This topic describes the syntax of geospatial functions and provides examples on how to use the functions.
Introduction
Geospatial functions that start with the ST_ prefix comply with the SQL/MM standard and the OpenGIS Abstract Specification of the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC). Geospatial functions use well-known text (WKT) representations to describe geometries, such as points, line strings, and polygons. The following table describes the geometries and the WKT representations that are used to describe the geometries.
Geometry | WKT representation |
Point | POINT (0 0) |
Line string | LINESTRING (0 0, 1 1, 1 2) |
Polygon | POLYGON((0 0, 4 0, 4 4, 0 4, 0 0), (1 1, 2 1, 2 2, 1 2, 1 1)) |
Multipoint | MULTIPOINT(0 0, 1 2) |
Multilinestring | MULTILINESTRING((0 0, 1 1, 1 2), (2 3, 3 2, 5 4)) |
Multipolygon | MULTIPOLYGON(((0 0, 4 0, 4 4, 0 4, 0 0), (1 1, 2 1, 2 2, 1 2, 1 1)), ((-1 -1, -1 -2, -2 -2, -2 -1, -1 -1))) |
Geometry collection | GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(POINT(2 3), LINESTRING(2 3, 3 4)) |
Functions
Type | Function | Syntax | Limit | Support for SQL | Support for SPL |
Constructors | ST_AsText(x) | Returns the WKT representation of a geometry. | √ | × | |
ST_GeometryFromText(x) | Returns a geometry from the specified WKT representation. | √ | × | ||
ST_LineFromText(x) | Returns a line string from the specified WKT representation. | √ | × | ||
ST_Polygon(x) | Returns a polygon from the specified WKT representation. | √ | × | ||
ST_Point(x, y) | Returns a point from the specified WKT representation. | √ | × | ||
Operator | ST_Boundary(x) | Returns the closure of the combinatorial boundary of a geometry. | √ | × | |
ST_Buffer(x, distance) | Returns a geometry that represents all points whose distance from the specified geometry is less than or equal to the specified distance. | √ | × | ||
ST_Difference(x, y) | Returns a geometry that represents the point set difference of two specified geometries. | √ | × | ||
ST_Envelope(x) | Returns the bounding rectangular polygon of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_ExteriorRing(x) | Returns a line string that represents the exterior ring of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_Intersection(x, y) | Returns a geometry that represents the point set intersection of two specified geometries. | √ | × | ||
ST_SymDifference(x, y) | Returns a geometry that represents the point set symmetric difference of two specified geometries. | √ | × | ||
Spatial relationship tests | ST_Contains(x, y) | Returns true if no points of the second geometry lie in the exterior of the first geometry and at least one point of the interior of the first geometry lies in the interior of the second geometry. If the array contains the specified element, the function returns true. | √ | × | |
ST_Crosses(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries have several interior points in common. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Disjoint(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries do not share a portion of two-dimensional space. If two specified geometries do not share a portion of two-dimensional space, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Equals(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries represent the same geometry. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Intersects(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries share a portion of two-dimensional space. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Overlaps(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries share space and have the same dimension but are not completely contained by each other. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Relate(x, y, patternMatrix string) | Returns true if two specified geometries have a spatial relationship. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Touches(x, y) | Returns true if two specified geometries have at least one point in common but their interiors do not intersect. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Within(x, y) | Returns true if the first geometry is completely inside the second geometry. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
Accessors | ST_Area(x) | Calculates the projected area of a geometry on a two-dimensional plane by using the Euclidean distance method. | √ | × | |
ST_Centroid(x) | Returns the point value that represents the mathematical centroid of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_CoordDim(x) | Returns the coordinate dimension of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_Dimension(x) | Returns the inherent dimension of a geometry. The inherent dimension must be less than or equal to the coordinate dimension. | √ | × | ||
ST_Distance(x, y) | Returns the minimum distance between two geometries. | √ | × | ||
ST_EndPoint(x) | Returns the last point of a line string. | √ | × | ||
ST_IsClosed(x) | Returns true if the start point of a line string coincides with the end point. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_IsEmpty(x) | Returns true if a geometry is empty. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_IsRing(x) | Returns true if a line string is closed and simple. If yes, the function returns true. | √ | × | ||
ST_Length(x) | Calculates the projected length of a line string on a two-dimensional plane by using the Euclidean distance method. If multiple line strings exist, the function returns the sum of the lengths of the multiple line strings. | √ | × | ||
ST_NumPoints(x) | Returns the number of points in a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_NumInteriorRing(x) | Returns the number of interior rings in a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_StartPoint(x) | Returns the first point of a line string. | √ | × | ||
ST_X(x) | Returns the first X-axis coordinate of the input point. | √ | × | ||
ST_XMax(x) | Returns the maximum first X-coordinate of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_XMin(x) | Returns the minimum first X-coordinate of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_Y(x) | Returns the first Y-axis coordinate of the input point. | √ | × | ||
ST_YMax(x) | Returns the maximum first Y-coordinate of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
ST_YMin(x) | Returns the minimum first Y-coordinate of a geometry. | √ | × | ||
Bing tiles | bing_tile(x, y, zoom_level) | The following function returns a Bing tile based on the X-coordinate, Y-coordinate, and zoom level. | √ | × | |
bing_tile(quadKey) | The following function returns a Bing tile based on the quadtree key. | √ | × | ||
bing_tile_at(x, y, zoom_level) | Returns a Bing tile based on the latitude, longitude, and zoom level. | √ | × | ||
bing_tile_coordinates(x) | Returns the X- and Y-coordinates of a Bing tile. | √ | × | ||
bing_tile_polygon(x) | Returns the polygon format of a Bing tile. | √ | × | ||
bing_tile_quadkey(x) | Obtain the quadtree key of a Bing tile. | √ | × | ||
bing_tile_zoom_level(x) | Obtain the zoom level of a Bing tile. | √ | × |
ST_AsText function
The ST_AsText function returns the WKT representation of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_AsText(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The varchar type.
Examples
Obtain the WKT representation of a point.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_AsText(ST_Point(1,1))Query and analysis results

