
VPN Gateway
Select the VPN gateway that you want to associate with the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, the VPN gateway VPNGW is selected.
In this example, the VPN gateway VPNGW is selected.
Routing Mode
Select a routing mode.
Destination Routing Mode: Traffic is forwarded based on the destination IP address.
Protected Data Flows: forwards traffic based on the source and destination IP addresses.
In this example, Protected Data Flows is selected.
In this example, Protected Data Flows is selected.
Local Network
Enter the CIDR block of the VPC with which the VPN gateway instance is associated.
CIDR block of the VPC: 10.0.0.0/8
CIDR block of the DTS server: 100.104.0.0/16
ImportantYou must add the CIDR block of the DTS server to the Local Network section. This helps DTS access the database of the peer end over the VPN gateway.
For more information about the CIDR blocks used by DTS, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
Remote Network
Enter the CIDR block of the data center.
In this example, 172.16.0.0/12 is used.
In this example, 172.16.0.0/12 is used.
Effective Immediately
Specifies whether the configuration immediately takes effect. Valid value:
Yes: starts negotiations after the configuration is complete.
No: starts negotiations when inbound traffic is detected.
In this example, Yes is selected.
In this example, Yes is selected.
BGP Configuration
If you want the IPsec-VPN connection to use the BGP protocol, turn on BGP. BGP is disabled by default.
In this example, the default value is used. BGP is disabled.
In this example, the default value is used. BGP is disabled.
Tunnel 1
Configure VPN parameters for the active tunnel.
By default, Tunnel 1 serves as the active tunnel and Tunnel 2 serves as the standby tunnel. You cannot modify this configuration.
Customer Gateway
Select the customer gateway that you want to associate with the active tunnel.
In this example, CustomerGW1 is selected.
In this example, CustomerGW1 is selected.
Pre-Shared Key
The pre-shared key of the active tunnel that is used to verify identities.
The pre-shared key must be 1 to 100 characters in length, and can contain digits, letters, and the following characters:
~ ` ! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) _ - + = { } [ ] \ | ; : ' , . < > / ?If you do not specify a pre-shared key, the system randomly generates a 16-character string as the pre-shared key.
ImportantThe IPsec-VPN connection and the peer gateway devices must use the same pre-shared key. Otherwise, the system cannot establish an IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, fddsFF123**** is used.
In this example, fddsFF123**** is used.
Encryption Configuration
Configure the parameters for the IKE, IPsec, dead peer detection (DPD), and NAT traversal features.
Select IKEv1 as the IKE version, and use the default settings for other features. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
Select IKEv1 as the IKE version, and use the default settings for other features. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
Tunnel 2
Configure VPN parameters for the standby tunnel.
Customer Gateway
Select the customer gateway that you want to associate with the standby tunnel.
In this example, CustomerGW2 is selected.
In this example, CustomerGW2 is selected.
Pre-Shared Key
Enter a pre-shared key for the standby tunnel to verify identities.
In this example, fddsFF456**** is used.
In this example, fddsFF456**** is used.
Encryption Configuration
Configure the parameters for the IKE, IPsec, dead peer detection (DPD), and NAT traversal features.
Select IKEv1 as the IKE version, and use the default settings for other features. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
Select IKEv1 as the IKE version, and use the default settings for other features. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in dual-tunnel mode.
In the Established dialog box, click OK.
On the IPsec Connections page, find the IPsec-VPN connection that you create and click Generate Peer Configuration in the Actions column.
The configurations of the IPsec peer refer to the VPN configurations that you need to add when you create the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, you need to add the VPN configurations to the gateway device of the data center.
In the IPsec-VPN Connection Configuration dialog box, copy and save the configurations to an on-premises machine. The configurations are required when you configure the gateway device of the data center.
Step 4: Add routes to the VPN gateway
After you create the IPsec-VPN connection, you must configure routes for the VPN gateway to transmit traffic. If you select Protected Data Flows as Routing Mode in Step 3, the system creates policy-based routes after the IPsec-VPN connection is created. The route is in the Unpublished state. You must perform the following operations to publish all policy-based routes of the VPN gateway to the VPC.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the VPN gateway resides.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the VPN gateway that you want to manage and click its ID.
On the details page of the VPN gateway, click the Policy-based Route Table tab, find the route that you want to manage, and then click Advertise in the Actions column.
In the Advertise Route message, click OK.
Step 5: Configure the gateway devices in the data center
After you create an IPsec-VPN connection on Alibaba Cloud, you need to add VPN and routing configurations to the gateway devices in the data center to connect the gateway devices to the IPsec-VPN connection. Then, network traffic is transmitted from the active tunnel to the VPC by default. If the active tunnel is down, the standby tunnel automatically takes over.
The following content contains third-party product information, which is only for reference. Alibaba Cloud does not make guarantees or other forms of commitments for the performance and reliability of the third-party tools, and potential impacts of operations on these tools.
The commands may vary with different vendors. Contact your vendor to obtain the information about specific commands.
