This topic describes how to distribute data to multiple destination Logstores in various scenarios. These scenarios include dynamic distribution, cross-account distribution, dynamic cross-account distribution, and multi-source dynamic distribution.
Background information
The data transformation feature of Log Service allows you to distribute data transformation results to multiple destination Logstores. When you save data transformation results, you can configure AccessKey pairs of different accounts. This way, you can distribute data transformation results to the Logstores of these accounts. You can also use the e_output or e_coutput function to dynamically set destination projects and Logstores, and distribute data transformation results to these Logstores.- In cross-account distribution scenarios, you can distribute data transformation results to a maximum of 20 Logstores that belong to different accounts.
- You can use the e_output function to send log data to specified Logstores. In this case, after log data is sent to the specified Logstores, the subsequent transformation rules do not take effect on the log data. If you want to use the subsequent transformation rules to transform the log data, you can replace the e_output function with the e_coutput function. For more information, see e_output and e_coutput. In the following scenarios, the e_output function is used to describe how to distribute log data.
Scenario 1: cross-account distribution
For example, assume that all access log entries of your website are stored in a Logstore. You want to distribute the log entries to Logstores of different accounts based on the value of the http_status field in the log entries.
In this scenario, you can use the data transformation feature to distribute the log entries.
- Raw log entries:
http_host: example.com http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https http_host: example.org http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http http_host: example.net http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https http_host: aliyundoc.com http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https - Distribution requirements
- Store the log entries whose http_status field value is 2XX as target0 in Logstore0 and set the topic of the log entries to success_event.
- Store the log entries whose http_status field value is 3XX as target1 in Logstore1 and set the topic of the log entries to redirection_event.
- Store the log entries whose http_status field value is 4XX as target2 in Logstore2 and set the topic of the log entries to unauthorized_event.
- Store the log entries whose http_status field value is 5XX as target3 in Logstore3 and set the topic of the log entries to internal_server_error_event.
The log entries that are stored as target0 belong to Account A and the log entries that are stored as target1, target2, and target3 belong to Account B.
- Transformation rule:
e_switch(e_match("status", r"2\d+"), e_set("__topic__", "success_event"), e_match("status", r"3\d+"), e_compose(e_set("__topic__", "redirection_event"), e_output("target1")), e_match("status", r"4\d+"), e_compose(e_set("__topic__", "unauthorized_event"), e_output("target2")), e_match("status", r"5\d+"), e_compose(e_set("__topic__", "internal_server_error_event`"), e_output("target3")) ) - Storage targetOn the Create Data Transformation Rule page, configure storage targets. For information about the parameters of storage targets, see Create a data transformation job.
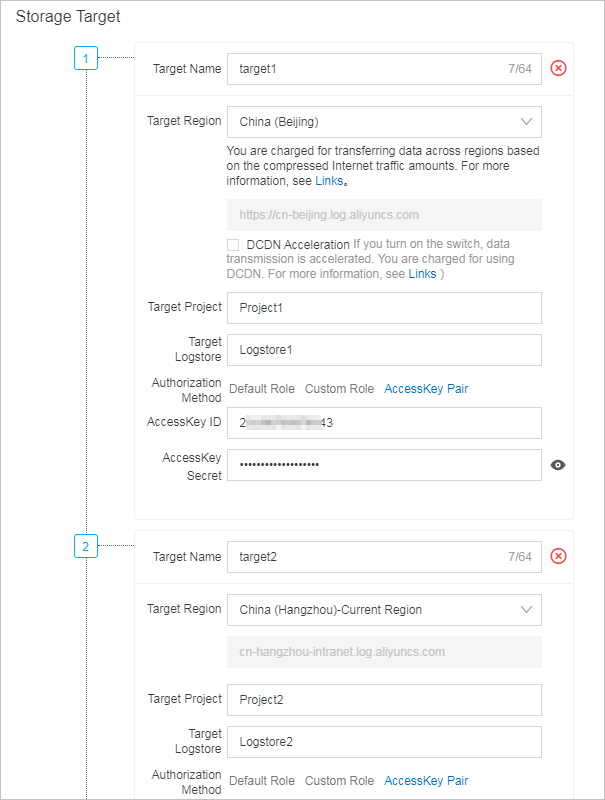
Label Storage target Destination project and Logstore AccessKey 1 target0 Project0 and Logstore0 The AccessKey pair of Account A 2 target1 Project1 and Logstore1 The AccessKey pair of Account B 3 target2 Project2 and Logstore2 The AccessKey pair of Account B 4 target3 Project3 and Logstore3 The AccessKey pair of Account B - Result:
## The log entries whose http_status field value is 2XX are distributed to Logstore0 of Account A. __topic__: success_event http_host: example.com http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https ## The log entries whose http_status field value is 3XX are distributed to Logstore1 of Account B. __topic__: redirection_event http_host: example.org http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http ## The log entries whose http_status field value is 4XX are distributed to Logstore2 of Account B. __topic__: unauthorized_event http_host: example.net http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https ## The log entries whose http_status field value is 5XX are distributed to Logstore3 of Account B. __topic__: internal_server_error_event http_host: aliyundoc.com http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https
Scenario 2: dynamic distribution
For example, assume that all access log entries of your website are stored in a Logstore. You want to distribute the log entries to different Logstores based on the project and logstore fields in the log entries.
