HTTPS secure acceleration encrypts HTTPS connections between clients and Alibaba Cloud CDN points of presence (POPs) to ensure data security during transmission. This topic introduces this feature and describes the configuration procedure.
Background
After you configure HTTPS secure acceleration in the Alibaba Cloud CDN console, requests that are transmitted from clients to POPs are encrypted over HTTPS.
POPs retrieve requested resources from origin servers and then return the resources to clients based on the HTTPS settings of the origin servers. We recommend that you configure and enable HTTPS for your origin server to implement end-to-end HTTPS encryption.
How it works
The following figure shows how HTTPS secure acceleration works.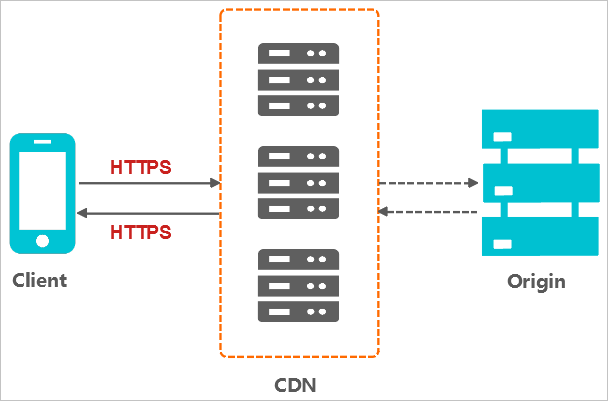
The client sends a request over HTTPS.
The server generates a public key and a private key. You can prepare the keys on your own or request them from an authority.
The server sends the public key certificate to the client.
The client verifies the certificate.
If the certificate is valid, the client generates a random number as a key. The client uses the public key to encrypt the random number and transmits the encrypted random number to the server.
If the certificate is invalid, the SSL handshake fails.
NoteA valid certificate must meet the following requirements: The certificate has not expired. The certificate is issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA). The digital signature of the issuer in the certificate can be decrypted with the public key of the issuer. The domain name in the certificate is the same as that of the server.
The server uses the private key to decrypt the encrypted random number.
The server uses the random number to encrypt data and transmits the data to the client.
The client uses the random number to decrypt the received data.
Benefits
HTTPS secure acceleration provides the following benefits:
HTTPS secure acceleration protects communications from eavesdropping, tampering, impersonation attacks, and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
HTTPS encrypts sensitive information such as session IDs and cookies before transmission. This minimizes the risk of sensitive information leaks.
HTTPS checks data integrity during transmission to protect the data from MITM attacks, such as DNS hijacking and tampering.
HTTPS is the new standard. If you choose to use HTTP, your website may be exposed to security risks. Users who visit your website by using mainstream browsers are prompted that this website is not secure. This compromises user experience and may reduce visits to the website.
Mainstream browsers prioritize HTTPS web URLs in the search results. In addition, mainstream browsers must support HTTPS before they can support HTTP/2. HTTPS is a more reliable choice in terms of security, market presence, and user experience. Therefore, we recommend that you upgrade your communication protocol to HTTPS.
Scenarios
The following table describes the scenarios of HTTPS secure acceleration.
Scenario | Description |
Enterprise applications | HTTPS protects confidential information on enterprise websites from being hijacked or intercepted. Leaks of the confidential information, such as customer relationship management (CRM) data and enterprise resource planning (ERP) data, may cause fatal damages to enterprises. |
Public service websites | HTTPS protects sensitive information on public service websites against attacks such as phishing and hijacking. Leaks of such information may compromise public trust. |
Payment systems | HTTPS protects sensitive data such as customer names and phone numbers used in payment transactions against hijacking and spoofing attacks. If sensitive data is leaked, attackers can use such data for fraudulent activities. This causes losses to both the customer and the enterprise. |
API operations | API operations can use HTTPS to encrypt important information, such as sensitive data and important instructions. This protects the information against hijacking. |
Enterprise websites | HTTPS improves user trust and experience. Web browsers display a lock icon in the address bar for websites with domain validated (DV) or organization validated (OV) certificates. The enterprise name is displayed together with the lock icon for websites that include extended validated (EV) certificates. |
Procedure
Purchase a certificate from Certificate Management Service.