Procedure if IKEv2 is used
Add the VPN configurations downloaded in Step 3 to the gateway devices in the data center.
Open the CLI of the gateway device.
Configure the IKEv2 proposal and policy.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ikev2 proposal alicloud encryption aes-cbc-128 //Configure the encryption algorithm. In this example, aes-cbc-128 is used. integrity sha1 //Configure the authentication algorithm. In this example, sha1 is used. group 2 //Configure the DH group. In this example, group 2 is used. exit ! crypto ikev2 policy Pureport_Pol_ikev2 proposal alicloud exit !Configure the IKEv2 keyring.
// Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1: crypto ikev2 keyring alicloud peer alicloud address 47.XX.XX.3 // Configure the public IP address of the active tunnel for the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, 47.XX.XX.3 is used. pre-shared-key fddsFF123**** // Configure the pre-shared key. In this example, fddsFF123**** is used. exit ! // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto ikev2 keyring alicloud peer alicloud address 47.XX.XX.169 // Configure the public IP address of the standby tunnel for the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, 47.XX.XX. 169. pre-shared-key fddsFF456**** // Configure the pre-shared key. In this example, fddsFF456**** is used. exit !Configure the IKEv2 profile.
// Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1: crypto ikev2 profile alicloud match identity remote address 47.XX.XX.3 255.255.255.255 // Match the public IP address of the active tunnel of the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, 47.XX.XX.3 is used. identity local address 211.XX.XX.36 // Configure the public IP address of Gateway Device 1. In this example, 211.XX.XX.36 is used. authentication remote pre-share // Set the authentication mode of the VPN gateway to PSK. authentication local pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the data center to PSK. keyring local alicloud //Invoke the IKEv2 keyring. exit ! // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto ikev2 profile alicloud match identity remote address 47.XX.XX.169 255.255.255.255 // Match the public IP address of the standby tunnel of the IPsec-VPN connection. In this example, 47.XX.XX.169 is used. identity local address 211.XX.XX.71 // Configure the public IP address of Gateway Device 2. In this example, 211.XX.XX.71 is used. authentication remote pre-share // Set the authentication mode of the VPN gateway to PSK. authentication local pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the data center to PSK. keyring local alicloud //Invoke the IKEv2 keyring. exit !Set transform.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ipsec transform-set TSET esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode tunnel exit !Create an ACL to implement access control.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: access-list 100 permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255Create an IPsec policy.
// Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1: crypto map ipsecpro64 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 47.XX.XX.3 set transform-set TSET set ikev2-profile alicloud set pfs group2 match address 100 // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto map ipsecpro64 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 47.XX.XX.169 set transform-set TSET set ikev2-profile alicloud set pfs group2 match address 100Set the IPsec tunnels.
// Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1: interface GigabitEthernet1 // Configure the IP address of the interface that is used for the active tunnel. ip address 211.XX.XX.36 255.255.255.0 crypto map ipsecpro64 // Apply the IPsec policy. negotiation auto ! // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: interface GigabitEthernet1 // Configure the IP address of the interface that is used for the standby tunnel. ip address 211.XX.XX.71 255.255.255.0 crypto map ipsecpro64 // Apply the IPsec policy. negotiation auto !
Add routing configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway 2 in the data center.
Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2.
// Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 1. ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 47.XX.XX.3 ip route 100.104.0.0 255.255.0.0 47.XX.XX.3 // Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 2. ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 47.XX.XX.169 ip route 100.104.0.0 255.255.0.0 47.XX.XX.169Add routes to the data center based on your network environment. The routes must allow network traffic to be transmitted from the data center to the VPC preferentially over On-premises Gateway Device 1. If On-premises Gateway Device 1 is down, On-premises Gateway Device 2 automatically takes over. Contact your vendor to obtain the information about specific commands.
Procedure if IKEv1 is used
Add the VPN configurations downloaded in Step 3 to the gateway devices in the data center.
Open the CLI of the gateway device.
Create an ISAKMP policy.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto isakmp policy 1 authentication pre-share encryption aes hash sha group 2 lifetime 86400Set a pre-shared key.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 in the data center: crypto isakmp key fddsFF123**** address 47.XX.XX.3 // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto isakmp key fddsFF456**** address 47.XX.XX.169Configure the IPsec protocol.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ipsec transform-set ipsecpro64 esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode tunnelCreate an ACL to implement access control.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2 in the data center: access-list 100 permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255Create an IPsec policy.
// Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1: crypto map ipsecpro64 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 47.XX.XX.3 set transform-set ipsecpro64 set pfs group2 match address 100 // Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto map ipsecpro64 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 47.XX.XX.169 set transform-set ipsecpro64 set pfs group2 match address 100Apply the IPsec policy.
// Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 1 in the data center: interface GigabitEthernet1 // Apply the IPsec policy to the interface that is assigned a public IP address. crypto map ipsecpro64 // Add the following configurations to Gateway Device 2 in the data center: interface GigabitEthernet1 // Apply the IPsec policy to the interface that is assigned a public IP address. crypto map ipsecpro64
Add routing configurations to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway 2 in the data center.
Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 1 and Gateway Device 2.
// Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 1. ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 47.XX.XX.3 ip route 100.104.0.0 255.255.0.0 47.XX.XX.3 // Add a route that points to the VPC to Gateway Device 2. ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 47.XX.XX.169 ip route 100.104.0.0 255.255.0.0 47.XX.XX.169Add routes to the data center based on your network environment. The routes must allow network traffic to be transmitted from the data center to the VPC preferentially over On-premises Gateway Device 1. If On-premises Gateway Device 1 is down, On-premises Gateway Device 2 automatically takes over. Contact your vendor to obtain the information about specific commands.
Step 6: Test the connectivity
After you complete the preceding configurations, the data center and the VPC can communicate with each other. You can perform the following operations to verify the network connectivity between the two ends.
Before the test, make sure that you understand the security group rules applied to the ECS instance in the VPC and the ACL rules applied to the data center. Make sure that the rules allow mutual access between the VPC and the data center. For more information about the security group rules, see View security group rules and Add a security group rule.
Log on to the ECS instance in the VPC.
For more information about how to log on to an ECS instance, see Connect to an instance.
Run the
pingcommand on the ECS instance to access the database server in the data center.If the ECS instance can receive echo reply packets, the data center and the VPC can communicate with each other.
ping <IP address of the database server in the data center>
Step 7: Create a DTS task to synchronize data
After the test is passed, you can create a DTS data synchronization task. After the task is configured, the data is automatically synchronized from the data center to the database in the VPC.
In this example, the data is synchronized to a MySQL instance. For more information about data synchronization in DTS, see Overview of data synchronization scenarios.
Use one of the following methods to go to the Data Synchronization page and select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
DTS console
Log on to the DTS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Synchronization.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
DMS console
NoteThe actual operations may vary based on the mode and layout of the DMS console. For more information, see Simple mode and Customize the layout and style of the DMS console.
Log on to the DMS console.
In the top navigation bar, move the pointer over Data Development and choose .
From the drop-down list to the right of Data Synchronization Tasks, select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
Click Create Task to go to the task configuration page.
Optional. Click New Configuration Page in the upper-right corner of the page.
NoteSkip this step if the Back to Previous Version button is displayed in the upper-right corner of the page.
Specific parameters in the new and previous versions of the configuration page may be different. We recommend that you use the new version of the configuration page.
Configure the source and destination databases. The following table describes the parameters.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The name of the DTS task. DTS automatically generates a task name. We recommend that you specify a descriptive name that makes it easy to identify the task. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Source Database
Database Type
The type of the destination instance. Select MySQL.
Access Method
The access method of the source database. Select Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
Instance Region
The region in which the source database resides.
In this example, China (Hohhot) is selected.
Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts
Specifies whether data is migrated across Alibaba Cloud accounts. Select No.
Connected VPC
Select a VPC in the China (Hohhot) region.
DTS accesses the database in the data center through the VPC and the VPN gateway.
Domain Name or IP
The host IP address of the source MySQL database.
In this example, enter 172.16.0.228.
Port Number
The service port of the source database. The port must be accessible over the Internet. Default value: 3306.
Database Account
The username that is used to access the source database.
Database Password
The password that is used to access the destination database.
Destination Database
Database Type
The type of the destination instance. Select MySQL.
Access Method
The access method of the source database. Select Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
Instance Region
The region in which the destination database resides.
In this example, China (Hohhot) is selected.
Connected VPC
Select a VPC in the China (Hohhot) region.
Domain Name or IP
The host IP address of the destination MySQL database.
In this example, enter 10.0.0.252.
Port Number
The service port of the destination database. The port must be accessible over the Internet. Default value: 3306.
Database Account
The username that is used to access the destination database.
Database Password
The password that is used to access the destination database.
In the lower part of the page, click Test Connectivity and Proceed.
Make sure that the security group rules applied to the ECS instance and the ACL rules applied to the data center allow access from DTS. For more information about the CIDR blocks used by DTS, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
WarningIf the CIDR blocks of DTS servers are automatically or manually added to the whitelist of the database, or to the ECS security group rules, security risks may arise. Therefore, before you use DTS to synchronize data, you must understand and acknowledge the potential risks and take preventive measures, including: enhancing the security of your usernames and passwords, limiting the ports that are exposed, authenticating API calls, regularly checking the whitelist or ECS security group rules and forbidding unauthorized CIDR blocks, or connecting the database to DTS by using Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
If the data center and the database in the VPC can be connected, the network connectivity between the databases is normal. In this case, the system redirects you to the Configure Objects and Advanced Settings step. You can continue to configure the DTS data synchronization task. After the task is configured, you can start to synchronize data. For more information about how to configure a DTS data synchronization task, see Configure two-way data synchronization between MySQL instances.
If the system detects that the data center cannot be connected to the database in the VPC, you are not redirected to the next step. In this case, troubleshoot the issue as prompted. For more information, see What do I do if an error is reported when I connect a database instance to DTS over VPN?