CloudFlow provides a low-code, graphical workflow designer Workflow Studio. You can create and edit a workflow in Workflow Studio, configure input and output filtering rules for steps in the workflow, and configure error handling rules. This topic describes the interface overview of Workflow Studio.
Workflow Studio provides the CloudFlow Studio and YAML editing modes and the Configure Workflow feature to help you create visualized workflows, edit their definitions, and manage their configurations. In CloudFlow Studio editing mode, you can design a process by dragging and dropping nodes to the workflow canvas. In YAML editing mode, you can precisely design a workflow by entering a YAML script. The Configure Workflow feature allows you to configure the basic information about a workflow and a role that grants required permissions to execute the workflow.
CloudFlow Studio
CloudFlow Studio provides a graphical interface to visualize a workflow when you create it. The following figure shows the sections on the Edit Workflow page in CloudFlow Studio editing mode.
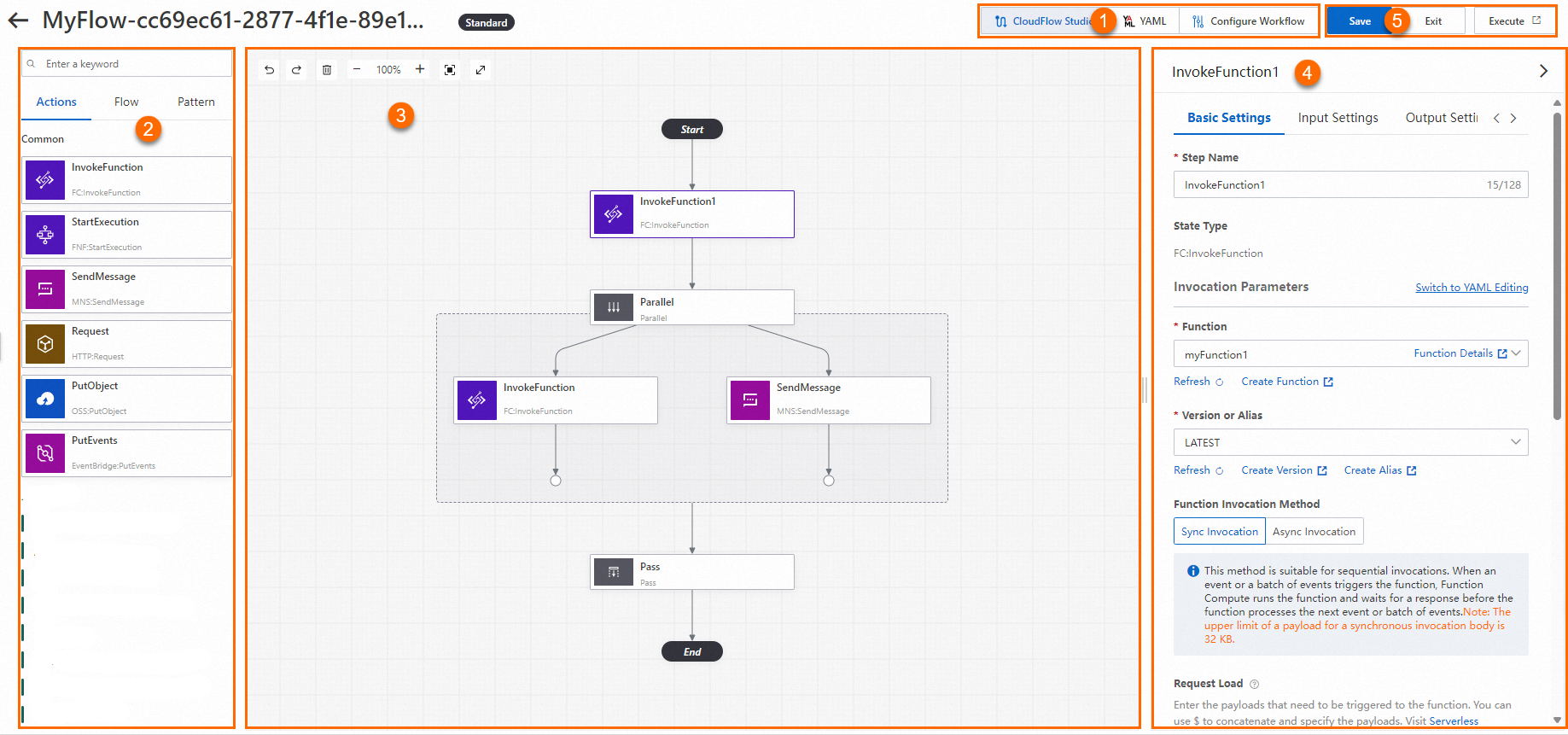
① Menu bar
In this section, you can switch among the CloudFlow Studio, YAML, and Configure Workflow tabs of Workflow Studio.