To enable HTTPS secure acceleration, you must own a certificate that corresponds to the domain name for CDN. You can apply for a free certificate or purchase an advanced certificate from Certificate Management Service.
Configure an HTTPS certificate.
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console
In the left navigation pane, click Configuration Management.
Choose .
Find the domain name that you want to configure and click Configure.
Click HTTPS. In the HTTPS Certificate section, click Modify.
Modify configuration items.
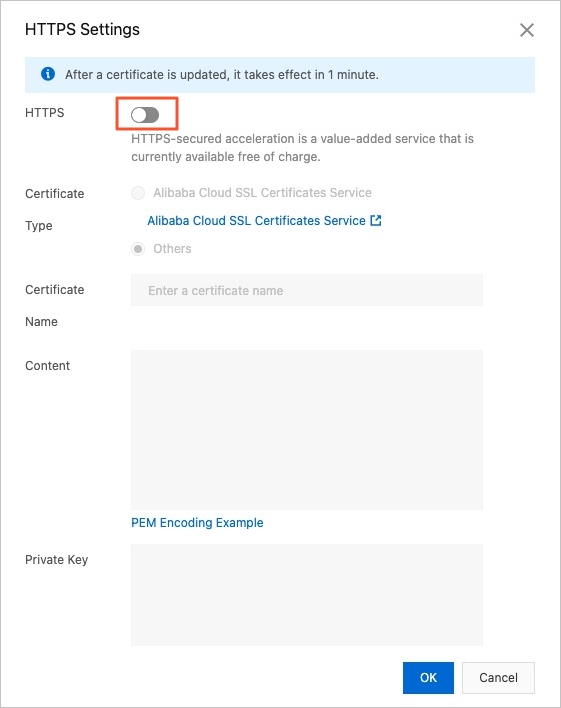 Note
NotePlayback failures may occur if your SSL certificate is expired or invalid. Make sure that you update the certificate.
Parameter
Description
Certificate Type
Certificate Management Service
You can apply for SSL certificates of various providers and types in the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Apply for a certificate.
After you apply for a free certificate, set the Certificate Type parameter to Certificate Management Service and select the free certificate.
Free SSL certificates are typically issued within one to two business days. During this period of time, you can choose to upload a custom certificate or select a certificate from Certificate Management Service.
NoteAfter you submit the application, the certificate may be issued within several hours to two business days. The time required to issue the certificate is based on the verification process defined by the CA.
A free SSL certificate is valid for three months. Before it expires, you do not need to apply for a new certificate each time you enable HTTPS acceleration. You must apply for a new certificate only if the current one has expired.
Others
If you cannot find a suitable certificate, upload a custom certificate. To upload a custom certificate, you must enter a certificate name and upload the certificate content and private key. The uploaded certificate is saved to Certificate Management Service. You can check the certificate on the SSL Certificate Management page.
NoteIf the certificate name you enter already exists in the system when you upload a custom certificate, you can modify the certificate name and upload the certificate again.
Certificate Name
Enter the certificate name.
Content
When the Certificate Type parameter is set to Others, you must enter the certificate content. For more information, click PEM Encoding Example under the Content field.
Private Key
When the Certificate Type parameter is set to Others, you must enter the certificate content. For more information, click PEM Encoding Example under the Private Key field.
Click OK.
What to do next
After an SSL certificate is uploaded, it takes effect within one minute. To verify that the HTTPS certificate takes effect, send HTTPS requests to access resources. If the URL is displayed with a lock icon in the address bar of the browser, HTTPS secure acceleration is working as expected.