When you call API operations to manage cloud resources using Alibaba Cloud SDKs, you must configure valid credential information. The Credentials tool of Alibaba Cloud provides a set of easy-to-use features and supports various types of credentials, including the default credential, AccessKey pairs, and Security Token Service (STS) tokens. The Credentials tool helps you obtain and manage credentials. This topic describes how to configure different types of credentials and the order based on which the Credentials tool obtains the default credential. You can develop a thorough knowledge of configuring and managing credentials in Alibaba Cloud SDKs. This ensures that you can perform operations on cloud resources in an efficient and secure manner.
Prerequisites
.NET Framework 4.5 or later.
.NET Standard 2.0 or later.
C# 4.0 or later.
Alibaba Cloud SDK for .NET V2.0.
Install the Credentials tool
If you have already installed the .NET Credentials tool, you can skip this step. Ensure that you use the latest version of the Credentials dependency package so that all credential types are supported. For information about all published versions, see ChangeLog.md.
You can install the Credentials tool in one of the following ways:
Method 1: Install the tool using the .NET command-line interface (CLI).
dotnet add package Aliyun.CredentialsMethod 2: Install the tool using the NuGet package manager.
In the
Solution Explorerpanel, right-click your project and selectManage NuGet Packages.On the
NuGet Package Managerpanel, click theBrowsetab and enterAliyun.Credentials.In the list that appears, select the official package where the value for
AuthorsisAlibaba Cloud, and then click Install.
After the installation is successful, you can run the following command. The output includes Aliyun.Credentials and its version number:
dotnet list packageParameters of the Credentials tool
The configuration parameters for the Credentials tool are defined in Aliyun.Credentials.Models.Config. Use the required type parameter to specify the credential type. After you specify the credential type, select the corresponding parameters. The following table lists the valid values for type and the parameters supported by each credential type. A check mark (√) indicates a required parameter, a hyphen (-) indicates an optional parameter, and an X mark (×) indicates an unsupported parameter.
Do not use credential types or parameters that are not listed in the following table.
Type | access_key | sts | ram_role_arn | ecs_ram_role | oidc_role_arn | credentials_uri | bearer |
AccessKeyId: The AccessKey ID. | √ | √ | √ | × | × | × | × |
AccessKeySecret: The AccessKey secret. | √ | √ | √ | × | × | × | × |
SecurityToken: The STS token. | × | √ | - | × | × | × | × |
RoleArn: The Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of the RAM role. | × | × | √ | × | √ | × | × |
RoleSessionName: The custom session name. The default format is | × | × | - | × | - | × | × |
RoleName: The RAM role name. | × | × | × | - | × | × | × |
DisableIMDSv1: Specifies whether to forcibly use the security hardening mode. Default value: | × | × | × | - | × | × | × |
BearerToken: The bearer token. | × | × | × | × | × | × | √ |
Policy: The custom permission policy. | × | × | - | × | - | × | × |
RoleSessionExpiration: The session time-to-live (TTL). Default value: 3600 seconds. | × | × | - | × | - | × | × |
OidcProviderArn: The ARN of the OIDC IdP. | × | × | × | × | √ | × | × |
OidcTokenFilePath: The path to the OIDC token file. | × | × | × | × | √ | × | × |
ExternalId: The external ID of the role. This feature prevents the confused deputy problem. For more information, see Use an external ID to prevent the confused deputy problem. | × | × | - | × | × | × | × |
CredentialsURI: The URI of the credential. | × | × | × | × | × | √ | × |
STSEndpoint: The endpoint of STS. VPC endpoints and public network endpoints are supported. For information about the valid values, see Endpoints. The default value is | × | × | - | × | - | × | × |
Timeout: The read timeout for HTTP requests. Default value: 5000 milliseconds. | × | × | - | - | - | - | × |
ConnectTimeout: The connection timeout for HTTP requests. Default value: 10000 milliseconds. | × | × | - | - | - | - | × |
Initialize a credential client
You can use one of the following methods to initialize a Credentials client as needed:
If you use a plaintext AccessKey pair in a project, the AccessKey pair may be leaked due to improper permission management on the code repository. This may threaten the security of all resources within the account to which the AccessKey pair belongs. We recommend that you store the AccessKey pair in environment variables or configuration files.
We recommend that you initialize the Credentials client in single-instance mode. This mode not only enables the credential caching feature of the SDK, but also effectively prevents traffic control issues and waste of performance resources caused by multiple API calls. For more information, see the Automatic update mechanism of session credentials section of this topic.
Method 1: Use the default credential provider chain
If you do not pass any parameters when you initialize the credential client, the Credentials tool uses the default credential provider chain to initialize the client. For more information about the default credential retrieval logic, see Default credential provider chain.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Do not specify a parameter or pass null.
var credential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client();
// var credential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(null);
}
}
}API call example
Method 2: Use an AccessKey
This method lets you create an AccessKey pair to initialize a Credentials client. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.
