If issues are detected in a Windows image by the image check feature, such as residual drivers on the system disk, residual Xen drivers, or configurations that disallow drivers to be installed, perform the operations described in this topic to troubleshoot the issues.
Delete residual drivers from the registry
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control registry tree contains configuration information that controls system startup and specific aspects of devices. The Class subkey contains specific filter drivers that are registered on a device. If the filter drivers are deleted but remain in the registry, the instances that use the image may fail to start. You must delete residual drivers from the registry. The following section describes how to delete residual drivers from the disk registry.
Log on to the source server on which you create image files.
Open Registry Editor.
In this example, Windows 10 is used. In the search box of the taskbar, enter
regeditand press theENTERkey to open Registry Editor.Open the disk registry key.
The path of the disk registry is
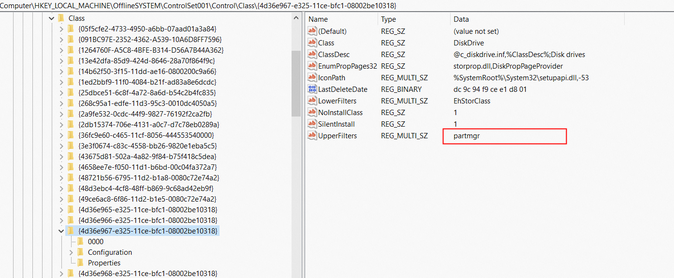
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Class\{4d36e967-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318}.Check for and delete any residual drivers.
Check the value of UpperFilter attribute to determine whether residual drivers remain in the system.
If the drivers no longer exist in the image but remain in UpperFilters, residual drivers remain in the system. You can view the drivers in the image in the
C:\Windows\System32\driversdirectory.Delete the names of the residual drivers from UpperFilters.
WarningProceed with caution. Make sure that the drivers that you want to delete are not built-in drivers to prevent system exceptions caused by accidental deletion of the drivers.
For example, the partmgr driver shown in the following figure is a built-in driver. In this case, you cannot delete the partmgr driver from UpperFilters.
Disable the Xen driver
The Xen driver is no longer used in virtual private clouds (VPCs), but may remain in some images of earlier versions. As a result, the instances that use such images may fail to start. You can disable the Xen driver in the registry.
Log on to the source server on which you create image files.
Open Registry Editor.
In this example, Windows 10 is used. In the search box of the taskbar, enter
regeditand press theEnterkey to open Registry Editor.Open the corresponding registry key.
The path of the registry is
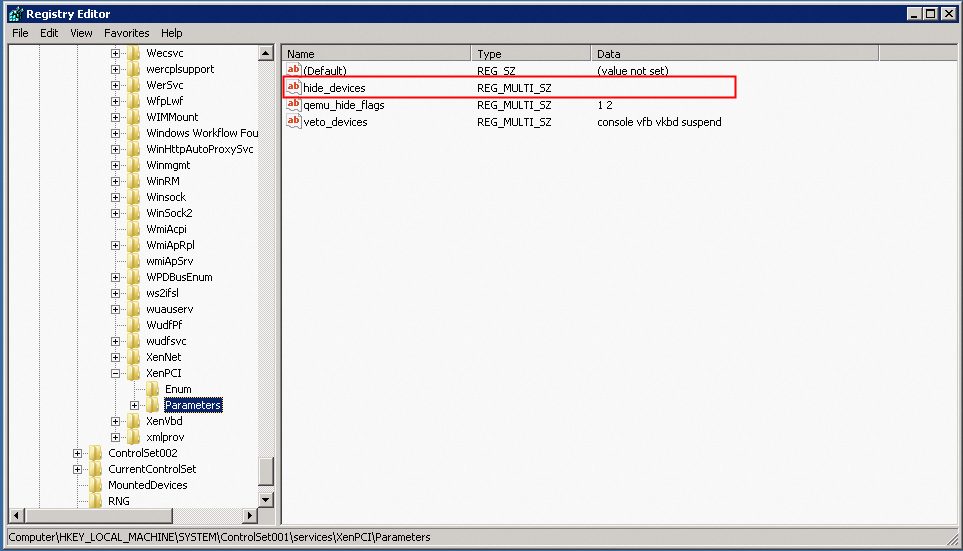
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\XenPCI\Parameters.Leave the hide_devices attribute empty.
Configure drivers to be installable
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services registry tree records all services in the system, some of which can control whether drivers can be installed. If a driver is not allowed to be installed in an image, the instances that use the image cannot update the driver. You must modify the registry attribute of the image to allow drivers to be installed.
Log on to the source server on which you create image files.
Open Registry Editor.
In this example, Windows 10 is used. In the search box of the taskbar, enter
regeditand press theEnterkey to open Registry Editor.Open the corresponding registry key.
For operating systems later than Windows Server 2008 R2, the path of the registry is
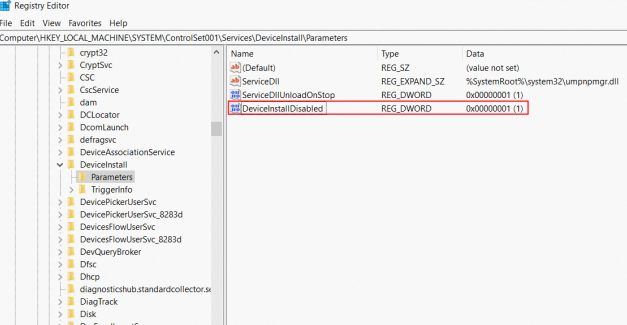
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\DeviceInstall\Parameters.For Windows Server 2008 R2 and earlier versions, the path of the registry is
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\DeviceInstall\Parameters.
Modify the registry attribute of the image to allow drivers to be installed. If the DeviceInstallDisabled attribute exists and the value of the attribute is not 0, change the value of the attribute to 0 or delete the attribute.
Example of Windows Server 2008 R2
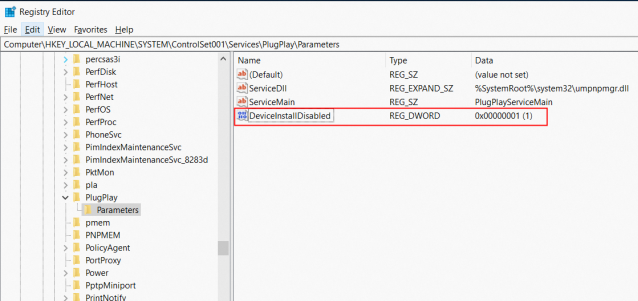
Example of Windows Server 2016