In this scenario, you can use the data transformation feature to distribute the log entries.
- Raw log entries:
__tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: example.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: demo.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: learn.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: guide.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https - Distribution requirements
- Distribute log entries based on the values of the project and logstore fields.
- Add the __tag:__type field to each log entry and set the value of the field to dynamic_dispatch.
- Transformation rule:
e_output(project=v("project"), logstore=v("logstore"), tags={"type": "dynamic_dispatch"})The e_output function extracts the values of the project and logstore fields from each log entry and distributes each log entry based on the values.
- Storage targetOn the Create Data Transformation Rule page, configure storage targets.Note In this scenario, the destination projects and Logstores are determined based on the settings of the project and logstore parameters in the e_output function. These projects and Logstores are irrelevant to the destination project and Logstore that you configure to store the default storage target (labeled 1) on the Create Data Transformation Rule page.
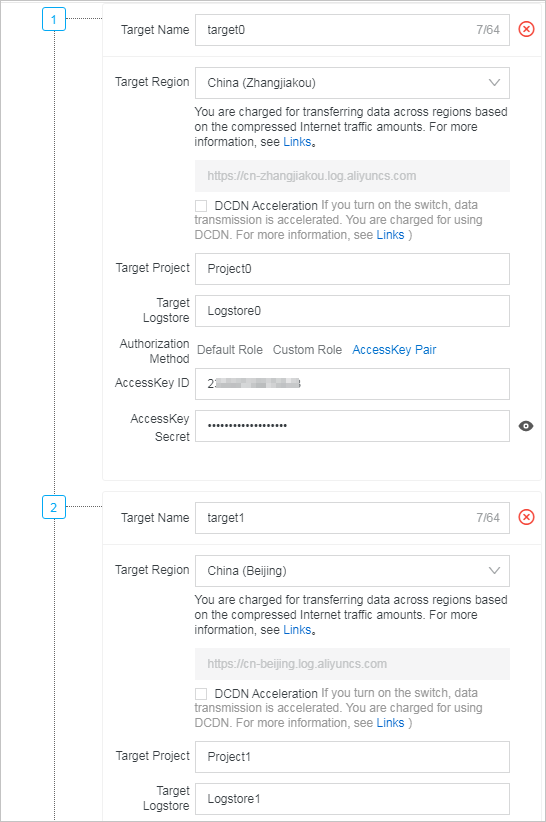
- Result:
## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore1 of Project1. __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: example.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore2 of Project1. __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: demo.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore1 of Project2. __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: learn.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore2 of Project2. __tag__:type: dynamic_dispatch host: guide.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https
Scenario 3: Dynamic cross-account distribution
For example, assume that all access log entries of your website are stored in a Logstore. You want to distribute the log entries to Logstores of different accounts based on the project and logstore fields in the log entries.
In this scenario, you can use the data transformation feature to distribute the log entries.
