If a requested resource is not cached on points of presence (POPs) of Alibaba Cloud CDN or the cache expires, the POPs send a request to the origin server to obtain the latest resource. The headers in the HTTP message returned by the origin server are origin response headers. You can modify incoming response headers to configure cache policies and cross-origin resource sharing (CORS). This improves the performance, security, and user experience of your website and effectively manages access to resources.
Background information
HTTP response headers are a component of the header section in response messages that are transmitted over HTTP. HTTP response headers include specific parameters that are sent to clients.
If a requested resource is not cached on POPs, the request is redirected to the origin server. Then, the origin server returns the requested resource to the POPs. You can rewrite incoming response headers from origin servers. This way, clients can easily identify response information. For example, you can rewrite the value of the Content-Type header before the header is returned to clients to ensure that the clients can parse the content that is retrieved from the origin server. If the Content-Type header returned by the origin server is invalid, garbled text appears. In this case, the value of Content-Type must be rewritten on POPs.

After an origin server receives a request from a POP, the origin server returns an HTTP message. A rewrite rule rewrites only HTTP headers in responses that are returned from an origin server. A rewrite rule does not rewrite HTTP headers in responses that are directly returned from POPs.
You cannot configure custom incoming response headers for wildcard domain names.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Configuration Management > CDN Configuration > Domain Names.
Find the domain name you want to manage and click Configure in the Actions column.
In the left navigation pane for the domain name, click Back-to-Origin.
Click the Origin HTTP Response Headers tab.
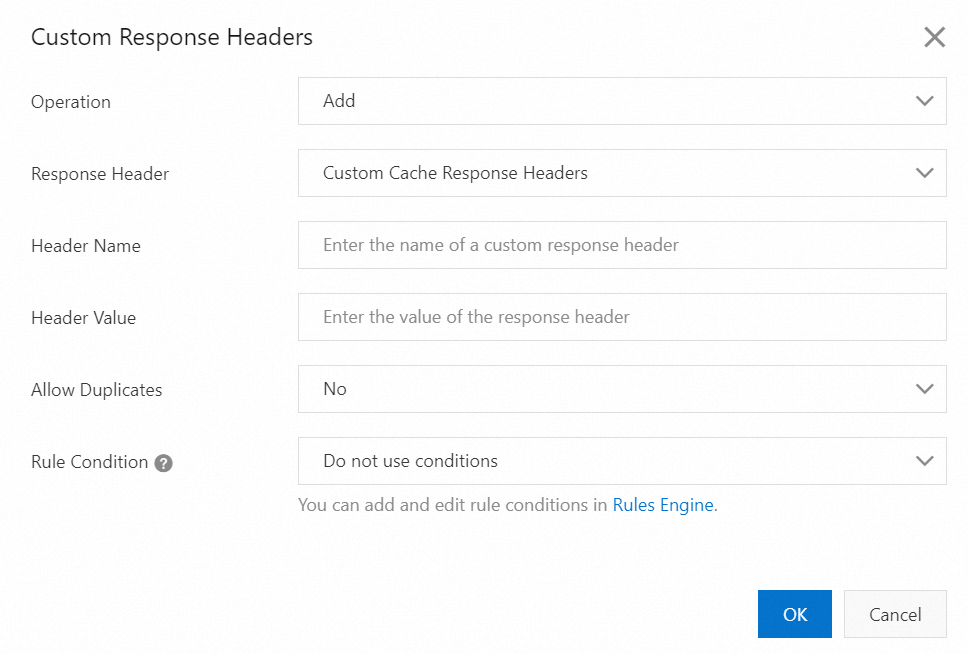
Click Add and configure the back-to-origin HTTP response header information.
ImportantWhen different operations are performed on the same response header at the same time, the operations have different priorities. The operations are prioritized in the following descending order: Replace > Add > Change or Delete. For example, if you perform the Add and Delete operations on the same response header at the same time, the response header is added and then deleted.
