This topic describes the causes of and solutions to the issue that the "Permission denied, please try again" error message appears when you connect to a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance from an SSH client.
Problem description
When you try to log on to a Linux simple application server by using an on-premises SSH client, even if you enter the correct password, an error message similar to the following one appears.
Permission denied, please try again.
The SSH server rejected your password. Try again.
Causes
The preceding issue may be caused by the following reasons:
Deny logons by the root user in the simple application server: The
PermitRootLoginorPasswordAuthenticationparameter in the/etc/ssh/sshd_configconfiguration file of the SSH service is set tono. For information about how to resolve the issue, see Deny logons by the root user.PermitRootLoginis set tono, logons by the root user are denied.PasswordAuthenticationis set tono, password-based logons are denied, but key-based logons are allowed.
The SELinux service is enabled on the server: If SELinux is enabled on a server, an error may be reported when you attempt to connect to the server as a root user or regular user.
Run the
cat /var/log/securecommand to query the secure log. If the log containserror: Could not get shadow information for root., SELinux is enabled. For information about how to resolve the issue, see Disable SELinux.
Solution if the issue is caused by Reason 1
Use the rescue feature to connect to the simple application server. For more information, see Connect to a Linux server by using the rescue feature.
Check the value of the
PermitRootLoginorPasswordAuthenticationparameter in the/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile.cat /etc/ssh/sshd_configThe command output shown in the following figure is returned. In the command output, the
PermitRootLoginandPasswordAuthenticationparameters are set tono, which indicates that logons by the root user and password-based logons are denied.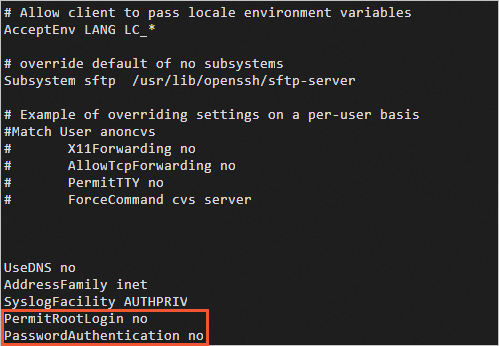
Change the values of the
PermitRootLoginandPasswordAuthenticationparameters based on your business requirements.Open the SSH configuration file.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configChange the values of the
PermitRootLoginandPasswordAuthenticationparameters.To allow logons by the root user, set the
PermitRootLoginparameter toyes.To allow password-based logons, set the
PasswordAuthenticationparameter toyes.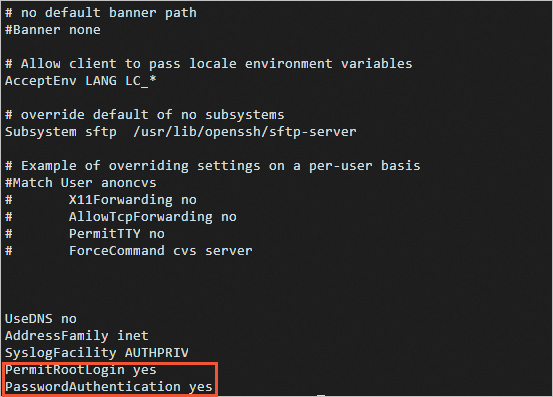
Press the Esc key and enter
:wqto save the changes.
Run the following command to restart the SSH service:
systemctl restart sshd.service
Solution if the issue is caused by Reason 2
You can temporarily or permanently disable SELinux based on your business requirements to resolve the issue.
Check the status of SELinux.
Use the rescue feature to connect to the simple application server. For more information, see Connect to a Linux server by using the rescue feature.
Run the following command to view the status of SELinux:
/usr/sbin/sestatus -vSample output:
SELinux status: enabledNoteValid values:
enabled: SELinux is enabled.
disabled: SELinux is disabled.
Disable SELinux.
Temporarily disable SELinux
Run the following command to temporarily disable SELinux:
setenforce 0Permanently disable SELinux
Run the following command to permanently disable SELinux:
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/configNoteYou can use the preceding command only if SELinux is in the
enforcingstate.Restart the server to allow the setting to take effect. For more information, see View server information.