- Raw log entries:
host: example.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https host: demo.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http host: learn.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https host: guide.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https - Distribution requirements
Distribute log entries to projects and Logstores of different accounts based on the values of the project and logstore fields. The destination projects include Project1 and Project2. Project1 includes two Logstores named Logstore1 and Logstore2 and belongs to Account A. Project2 includes two Logstores named Logstore1 and Logstore2 and belongs to Account B.
- Transformation rule:
e_switch(e_match(v("project"), "Project1"), e_output(name="target1", project=v("project"), logstore=v("logstore")), e_match(v("project"), "Project2"), e_output(name="target2", project=v("project"), logstore=v("logstore"))) - Storage targetOn the Create Data Transformation Rule page, configure storage targets. For information about the parameters of storage targets, see Create a data transformation job.Note In this scenario, the destination projects and Logstores are determined based on the settings of the project and logstore parameters in the e_output function. These projects and Logstores are irrelevant to the destination project and Logstore that you configure to store the default storage target (labeled 1) on the Create Data Transformation Rule page.
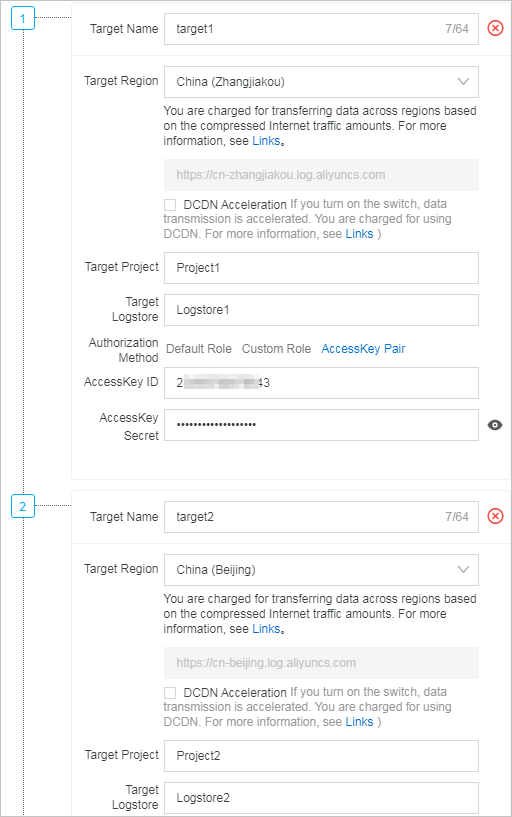
Label Storage target Destination project and Logstore AccessKey 1 target0 Project0 and Logstore0 None 2 target1 Randomly selected by the e_output function The AccessKey pair of Account A 3 target2 Randomly selected by the e_output function The AccessKey pair of Account B - Result:
## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore1 of Project1 that belongs to Account A. host: example.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 200 request_method: GET request_uri: /pic/icon.jpg scheme: https ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore2 of Project1 that belongs to Account A. host: demo.aliyundoc.com project: Project1 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 301 request_method: POST request_uri: /data/data.php scheme: http ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore1 of Project2 that belongs to Account B. host: learn.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore1 http_status: 404 request_method: GET request_uri: /category/abc/product_id scheme: https ## Log entry that is distributed to Logstore2 of Project2 that belongs to Account B. host: guide.aliyundoc.com project: Project2 logstore: Logstore2 http_status: 504 request_method: GET request_uri: /data/index.html scheme: https
Scenarios 4: multi-source dynamic distribution
For example, assume that you advertise a game and store log entries of all API requests of the game in a Logstore. You want to parse the user-agent request header and then distribute the log entries of the requests from iOS, Android, and Windows platforms based on the user-agent request header. You also want to analyze the advertisement conversion rate based on the request_method field.
In this scenario, you can use the data transformation and query features to distribute the log entries.
- Raw log entry:
__source__:127.0.0.0 __tag__:__receive_time__: 1589541467 ip:10.0.0.0 request_method: GET user_agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.9; rv:50.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/50.0 - Distribution requirements
- Store log entries of requests from Windows users as target1 in Logstore1.
- Store log entries of requests from iOS users as target2 in Logstore2.
- Store log entries of requests from Android users as target3 in Logstore3.