② State display section
This section contains the Actions, Flow, and Pattern tabs.
On the Actions tab, you can view the API operations of other Alibaba Cloud services that can be integrated with CloudFlow, including services in the sectors of elastic computing, Internet middleware, databases, and AI. You can drag and drop the API operation nodes to the workflow canvas. Each API operation node is a task state node.
The flow tab provides a list of state nodes that can be used to display state transitions but does not provide specific execution content. Workflow Studio provides the following flow nodes: Choice, Parallel, Map, Pass, Wait, Succeed, and Fail.
On the Pattern tab, you can view the workflow building modules that are preset by CloudFlow. You can drag and drop the modules to the workflow canvas to create a workflow.
③ Workflow canvas section
You can drag nodes from the Actions, Flow, and Pattern tabs in the state display section to the workflow canvas section. You can also drag and drop existing state nodes in a workflow to adjust their order and create a custom workflow.
④ Parameter configuration section
After you click a state node in a custom workflow on the workflow canvas, you can configure and view the properties of the state node in the parameter configuration section.
⑤ Function button section
This section provides common function buttons for workflows, including Save, Exit, and Execute.
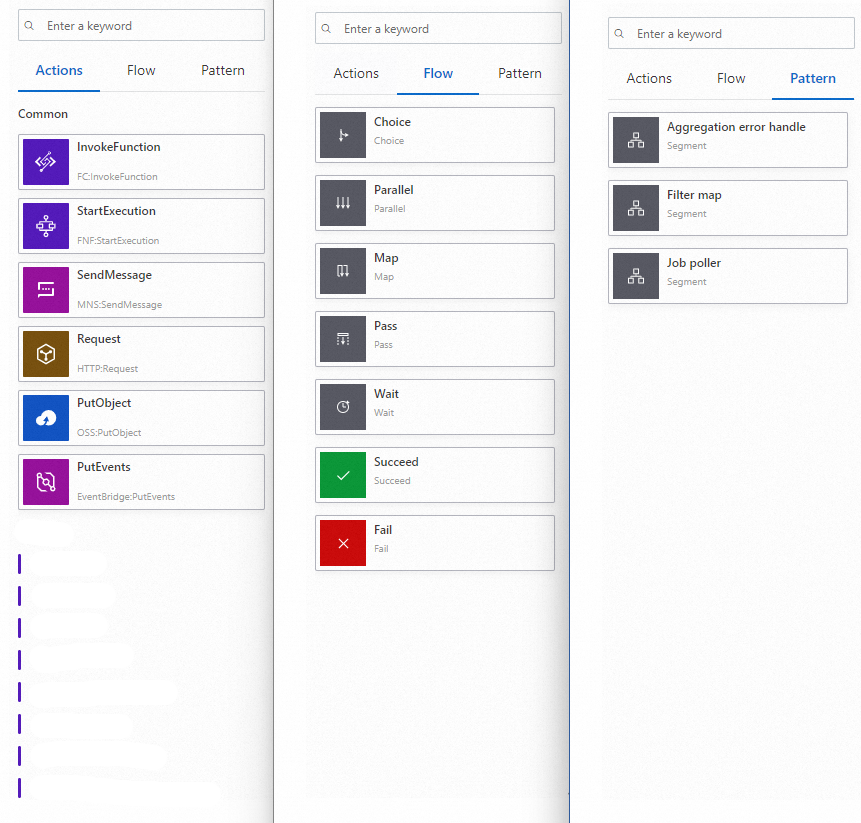
You can perform the following operations in the three operation sections on the CloudFlow Studio tab.
State display section
In the state display section, you can click the Actions, Flow, or Pattern tab. Then, drag a state node (API operation node) or a flow node to the canvas. You can also enter a keyword in the search box at the top of the state display section to search for a node.

Workflow canvas section
On the workflow canvas, you can drag and drop nodes to create custom flowcharts. You can also debug workflows in online mode to generate executable workflows when you edit the workflows.
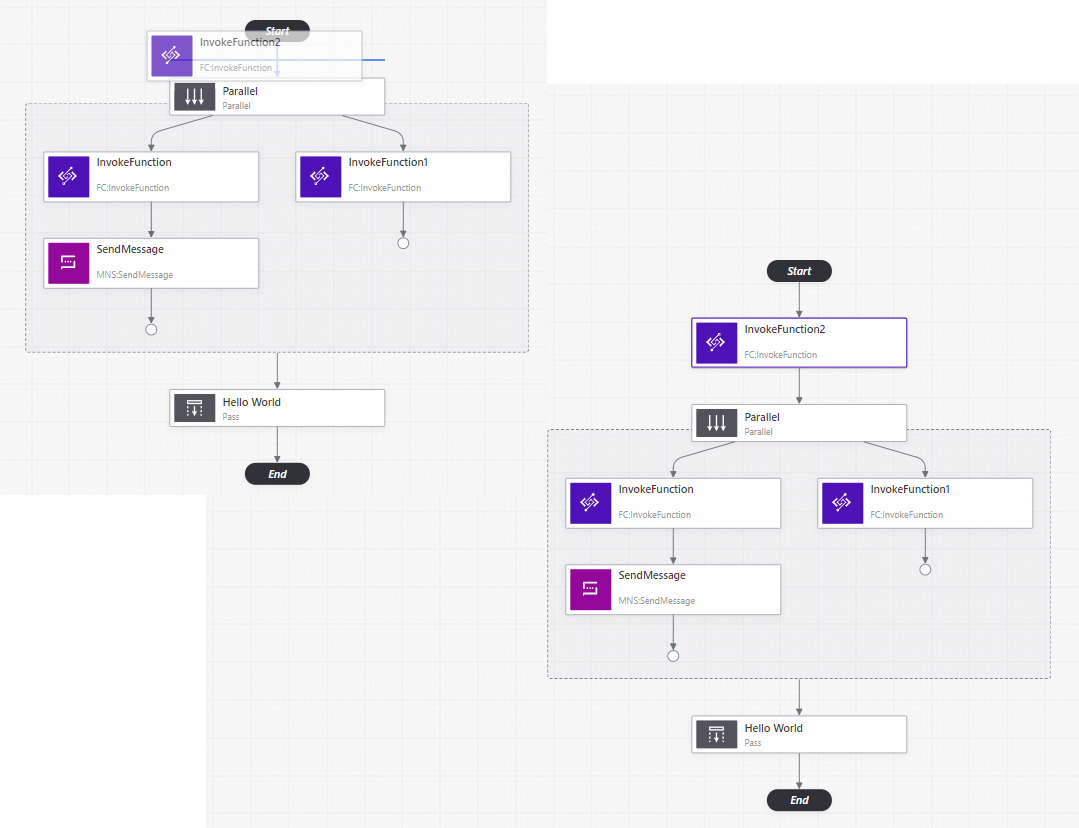
Generate a flowchart
You can drag state nodes (API operation nodes) or flow nodes from the state display section to appropriate positions in the workflow canvas section until a horizontal or vertical line appears. This way, you can create a custom flowchart that meets your business requirements. Workflow Studio automatically generates code when it generates a flowchart. You do not need to manually write code.
You can also click the buttons in the upper-left corner of the workflow canvas to zoom in or out the canvas, center the flowchart, delete a selected state node (API operation node) or flow node, and undo the previous action.
Debug workflows
If you have configured parameters for a state node, you can debug the workflow in online mode when you edit a flowchart. Move the pointer over a state node and click the ![]() icon to the right of the state node to debug the workflow. After the debugging is complete, click the
icon to the right of the state node to debug the workflow. After the debugging is complete, click the ![]() icon to view the debugging result.
icon to view the debugging result.
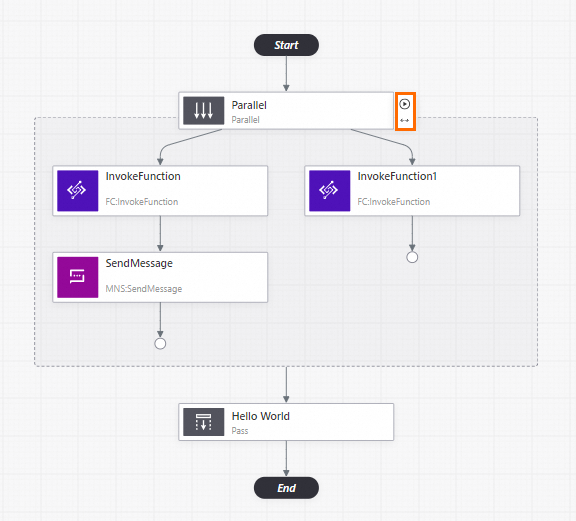
Parameter configuration section
After you drag and drop a state node (API operation node) or a flow node from the state display section to the workflow canvas section, you must configure the node. Click the node that you want to configure on the canvas. Then, complete the Basic Settings, Input Settings, Output Settings, and Troubleshooting configurations in the parameter configuration section.
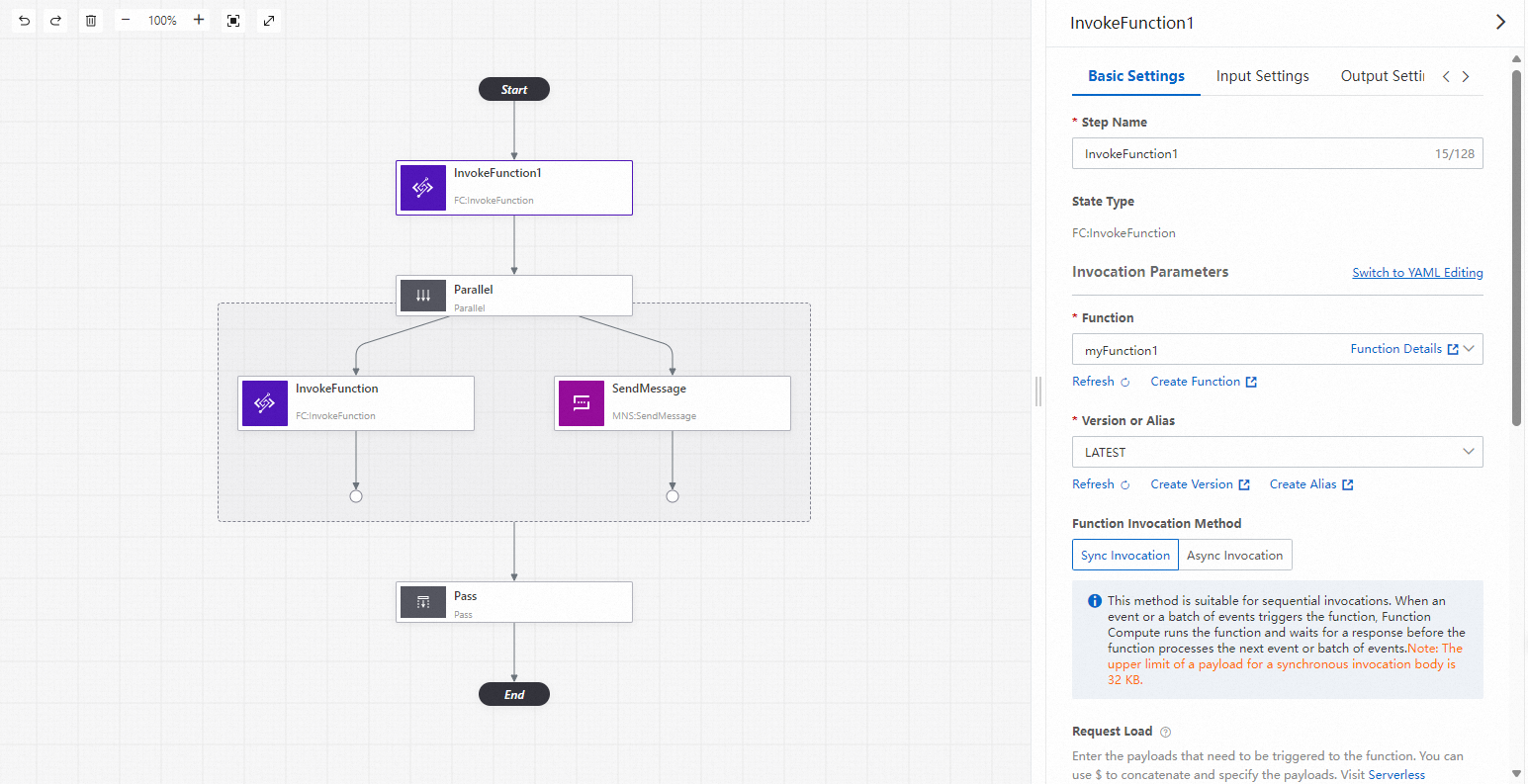
The following table describes the key parameters that you must configure for the InvokeFunction task state node. For other parameters, use the default values.
Category | Parameter | Description | Example |
Basic Settings | State Name | The name of the state node. The name describes the feature of the state. | InvokeFunction |
Invocation Parameters | The name, version or alias, and invocation method of the function that you want to invoke, and payloads that trigger the function. You can also click Switch to YAML Editing next to Invocation Parameters to specify the name, version or alias, and invocation method of the function in a YAML script. | A sample YAML script: | |
Function | The name of the function that you want to invoke. | myfunction | |
Version or Alias | The version or alias of the function that you want to invoke. | LATEST | |
Function Invocation Method | The method that you want to use to invoke the function. Valid values: Sync Invocation and Async Invocation. For more information about function invocation methods, see Function invocation. | Sync Invocation | |
Request Load | The payloads that trigger the function. You can enter payloads in the YAML or JSON format. | | |
Next State | The next state to which you want the workflow to transition. The setting takes effect in real time. | Parallel | |
Input Settings | The filtering method of inputs. Valid values:
| ||
Output Settings | The filtering method of outputs. Valid values:
| ||
Troubleshooting | Retry upon Error: The retry policy that is applied when an error is caught. Click Add Retry to add retry policies. | ||
Error Type | The error types that can be hit. You can select one or more error types. | FC.BadResponse | |
Maximum Retries | The allowed maximum number of retries. | 5 | |
Retry Interval Seconds | The retry interval. Maximum value: 86400. Unit: seconds. | 3 | |
Backoff Multiplication Factor | The multiplier by which the retry interval increases. | 1 | |
Maximum Backoff Seconds | The maximum number of seconds within which retries must be performed in exponential fallback mode. | 5 | |
Capture errors and exceptions: The capture rule that is applied to restore the workflow to an expected state when an error or exception is caught. Click Add Capture Rule to add capture rules. | |||
Error Type | The error types that can be hit. You can select one or more error types. | FC.EntitvToolLarge | |
Fallback Status | The state to which the workflow returns when a specified error is caught. | Hello World | |
Response | The result that is returned when a specified error is caught. The result contains the error and the error is added to the input of the fallback state node. You can configure a response in the YAML or JSON format. | | |
YAML
The YAML editing mode provides a YAML code editor and a visualization tool to visualize your written code in real time. The following figure shows the sections on the Edit Workflow page in YAML editing mode.
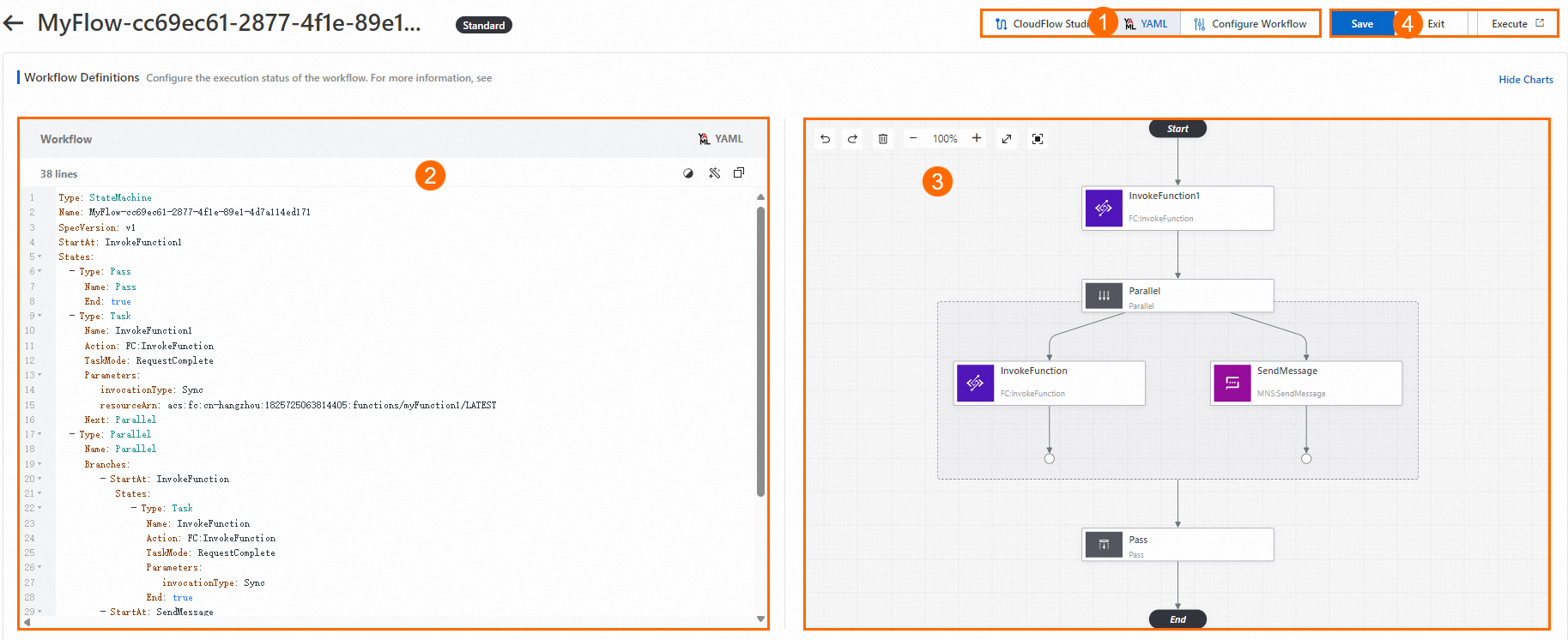
① Menu bar
In this section, you can switch among the CloudFlow Studio, YAML, and Configure Workflow tabs of Workflow Studio.
② YAML code editing section
In this section, you can write and edit the process of a workflow in the YAML format.
③ Visualization section
This section provides a visualized workflow in real time. You can delete specific nodes from the workflow.
④ Function button section
This section provides common function buttons for workflows, including Save, Exit, and Execute.

You can perform the following operations in the two operation sections on the YAML tab.
YAML code editing section
The YAML code editor allows you to write and edit workflows in WorkFlow Studio in the YAML format. When you update the definition of a workflow in the YAML code editor, the visualization tool renders a real-time chart of the workflow in the visualization section. You can also view the updated flowchart on the CloudFlow Studio tab.
If you change the order of, delete, or add a state node on the CloudFlow Studio tab or delete a state node in the visualization section of the YAML tab, the YAML code is automatically updated.
Visualization section
The visualization section allows you to view the overall architecture of a workflow in real time. When you write the definition of a workflow in the YAML code editor, the visualization tool renders a real-time chart of the workflow. If you delete a state node of a workflow in the visualization section, the definition of the workflow in the code editor is automatically updated. If you update the workflow definition, change the order of, delete, or add a state node in the YAML code editor, the visualized flowchart is automatically updated.
If the YAML code that specifies the definition of a workflow is invalid, the visualization tool pauses rendering.
Configure Workflow
The Configure Workflow feature allows you to configure the basic information about a workflow and a role that is used to execute the workflow. The following figure shows the sections on the Edit Workflow page.

① Menu bar
In this section, you can switch among the CloudFlow Studio, YAML, and Configure Workflow tabs of Workflow Studio.
② Basic Configuration
In the Basic Configuration section, you can enter a description of the workflow to help you identify and understand the business content of the workflow. The description is displayed in the workflow list.
③ Role Configuration
Select an existing execution role: Select an existing execution role from the drop-down list. Make sure that the policy attached to the role contains the permissions that you want the state machine to assume.
Create Role: Click Create Role to create a role on the Roles page in the Resource Access Management (RAM) console. For more information, see the "Create an execution role" section of the Create execution roles topic.
④ Function button section
This section provides common function buttons for workflows, including Save, Exit, and Execute.