ST_GeometryFromText function
The ST_GeometryFromText function returns a geometry from the WKT representation that you specify.
Syntax
ST_GeometryFromText(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Construct multiple polygons.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_GeometryFromText('multipolygon(((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))')Query and analysis results

ST_LineFromText function
The ST_LineFromText function returns a line string from the WKT representation that you specify.
Syntax
ST_LineFromText(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
The linestring type.
Examples
Construct a line string.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_LineFromText('linestring(10 10,20 20)')Query and analysis results

ST_Polygon function
The ST_Polygon function returns a polygon from the WKT representation that you specify.
Syntax
ST_Polygon(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
The polygon type.
Examples
Construct a polygon.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Polygon('polygon((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10))')Query and analysis results

ST_Point function
The ST_Point function returns a point from the WKT representation that you specify.
Syntax
ST_Point(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The point type.
Examples
Construct a point.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Point(0,0)Query and analysis results

ST_Boundary function
The ST_Boundary function returns the closure of the combinatorial boundary of a geometry.
The closure of the combinatorial boundary of a point is empty. If the geometry that you specify is a point, the function returns POINT EMPTY.
The closure of the combinatorial boundary of a line string is composed of the end points of the line string.
The closure of the combinatorial boundary of a polygon is composed of line strings, including the exterior and interior rings of the polygon.
Syntax
ST_Boundary(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geography type. |
Return value type
The geography type.
Examples
Use the ST_Polygon function to return a polygon. Then, use the ST_Boundary function to return the closure of the combinatorial boundary of the polygon.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Boundary(ST_Polygon('polygon((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10))'))Query and analysis results

