This topic describes how Network Load Balancer (NLB) is billed.
Billing methods
NLB supports the pay-as-you-go and subscription billing methods.
Pay-as-you-go: You are charged for the actual usage of each billable item. Fees are deducted after resources are consumed. This billing method is ideal for scenarios in which the usage of resources is difficult to predict.
Subscription (resource plans): You purchase resources in advance to offset fees. Resource plans are ideal for scenarios in which the usage of resources is easy to predict.
The subscription billing method is more cost-effective than the pay-as-you-go billing method.
Resource overages are billed based on the pay-as-you-go billing method and included in the bills. We recommend that you purchase resource plans based on the estimated amount of resource usage.
Billable items
The following figure shows the billable items of NLB.
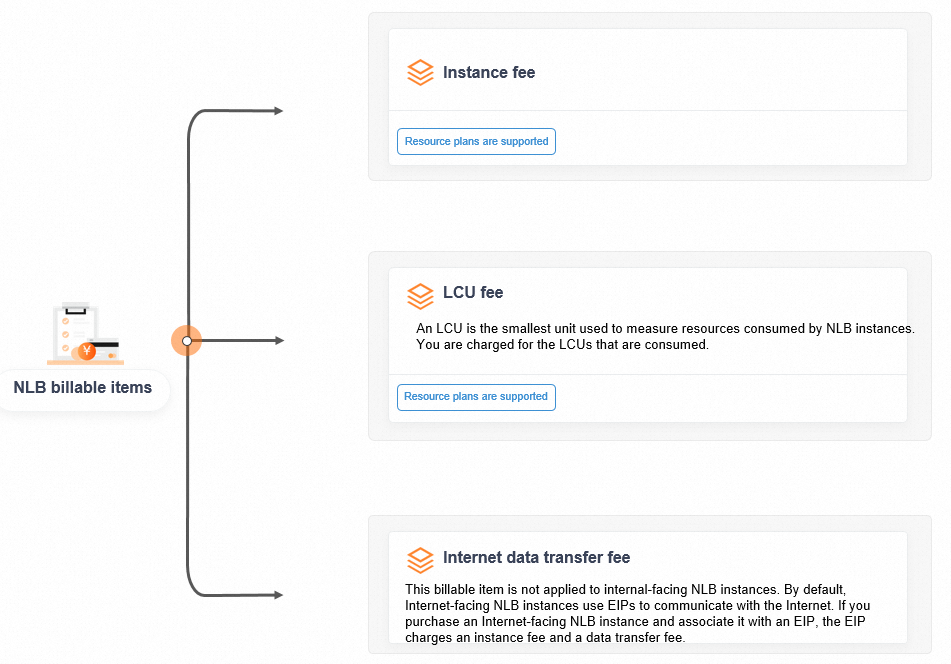
Billing cycle
Instance fees and LCU fees of NLB instances are calculated each hour based on the usage. In most cases, bills are generated 1 hour after a billing cycle ends. The time when bills are generated is determined by the system.
Internet-facing NLB instances charge an Internet data transfer fee. By default, Internet-facing NLB instances use elastic IP addresses (EIPs) to communicate with the Internet.
If an NLB instance uses an EIP to communicate with the Internet, the Internet data transfer fee is managed by the EIP. The billing cycle, bill generation time, and fee deduction time of the EIP apply. For more information, see Billing cycles.
If an NLB instance uses an Anycast EIP to communicate with the Internet, the Internet data transfer fee is managed by the Anycast EIP. The billing cycle, bill generation time, and fee deduction time of the Anycast EIP apply. For more information, see Supported regions and Billing rules.
Pricing
For more information about the pricing of each NLB billable item, see NLB billing rules and NLB resource plans. The prices on the buy page shall prevail.
You can use the NLB LCU Calculator to estimate the number of LCUs consumed by your service.