Parameters of the Add operation
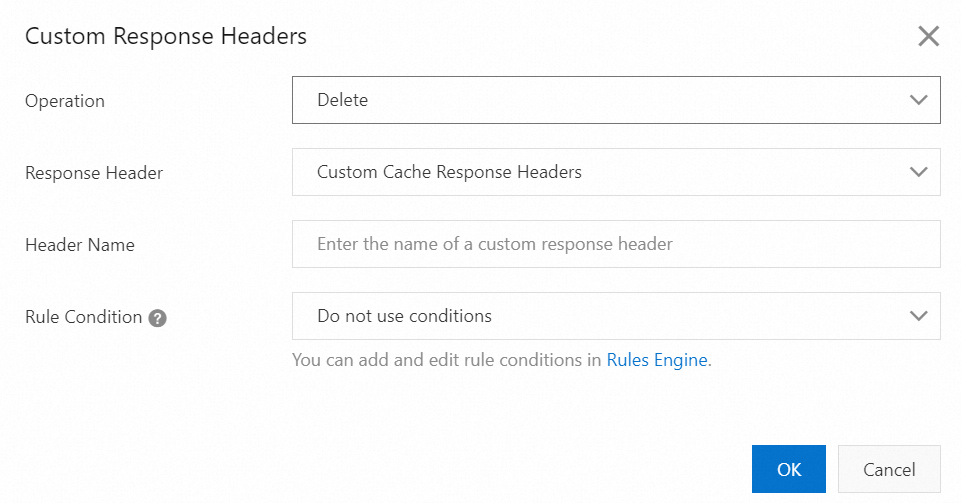
Parameters of the Delete operation
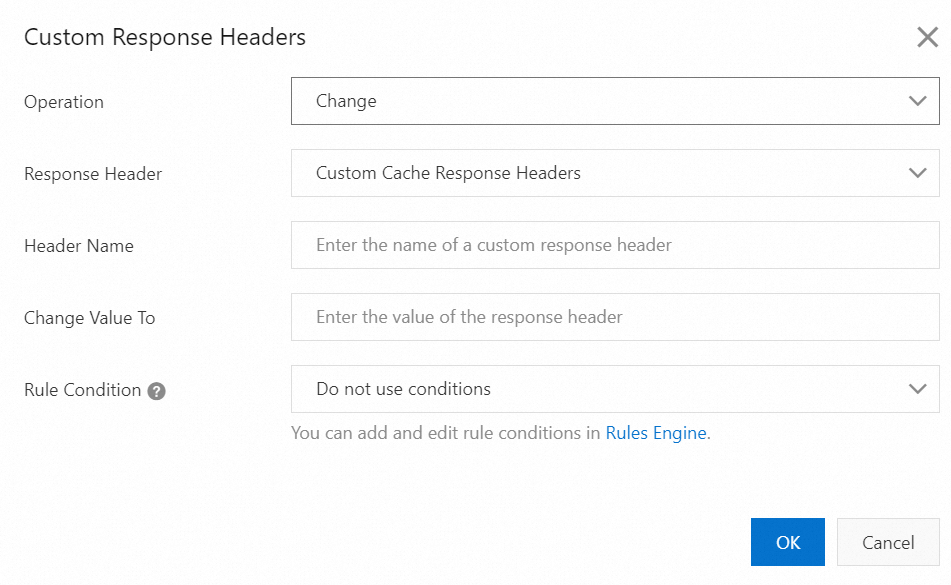
Parameters of the Change operation
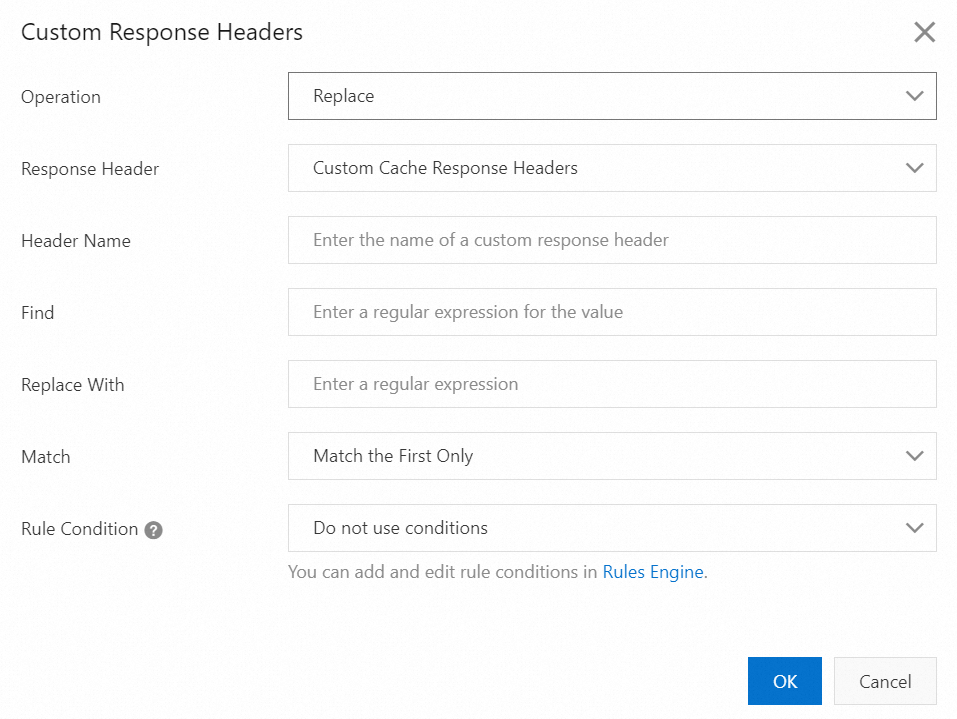
Parameters of the Replace operation
Click OK to complete the configuration.
Examples
Example 1: Specify that the content that is returned to users is of the MIME type
Sample scenario
Add a response header to specify that the content that is returned to users is of a specified MIME type.
MIME content includes the following types:
Text: including text files such as .txt and .csv files, and HTML files such as .html, .htm, .and shtml files.
Images: including common image files such as .jpg, .png, and .gif files.
Audio: including audio files such as .mp3 and .wav files.
Video: including video files such as .mp4 and .avi files.
Application: including application files such as .pdf, .doc, and .xls files.
Configurations
Operation: Add
Response Header: Content-Type
Header Value: text/html
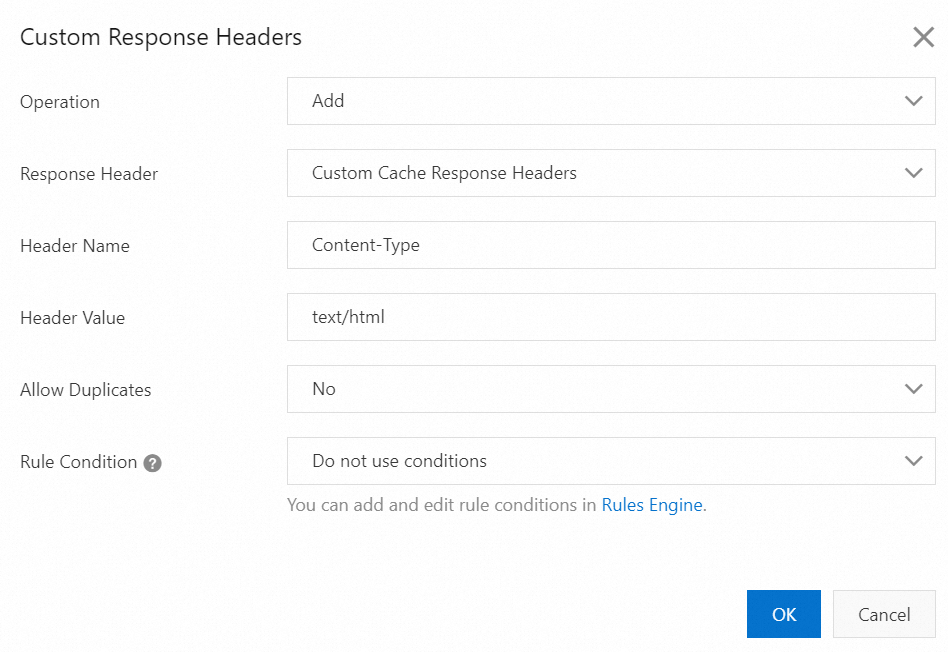
Expected result: The origin server adds the Content-Type header whose value is text/html to the response that is returned to POPs. If the configuration is updated, the value is overwritten.
Example 2: Delete a response header
Sample scenario
Delete a response header from responses.
Configurations
Operation: Delete
Response Header: Content-Type
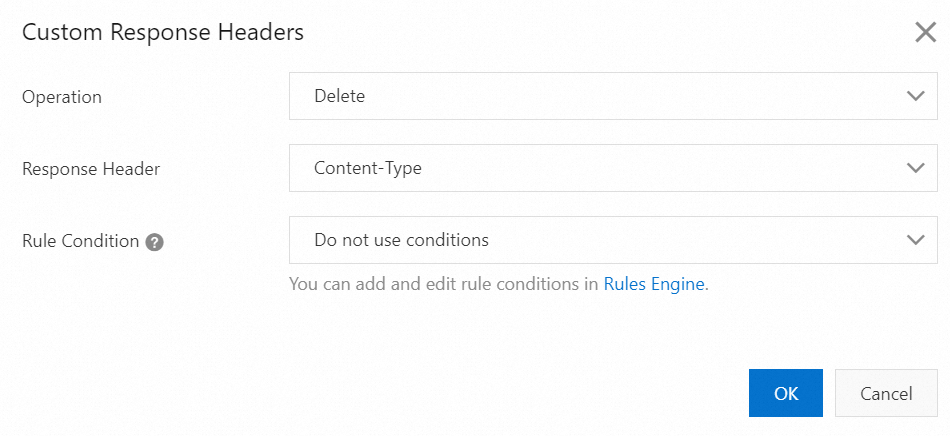
Expected result: The Content-Type header is deleted from the response before the header is returned to the user.
If the Add operation in Example 1 and the Delete operation in Example 2 are performed, the Content-Type header that has the value text/html is added to the response and then deleted. As a result, the content that is returned to the user is of the original type instead of a specified MIME type.