ST_Buffer function
The ST_Buffer function returns a geometry that represents all points whose distance from the specified geometry is less than or equal to the specified distance.
Syntax
ST_Buffer(x, distance)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
distance | The distance. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Use the ST_Point function to return a point. Then, use the ST_Buffer function to return a polygon that represents all points whose distance from the point is less than or equal to the specified distance.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Buffer(ST_Point(1,1),1)Query and analysis results
ST_Difference function
The ST_Difference function returns a geometry that represents the point set difference of two specified geometries.
Syntax
ST_Difference(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
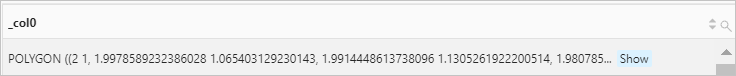
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Difference function to return a geometry that represents the point set difference of the two geometries.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Difference( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,0 15,0 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) ) AS "Difference"Query and analysis results
ST_Envelope function
The ST_Envelope function returns the bounding rectangular polygon of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_Envelope(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
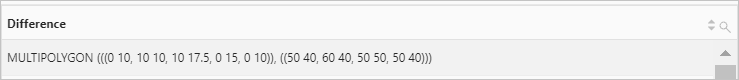
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_Envelope function to return the bounding rectangular polygon of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Envelope( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_ExteriorRing function
The ST_ExteriorRing function returns a line string that represents the exterior ring of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_ExteriorRing(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_ExteriorRing function to return a line string that represents the exterior ring of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_ExteriorRing( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Intersection function
The ST_Intersection function returns a geometry that represents the point set intersection of two specified geometries.
Syntax
ST_Intersection(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Intersection function to return a geometry that represents the point set intersection of the two geometries.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Intersection( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_SymDifference function
The ST_SymDifference function returns a geometry that represents the point set symmetric difference of two specified geometries.
Syntax
ST_SymDifference(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_SymDifference function to return a geometry that represents the point set symmetric difference of the two geometries.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_SymDifference( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Contains function
The ST_Contains function checks whether no points of the second geometry lie in the exterior of the first geometry and at least one point of the interior of the first geometry lies in the interior of the second geometry. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Contains(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Contains function to check whether no points of the second geometry lie in the exterior of the first geometry and at least one point of the interior of the first geometry lies in the interior of the second geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Contains( ST_GeometryFromText( 'polygon((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'point(11 11)' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Crosses function
The ST_Crosses function checks whether two specified geometries have several interior points in common. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Crosses(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Crosses function to check whether the two geometries have several interior points in common.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Crosses( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10, 10 20, 20 20, 20 15 , 10 10), (50 40, 50 50, 60 50, 60 40, 50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10, 10 20, 20 20, 20 15 , 10 10), (50 40, 50 50, 60 50, 60 40, 50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Disjoint function
The ST_Disjoint function checks whether two specified geometries share a portion of two-dimensional space. If not, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Disjoint(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Disjoint function to check whether the two geometries do not share any portion of two-dimensional space.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Disjoint( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Equals function
The ST_Equals function checks whether two specified geometries represent the same geometry. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Equals(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Equals function to check whether the two geometries represent the same geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Equals( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon(((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10),(50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon(((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10),(50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Intersects function
The ST_Intersects function checks whether two specified geometries share a portion of two-dimensional space. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Intersects(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Intersects function to check whether the two geometries share a portion of two-dimensional space.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Intersects( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Overlaps function
The ST_Overlaps function checks whether two specified geometries share space and have the same dimension but are not completely contained by each other. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Overlaps(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Overlaps function to check whether the two geometries share space and have the same dimension but are not completely contained by each other.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Overlaps( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Relate function
The ST_Relate function checks whether two specified geometries have a spatial relationship. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Relate(x, y, patternMatrix string)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
patternMatrix string | The DE-9IM pattern matrix string. The value of this parameter is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Relate function to check whether the two geometries have a spatial relationship.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Relate( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ), '****T****' )Query and analysis results

ST_Touches function
The ST_Touches function checks whether two specified geometries have at least one point in common but their interiors do not intersect. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Touches(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Touches function to check whether the two geometries have at least one point in common but their interiors do not intersect.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Touches( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Within function
The ST_Within function checks whether the first geometry is completely inside the second geometry. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_Within(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries. Then, use the ST_Within function to check whether the first geometry is completely inside the second geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Within( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Area function
The ST_Area function calculates the projected area of a geometry on a two-dimensional plane by using the Euclidean distance method.
Syntax
ST_Area(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
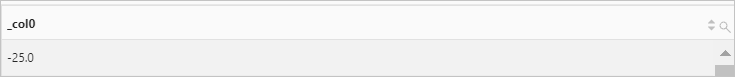
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_Area function to calculate the projected area of the geometry on a two-dimensional plane.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Area( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results
ST_Centroid function
The ST_Centroid function returns the point value that represents the mathematical centroid of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_Centroid(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The geometry type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_Centroid function to return the point value that represents the mathematical centroid of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Centroid( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_CoordDim function
The ST_CoordDim function returns the coordinate dimension of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_CoordDim(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_CoordDim function to return the coordinate dimension of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_CoordDim( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Dimension function
The ST_Dimension function returns the inherent dimension of a geometry. The inherent dimension must be less than or equal to the coordinate dimension.
Syntax
ST_Dimension(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type.
|
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_Dimension function to return the inherent dimension of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Dimension( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Distance function
The ST_Distance function returns the minimum distance between two geometries.
Syntax
ST_Distance(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return two geometries.Then, use the ST_Distance function to return the minimum distance between the two geometries.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Distance( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 50)))' ), ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_EndPoint function
The ST_EndPoint function returns the last point of a line string.
Syntax
ST_EndPoint(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The point type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_EndPoint function to return the last point of the line string.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_EndPoint( ST_LineFromText( 'linestring (10 10,20 20)' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_IsClosed function
The ST_IsClosed function checks whether the start point of a line string coincides with the end point. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_IsClosed(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_IsClosed function to check whether the start point of the line string coincides with the end point.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_IsClosed( ST_LineFromText( 'linestring (10.05 10.28 , 20.95 20.89 )' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_IsEmpty function
The ST_IsEmpty function checks whether a geometry is empty. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_IsEmpty(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
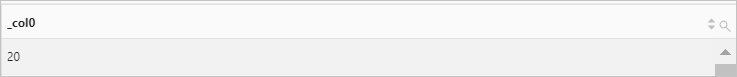
Use the ST_Point function to return a point. Then, use the ST_IsEmpty function to check whether the point is empty.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_IsEmpty(ST_Point(1,1))Query and analysis results

ST_IsRing function
The ST_IsRing function checks whether a line string is closed and simple. If yes, the function returns true.
Syntax
ST_IsRing(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_IsRing function to check whether the line string is closed and simple.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_IsRing( ST_LineFromText( 'linestring (10.05 10.28,20.95 20.89 )' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Length function
The ST_Length function calculates the projected length of a line string on a two-dimensional plane by using the Euclidean distance method. If multiple line strings exist, the function returns the sum of the lengths of the multiple line strings.
Syntax
ST_Length(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_Length function to calculate the projected length of the line string.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Length( ST_LineFromText( 'linestring (10.05 10.28,20.95 20.89)' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_NumPoints function
The ST_NumPoints function returns the number of points in a geometry.
Syntax
ST_NumPoints(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_NumPoints function to return the number of points in the line string.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_NumPoints( ST_LineFromText('linestring (10 10,20 20)') )Query and analysis results
ST_NumInteriorRing function
The ST_NumInteriorRing function returns the number of interior rings in a geometry.
Syntax
ST_NumInteriorRing(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_NumInteriorRing function to return the number of interior rings in the geometry.
Query statement
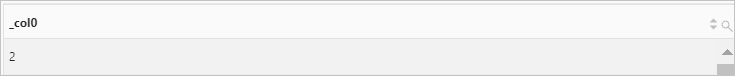
* | SELECT ST_NumInteriorRing( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_StartPoint function
The ST_StartPoint function returns the first point of a line string.
Syntax
ST_StartPoint(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The point type.
Examples
Use the ST_LineFromText function to return a line string. Then, use the ST_StartPoint function to return the first point of the line string.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_StartPoint( ST_LineFromText( 'linestring (10 10,20 20 )' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_X function
The ST_X function returns the X-coordinate of a specified point.
Syntax
ST_X(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the point type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_Point function to return a point. Then, use the ST_X function to return the X-coordinate of the point.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_X(ST_Point(1,3))Query and analysis results

ST_XMax function
The ST_XMax function returns the maximum first X-coordinate of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_XMax(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_XMax function to return the maximum first X-coordinate of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_XMax( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_XMin function
The ST_XMin function returns the minimum first X-coordinate of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_XMin(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_XMin function to return the minimum first X-coordinate of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_XMin( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_Y function
The ST_Y function returns the Y-coordinate of a specified point.
Syntax
ST_Y(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the point type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_Point function to return a point. Then, use the ST_Y function to return the Y-coordinate of the point.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_Y(ST_Point(1,3))Query and analysis results

ST_YMax function
The ST_YMax function returns the maximum first Y-coordinate of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_YMax(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_YMax function to return the maximum first Y-coordinate of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_YMax( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

ST_YMin function
The ST_YMin function returns the minimum first Y-coordinate of a geometry.
Syntax
ST_YMin(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the geometry type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Use the ST_GeometryFromText function to return a geometry. Then, use the ST_YMin function to return the minimum first Y-coordinate of the geometry.
Query statement
* | SELECT ST_YMin( ST_GeometryFromText( 'multipolygon (((10 10,10 20,20 20,20 15,10 10), (50 40,50 50,60 50,60 40,50 40)))' ) )Query and analysis results

bing_tile function
The bing_tile function returns a Bing tile.
Syntax
The following function returns a Bing tile based on the X-coordinate, Y-coordinate, and zoom level.
bing_tile(x, y, zoom_level)The following function returns a Bing tile based on the quadtree key.
bing_tile(quadKey)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The X-coordinate. The value of this parameter is of the integer type. |
y | The Y-coordinate. The value of this parameter is of the integer type. |
zoom_level | The zoom level. Valid values: [1,23]. The value of this parameter is of the integer type. |
quadKey | The quadtree key. |
Return value type
The BingTile type.
Examples
Example 1: Create a Bing tile based on the X-coordinate, Y-coordinate, and zoom level.
Query statement
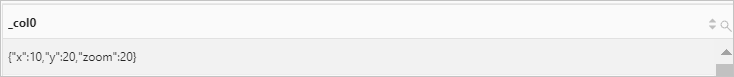
* | SELECT bing_tile(10, 20, 20)Query and analysis results
Example 2: Create a Bing tile based on the quadtree key.
Query statement
* | SELECT bing_tile(bing_tile_quadkey(bing_tile(10, 20, 20)))Query and analysis results

bing_tile_at function
The bing_tile_at function returns a Bing tile based on the latitude, longitude, and zoom level.
Syntax
bing_tile_at(x, y, zoom_level)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The latitude. Valid values: [-85.05112878,85.05112878]. The value of this parameter is of the double type. |
y | The longitude. Valid values: [-180,180]. The value of this parameter is of the double type. |
zoom_level | The zoom level. Valid values: [1,23]. The value of this parameter is of the integer type. |
Return value type
The BingTile type.
Examples
Create a Bing tile.
Query statement
* | SELECT bing_tile_at(47.265511, -122.465691, 12)Query and analysis results

bing_tile_coordinates function
The bing_tile_coordinates function returns the X- and Y-coordinates of a Bing tile.
Syntax
bing_tile_coordinates(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the BingTile type. |
Return value type
The array(integer,integer) type.
Examples
Obtain the X- and Y-coordinates of a Bing tile.
Query statement
* | SELECT bing_tile_coordinates(bing_tile_at(47.265511, -122.465691, 12))Query and analysis results

bing_tile_polygon function
The bing_tile_polygon function returns the polygon representation of a Bing tile.
Syntax
bing_tile_polygon(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the BingTile type. |
Return value type
The polygon type.
Examples
Obtain the polygon representation of a Bing tile.
Query statement
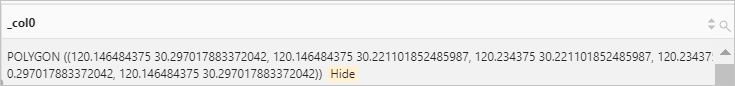
* | SELECT bing_tile_polygon(bing_tile_at(30.26, 120.19, 12))Query and analysis results
bing_tile_quadkey function
The bing_tile_quadkey function returns the quadtree key of a Bing tile.
Syntax
bing_tile_quadkey(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the BingTile type. |
Return value type
The varchar type.
Examples
Obtain the quadtree key of a Bing tile.
Query statement
* | SELECT bing_tile_quadkey(bing_tile(10, 20, 20))Query and analysis results

bing_tile_zoom_level function
The bing_tile_zoom_level function returns the zoom level of a Bing tile.
Syntax
bing_tile_zoom_level(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the BingTile type. |
Return value type
The double type.
Examples
Obtain the zoom level of a Bing tile.
Query statement
* | SELECT bing_tile_zoom_level(bing_tile(10, 20, 20))Query and analysis results