You can query time series data within a specific time range in a time series. If you are uncertain about the time series information, such as the metric name and data source, you can first query the time series by specifying conditions, and then query the time series data.
Overview
You can call the GetTimeseriesData operation to query time series data that meets the specified conditions in a time series.
When you query time series data, you must specify the time series information and query conditions based on your business requirements.
You can specify whether to read data in reverse chronological order to obtain the latest data.
You can specify the data columns that you want to return. By default, all data columns are returned.
You can specify the maximum number of rows to return at a time.
Procedure
You can query time series data within a specific time range in a time series in the Tablestore console.
Go to the Instance Management page.
Log on to the Tablestore console.
In the top navigation bar, select a resource group and a region.
On the Overview page, click the instance alias or click Manage Instance in the Actions column.
On the Instance Details tab, click the Time Series Tables tab.
On the Time Series Tables tab, click Manage Data in the Actions column of the time series table that you want to manage.
On the Query Data tab, click Query Data in the Actions column of the time series that you want to manage.
Specify query conditions.
By default, the query results are sorted in chronological order. If you want to read data in reverse chronological order, set Reverse Chronological Order to No.
Select a search method and specify a time range.
Click Search.
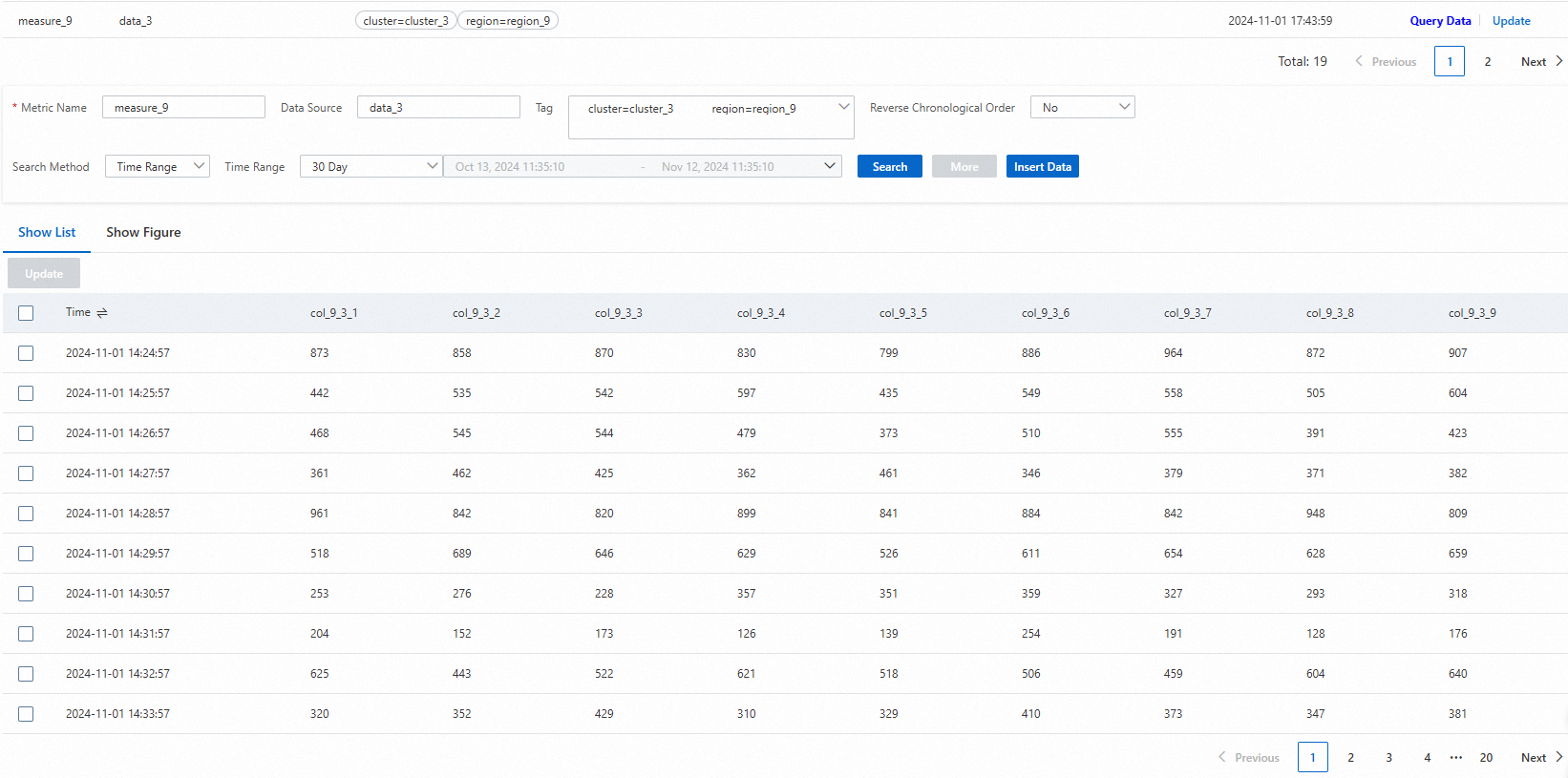
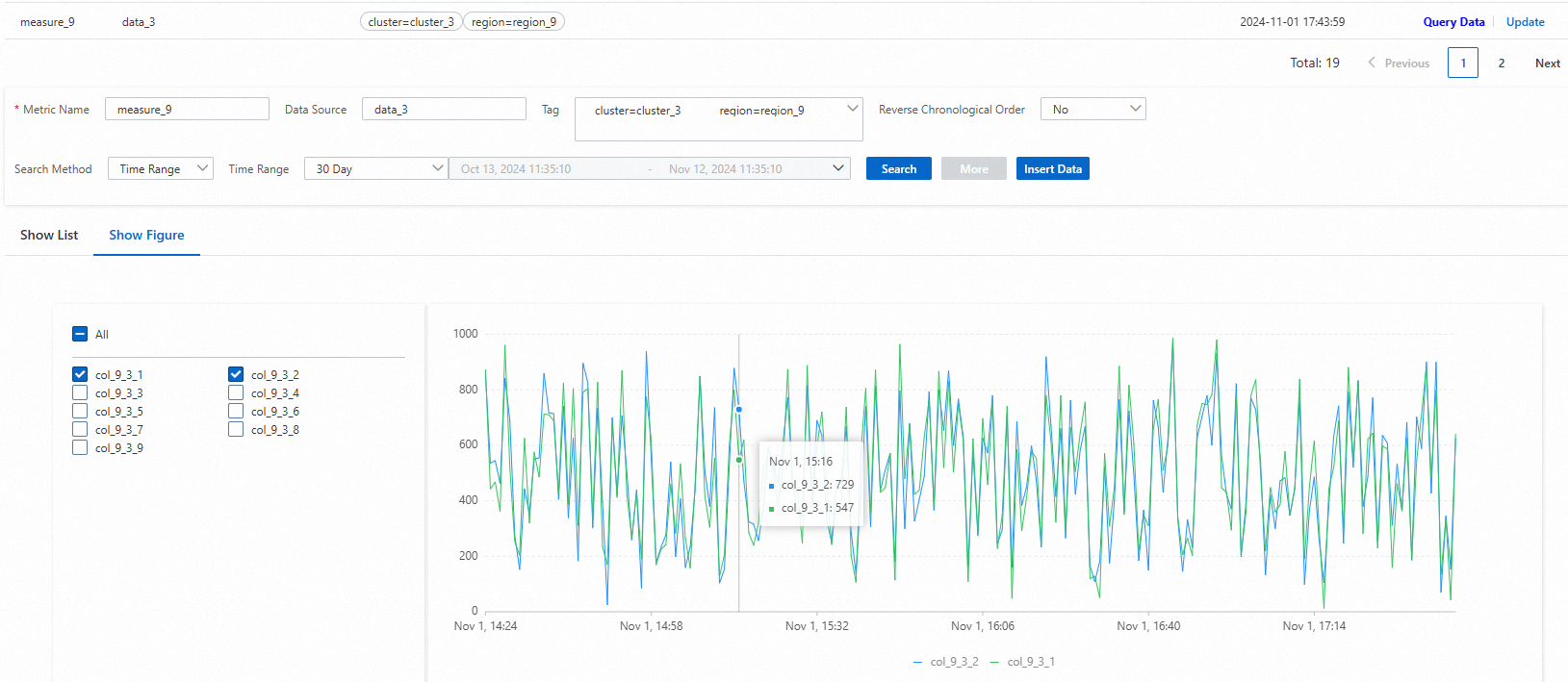
The data that meets the query conditions is displayed on the Query Data tab. The query results can be displayed in a list or a graph.
Display data in a list
Display data in a graph
Development integration
You can use the following Tablestore SDKs or the Tablestore CLI to query time series data:
FAQ
References
You can also execute SQL statements to query time series data. For more information, see Use SQL to query time series data.
To visualize time series data, you can connect Tablestore to Grafana. For more information, see Connect Tablestore to Grafana.
To store time series data at low costs and quickly query and analyze time series data, you can use time series analytics stores. For more information, see Analytical store for time series.