- Transformation rule:
In this scenario, you can use the ua_parse_os function to parse the user_agent field and use the dct_get function to retrieve the information of the operating system from the user_agent request header. Then, you can use the e_set function to add the os field to each log entry and use the e_output and e_if functions to distribute log entries. The value of the os field is the information of the operating system.
e_set("os", dct_get(ua_parse_os(v("user_agent")),"family")) e_if(e_search("os==Windows"),e_output(name="target1")) e_if(e_search("os=iOS"),e_output(name="target2")) e_if(e_search("os==Android"),e_output(name="target3")) - Storage target
On the Create Data Transformation Rule page, configure storage targets. For information about the parameters of storage targets, see Create a data transformation job.
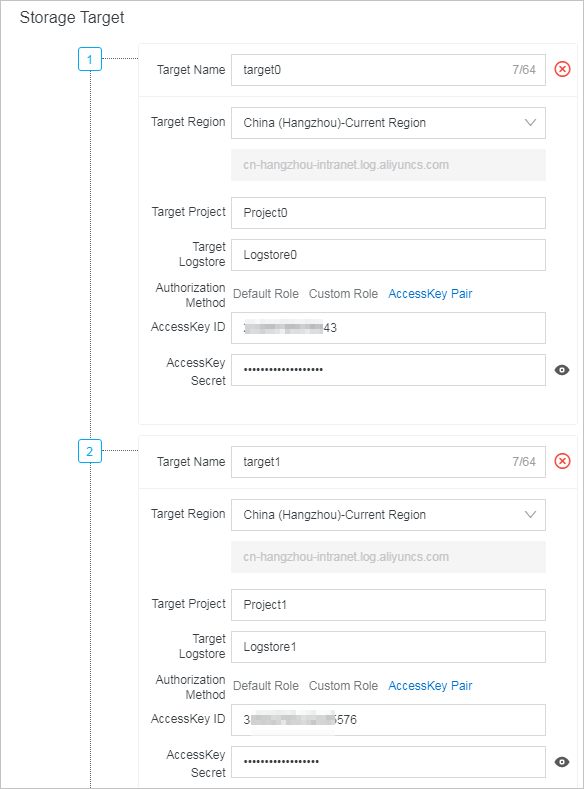
Label Storage target Destination project and Logstore 1 target0 Project0 and Logstore0 2 target1 Project1 and Logstore1 3 target2 Project2 and Logstore2 4 target3 Project3 and Logstore3 - Log query and analysis
You can query log data in the destination Logstores to retrieve the advertisement conversion rate. The following query results show that Android users have a higher advertisement conversion rate. For more information about how to query log data, see Query and analyze logs.
- On the Search & Analysis page of Logstore2, run the following query statement to retrieve the ratio of GET and POST requests from iOS users:
* | SELECT Request_method, COUNT(*) as number GROUP BY Request_method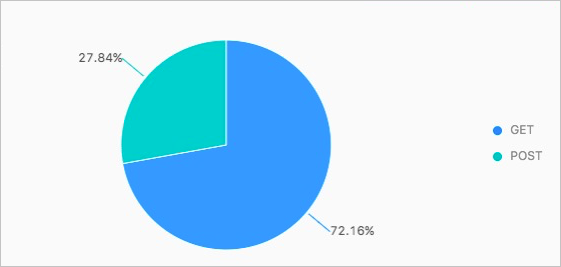
- On the Search & Analysis page of Logstore3, run the following query statement to retrieve the ratio of GET and POST requests from Android users:
* | SELECT Request_method, COUNT(*) as number GROUP BY Request_method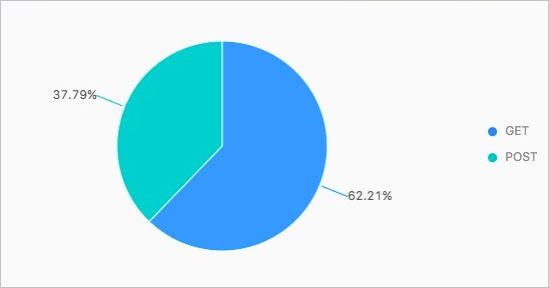
- On the Search & Analysis page of Logstore2, run the following query statement to retrieve the ratio of GET and POST requests from iOS users: