This topic provides answers to some frequently asked questions about the detection and response module of Security Center.
How do I check mining programs in my assets?
If the CPU utilization of your server significantly increases, such as to 80% or higher, and an unknown process continues to send packets, a mining program is running on your server.
If Security Center detects mining programs on your assets, Security Center sends alert notifications by text message or email. You can handle the alerts that are generated for mining programs on the CWPP tab of the Alert page. If mining programs are associated with other alerts, such as alerts on communication with mining pools and alerts on access to malicious domain names, we recommend that you also handle the associated alerts. For more information, see View and handle security alerts.
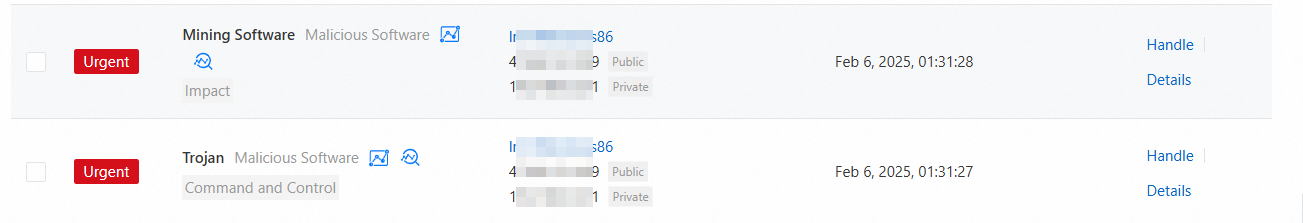
What do I do if antivirus is not enabled and a mining attack is launched on my server?
To handle alerts that are generated for mining attacks and turn on Malicious Host Behavior Prevention, perform the following operations:
Only the Anti-virus, Advanced, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Security Center support handling mining alerts.
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
NoteIf you have activated the Agentic SOC feature, the left-side navigation pane will change to .
On the Alerts page, under the CWPP tab, find the alert that you want to handle and click Handle in the Actions column.
In the dialog box that appears, select Virus Detection and Removal.
Click Process Now. The alert is handled.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Settings page, click the Settings tab and then the Host Protection Settings tab. In the Proactive Defense section, turn on Malicious Host Behavior Prevention. The malicious host behavior defense feature is enabled.
I accidentally added a mining alert to the whitelist of alerts. What do I do to remove the alert from the whitelist?
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, set the status filter condition to Handled to search for all handled alerts.
Find the alert that you added to the whitelist and click Remove from Whitelist in the Actions column. The alert is displayed in the alert list.
How do I check whether automatic virus blocking takes effect?
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China. In the left-side navigation pane, choose System Configuration > Feature Settings. On the Feature Settings page, turn on Malicious Host Behavior Prevention. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, select Precision defense for Alert Type. If the status of the alerts displayed after filtering is Blocked, automatic virus blocking takes effect.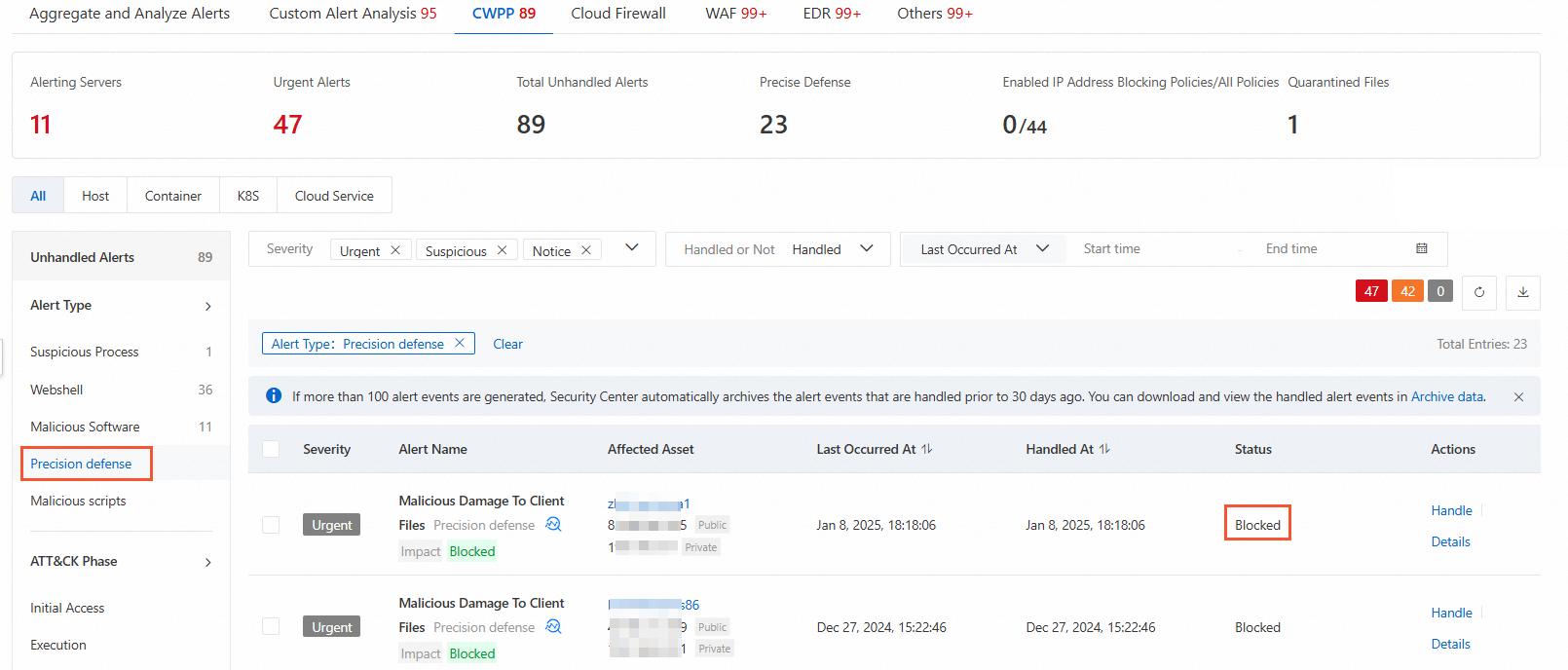
How does Security Center detect intrusions?
Security Center scans your assets, and Alibaba Cloud security engineers analyze and verify user traffic data to detect intrusions.
What are common intrusions?
Common intrusions include webshells, brute-force attacks, and mining attacks. Security Center generates alerts for these intrusions. For more information, see Overview of CWPP (Cloud Workload) security alerts.
Why is an alert generated when I call the phpinfo function? Is the alert a false positive?
No, the alert is not a false positive.
The phpinfo file contains a large amount of sensitive information, such as the absolute path of a website. When you call the phpinfo function to obtain the phpinfo file, attackers may exploit the information in the phpinfo file to attack your asset. Most attackers first upload the phpinfo file to obtain more information for subsequent penetration. If the file is required by your business, you can perform the following operations to add the alert to the whitelist:
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, add the alert to the whitelist.
Can Security Center automatically quarantine webshell files?
No, Security Center cannot automatically quarantine webshell files. Webshell files may contain your business information. You must manually identify and quarantine webshell files. You can find the quarantined files in the File Quarantine box panel. You can also restore quarantined files within 30 days after you quarantine the files. For more information, see Evaluate and handle security alerts.
How does Security Center detect webshells?
Security Center detects website script files, such as PHP, ASP, and JSP files, by using the following methods:
Disk-based detection: After a file is uploaded or downloaded to your server, Security Center scans the file. If malicious files are detected, Security Center generates alerts.
Real-time monitoring of web directories.
Scheduled scan of web directories.
What alerts can I add to the whitelist?
You can add alerts that are generated for malware to the whitelist. If you add an alert that is generated for a malicious process to the whitelist, only the source file of the malicious process is added to the whitelist. The following table describes the types of alerts that can be added to the whitelist.
Alert type | Description |
Malware | Adds the MD5 hash value to the whitelist. |
Unusual logon | Adds the IP addresses that are used for unusual logons to the whitelist. |
Access to malicious IP addresses or communication by using mining pools | Adds the related IP addresses to the whitelist. |
Access to malicious domain names | Adds the related domain names to the whitelist. |
Access or connection to malicious download sources | Adds the source URLs to the whitelist. |
WebShell | Adds the web directories to the whitelist based on the configurations of the directories. |
Malicious script | Adds the MD5 hash value and path to the whitelist. |
Cloud threat detection | Configures whitelist rules in the Security Center console. |
Suspicious process | Adds the command lines to the whitelist. |
Persistent webshells | Adds the MD5 hash values and characteristic values to the whitelist. |
Tampering of sensitive files | Adds the file path to the whitelist. |
Intrusion into applications | Adds the command lines to the whitelist. |
Threat to web applications | Adds the related domain names or URLs to the whitelist. |
Suspicious network connection | Adds the command lines, destination IP addresses, and destination ports to the whitelist. If some fields are missing, only the existing fields are added to the whitelist. |
Why are some alerts in the Expired state?
Security Center changes the status of the alerts that are generated before the previous 30 days to Expired. If the alerts are regenerated after the change, Security Center updates the alert generation time and changes the alert status to Unhandled.
Why is the point in time when an alert is generated for the access to a suspicious domain name for the first time different from the point in time when the access to the suspicious domain name is detected?
Domain Name System (DNS) data is sent to Security Center at a latency. When Security Center receives DNS data, Security Center uses the required algorithm to analyze and process the DNS data. As a result, the point in time when an alert is generated for the access to a suspicious domain name for the first time is later than the point in time when the access to a suspicious domain name is detected. A difference within 5 hours is acceptable.
How does Security Center detect unusual logons and generate alerts for unusual logons?
After you install the Security Center agent on your server, Security Center can detect logons from unapproved locations and generate alerts for these logons. You can view the alerts generated for unusual logons under the CWPP tab on the Alert page in the Security Center console.
The Security Center agent regularly collects logon logs of your server, and uploads the logs to the cloud for analysis and matching. If Security Center detects a logon from an unapproved location, unapproved IP address, unapproved time range, or unapproved account, Security Center generates alerts for the logon. The following list describes how Security Center identifies unusual logons from different IP addresses:
The first time you use Security Center to protect your server, Security Center does not generate alerts for a logon because you do not specify approved logon locations.
The first time a logon from a public IP address to the server succeeds, the location of the IP address is marked as an approved logon location. All locations of the public IP addresses that are used to log on to the server within 24 hours after the point in time are marked as approved logon locations. After 24 hours, all logons that are not from the preceding approved logon locations are considered logons from unapproved locations. Security Center generates alerts for these logons.
If Security Center identifies a logon from an IP address as a logon from an unapproved logon location, Security Center generates an alert and sends an alert notification by using text messages. The alert notification is sent only for the first logon. If six or more logons from the IP address succeed, Security Center automatically marks the location of the IP address as an approved logon location.
NoteSecurity Center marks unapproved logon locations only based on public IP addresses.
The following list describes how Security Center generates alerts for logons from unapproved IP addresses:
Security Center sends alert notifications only for the first logon from an unapproved IP address. The alert notifications are sent by using text messages. If more logons are continuously initiated from the IP address, Security Center generates alerts only in the console. If six or more logons from the IP address succeed, Security Center automatically marks the location of the IP address as an approved logon location.
If you use the Advanced, Enterprise, or Ultimate edition of Security Center, you can specify approved logon locations, IP addresses, time ranges, and accounts for your server. Security Center generates alerts for unapproved logon locations, IP addresses, time ranges, and accounts. The settings that you configure are assigned a higher priority than the default identification mechanism of Security Center.
What types of unusual logons can be detected by Security Center and can trigger alerts?
Security Center can detect the following types of unusual logons and generate alerts for the logons:
Logon from a malicious IP address (The logon destinations include servers, FTP applications, MySQL, and SQL Server.)
Server logon by using a backdoor account
Server logon by using an account with a weak password
Suspicious external logon scanning
Logon from an unusual location
Logon by using an unusual account
ECS instance logon after successful brute-force attacks, which can be initiated by using multiple invalid users on Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or SSH
ECS instance logon over SSH before suspicious command sequence execution
ECS instance logon in an unapproved time range, from an unapproved location or IP address, or with an unapproved account
For more information about how Security Center generates alerts, see Alerts.
How do I avoid the situation in which I properly log on to a server but Security Center prompts that the logon is unusual?
Log on to the Security Center console. Navigate to and click Common Logon Management. In the panel that appears, specify approved logon locations, IP addresses, time ranges, and accounts. If Security Center detects unapproved logons, Security Center generates alerts. You can manually add approved logon locations or configure the system to automatically update approved logon locations. You can also specify the assets on which alerts are generated when logons from unapproved locations are detected.
What do I do if an alert is triggered by the defense rule against brute-force attacks on an ECS instance due to accidental operations?
The password used to log on to an ECS instance is complex. Therefore, you may enter incorrect passwords multiple times before you can log on to the instance. In this case, Security Center identifies your logon attempts as brute-force attacks based on the model against brute-force attacks and generates an alert. If you confirm that the alert is a false positive, you can ignore the alert. For more information about how to ignore an alert, see Evaluate and handle security alerts.
What do I do if Security Center still displays an unusual logon after I specify approved logon IP addresses, time ranges, and accounts and properly log on to a server?
In this case, you must check whether the alert is triggered by a logon from an unapproved IP address, location, or account. Logon IP addresses, locations, accounts, and time ranges are the factors that may trigger an alert. These factors do not have priorities. If a factor is identified as abnormal, an alert is triggered.
An alert that indicates an unusual logon is triggered. Is the logon successful or blocked?
If an alert is triggered by an unusual logon, the logon is still successful. However, the logon behavior is considered suspicious by Security Center. Therefore, Security Center generates an alert for the logon.
A logon triggers an alert that indicates an unusual logon and is identified as a logon from an attacker. What do I do?
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, find the required alert and click Handle in the Actions column. In the dialog box that appears, set the Handling Method parameter to Block for and the Rule Validity Period parameter to 12 Hours, and click Process Now. This way, the attacker cannot log on to your server. We recommend that you change your account password at the earliest opportunity and check whether other unknown accounts and unknown public keys exist on your server to prevent SSH password-free logons.
I receive an alert indicating that a suspicious command sequence is executed after ECS logons over SSH. Is the command sequence executed?
The command sequence is executed. We recommend that you update the server logon password at the earliest opportunity and check whether other abnormal activities exist on the ECS instance. The abnormal activities include startup of unknown processes.
What logs can I view on my server after an alert is triggered by an unusual logon?
You can view the logs in the /var/log/secure directory on the server. For example, you can run the grep 10.80.22.22 /var/log/secure command to view the logs.
How do I view the number of brute-force attacks to my server or the attack blocking details on my server?
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Attack Analysis page, you can view the information about the SSH brute-force attacks that are blocked by Security Center.
How do I protect servers from brute-force attacks?
You can specify approved logon IP addresses or use the certificate logon method. For more information about how to specify approved logon IP addresses, see Configure alert settings.
What do I do if an accidental operation causes the defense against brute-force attacks to take effect?
If the number of logon attempts exceeds the upper limit specified in a defense rule against brute-force attacks, the rule takes effect, and you cannot log on to your server. In this case, you can perform the following operations:
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, click a number below Enabled IP Address Blocking Policies/All Policies. In the IP Policy Library panel, find the required rule and set the Policy Status parameter to Disabled.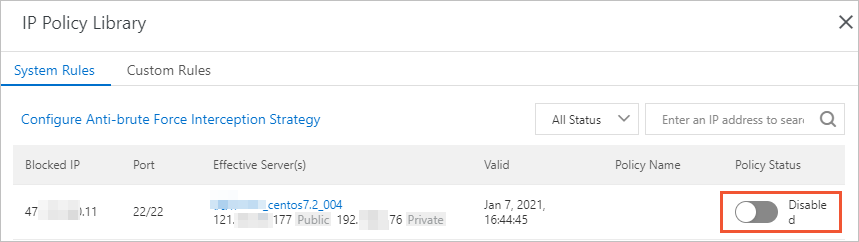
Can Security Center protect web applications and websites from brute-force attacks?
No,
Security Center can protect only the servers that allow logons over RDP or SSH.
What do I do if my server passwords are cracked?
If your server passwords are cracked, attackers may have intruded into your servers and installed malicious programs. To resolve this issue, perform the following operations: Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to manage. You can select China or Outside China. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Alert page, under the CWPP tab, check whether alerts generated for brute-force attacks exist.
If alerts that indicate ECS instance logons by using brute-force attacks are generated on your assets, your server passwords are cracked. We recommend that you perform the following operations to reinforce the security of your server:
Handle the related alerts
Go to the Alerts page, under the CWPP tab, find the required alert, and then click Process in the Actions column. In the dialog box that appears, set Process Method to Block and click Process Now. Security Center generates defense rules for the security group of the ECS instance to block access requests from malicious IP addresses. For more information, see View and handle alert events.
Change server passwords
Change the server passwords that are cracked at the earliest opportunity. We recommend that you use complex passwords.
Run baseline checks to detect risks
Use the baseline check feature of Security Center to detect risks on your servers, and handle the detected risks based on the suggestions that are provided by Security Center.
NoteThe Advanced, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Security Center support the baseline check feature.
Why do I still receive alert notifications for brute-force attacks after I change my weak password?
The new password that you specify takes effect the next day after you change the password. Before the new password takes effect, Security Center continues to send alert notifications about brute-force attacks. For example, if you change your logon password at 10:00 on January 15, 2023, the baseline check model collects the new logon password and updates the weak password database at approximately 24:00 on the current day. However, the abnormal logon detection model loads the old password in the weak password database before 24:00 on January 15, 2023. Therefore, the alert that is triggered by brute-force attacks still exists.
If you confirm that the weak password is changed and no weak passwords are detected during baseline checks, you can ignore the alert.
If the password of your server is cracked by a brute-force attack, we recommend that you reinforce the security of your server at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see What do I do if my server passwords are cracked?
Records on RDP brute-force attacks are generated even after RDP requests on port 3389 are blocked by security group rules or firewall rules. Why?
Due to the special logon audit mechanism in Windows, the audit activities of logons based on Inter-Process Communication (IPC), RDP, and Samba are recorded in the same log, but the logon methods are not specified. If you find records on RDP brute-force attacks after the requests to the RDP service port are blocked, you must check whether IPC or Samba is enabled.
Check whether port 135, port 139, or port 445 is enabled for your ECS instance and whether public IP addresses can access these ports. Check whether the Windows security logs contain logon records within the attack period.
Does Security Center detect only weak passwords of RDP and SSH services?
Security Center detects weak passwords of RDP and SSH services. Security Center also detects weak passwords that are used by administrators to log on to content management systems (CMSs).
What is the source of the statistics that are displayed on the Attack Awareness page?
The statistics displayed on the Attack Awareness page consist of attack data collected after Security Center automatically identifies and blocks basic attacks as well as attack data from Alibaba Cloud Web Application Firewall (WAF). The statistics include data on the assets that are protected by Security Center and WAF. You can view the assets in the Assets module.