Learn more
Payment status | Suspension policy | Solution |
Near due | The system checks whether your account balance is sufficient to pay for the next three billing cycles based on the average payable amount during the last 7 hours. If you do not have a sufficient balance in your Alibaba Cloud account, the system notifies you by text messages or emails. Warning You are notified if your service is about to be suspended due to an overdue payment. To ensure service continuity, renew your service at the earliest opportunity. | After you top up the account balance, your service is resumed. |
Overdue | If your Alibaba Cloud account has an overdue payment, all pay-as-you-go instances within your account are affected.
| |
Fifteen days after an NLB instance is stopped due to an overdue payment, the NLB instance is released. The configurations and data of the instance are deleted and cannot be recovered. | You cannot restore these instances. |
View amount due
Log on to the Expenses and Costs console.
On the Account Overview page, view overdue payments.
View resource usage
Log on to the Expenses and Costs console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
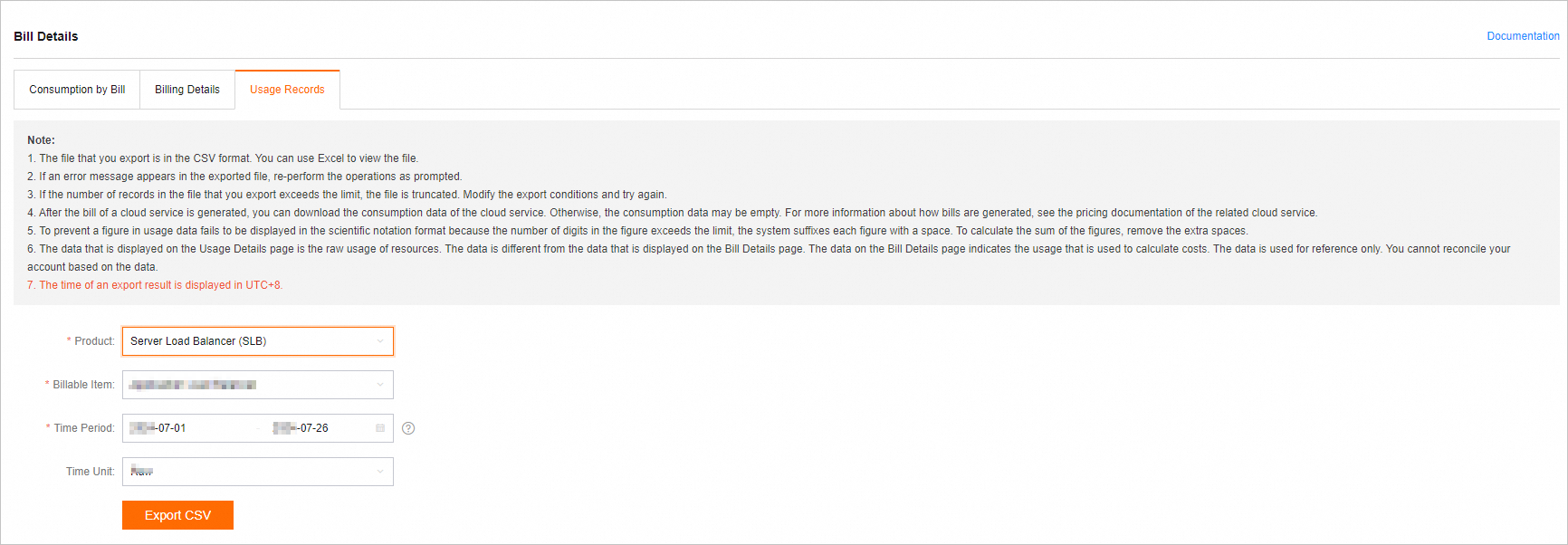
On the Bill Details page, click the Usage Records tab. Set Product to Server Load Balancer (SLB), specify a billable item, a time period, and a time unit, and then click Export CSV.
Set Billable Item to the load balancing service that you want to query. In this example, Network Load Balancer is selected.
After you open the downloaded file, you can view the resource usage by instance ID, region, or IP address.
Query billing and spending details
Log on to the Expenses and Costs console and go to the Bill Details page.
On the Bill Details page, click the Consumption by Bill, Billing Details, or Usage Records tab to view the required information. For more information, see Consumption by bill, Billing details, and Usage records.