An Alibaba Cloud account has full permissions on resources within the account. AccessKey pair leaks of an Alibaba Cloud account pose critical threats to the system.
Therefore, we recommend that you use an AccessKey pair of a RAM user that is granted permissions based on the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to initialize a Credentials client.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "access_key",
AccessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
AccessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
};
var akCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
string accessKeyId = akCredential.GetAccessKeyId();
string accessSecret = akCredential.GetAccessKeySecret();
string credentialType = akCredential.GetType();
}
}
}API call example
Method 3: Use an STS token
This method lets you use a static STS token to initialize a Credentials client. For more information about how to obtain an STS token, see What is STS? The following example shows how to initialize a Credentials client using an STS token. The example does not show how to obtain an STS token.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "sts",
// Get the AccessKey ID from an environment variable.
AccessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
// Get the AccessKey secret from an environment variable.
AccessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"),
// The temporary SecurityToken obtained from an environment variable.
SecurityToken = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("<ALIBABA_CLOUD_SECURITY_TOKEN>")
};
var stsCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
string accessKeyId = stsCredential.GetAccessKeyId();
string accessSecret = stsCredential.GetAccessKeySecret();
string credentialType = stsCredential.GetType();
string securityToken = stsCredential.GetSecurityToken();
}
}API call example
Method 4: Use an AccessKey and RamRoleArn
The underlying implementation of this method is an STS token. By specifying the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of a RAM role, the Credentials tool can help developers obtain an STS token from STS. You can also assign a value to the Policy parameter to restrict the RAM role to a smaller set of permissions.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "ram_role_arn",
AccessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
AccessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"),
// The ARN of the RAM role to assume. Example: acs:ram::123456789012****:role/adminrole. You can set RoleArn using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN environment variable.
RoleArn = "<RoleArn>",
// The role session name. You can set RoleSessionName using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_SESSION_NAME environment variable.
RoleSessionName = "<RoleSessionName>",
};
var arnCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
string accessKeyId = arnCredential.GetAccessKeyId();
string accessSecret = arnCredential.GetAccessKeySecret();
string credentialType = arnCredential.GetType();
string securityToken = arnCredential.GetSecurityToken();
}
}
}API call example
Method 5: Use an instance RAM role
Both ECS and ECI instances support attaching an instance RAM role. Programs that run on these instances can use the Credentials tool to automatically retrieve the STS token for the role, which completes the initialization of the credential client.
By default, the Credentials tool accesses the ECS instance metadata service in security hardening mode (IMDSv2). If an exception occurs in this mode, the tool falls back to the normal mode to retrieve the access credential. You can also set the disableIMDSv1 parameter or the ALIBABA_CLOUD_IMDSV1_DISABLE environment variable to execute different exception handling logic:
If the value is false (default), the tool continues to retrieve the access credential in normal mode.
If the value is true, the tool can only retrieve the access credential in security hardening mode, and an exception is thrown.
Whether the server-side supports IMDSv2 depends on your server configuration.
In addition, you can set the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ECS_METADATA_DISABLED=true environment variable to disable credential access from ECS metadata.
If you retrieve a temporary identity credential in security hardening mode, the Credentials version must be 1.4.2 or later.
For more information about ECS instance metadata, see Instance metadata.
For more information about how to grant a RAM role to an ECS or ECI instance, see Create a RAM role and grant it to an ECS instance and Grant an instance RAM role to an ECI instance.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var config = new Config()
{
Type = "ecs_ram_role",
// Optional. The name of the ECS role. If not specified, it is automatically obtained. We recommend that you add it to reduce the number of requests. You can set RoleName using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ECS_METADATA environment variable.
RoleName = "<RoleName>"
};
// Optional. Default value: false. true: Forces the use of security hardening mode. false: The system first tries to get the credential in security hardening mode. If it fails, it switches to normal mode (IMDSv1) to try again.
// config.DisableIMDSv1 = true;
var ecsCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
string accessKeyId = ecsCredential.GetAccessKeyId();
string accessSecret = ecsCredential.GetAccessKeySecret();
string credentialType = ecsCredential.GetType();
string securityToken = ecsCredential.GetSecurityToken();
}
}
}API call example
Method 6: Use an OIDCRoleArn
To ensure the security of cloud resources and enable untrusted applications to securely obtain required STS tokens, you can use the RAM Roles for Service Accounts (RRSA) feature to grant minimum necessary permissions to an application. ACK creates and mounts corresponding OpenID Connect (OIDC) token files for different application pods, and passes relevant configuration information to environment variables. The Credentials tool obtains the configuration information from the environment variables and calls the AssumeRoleWithOIDC operation of STS to obtain the STS token for attached roles.
The following environment variables are injected into the pod:
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN: the ARN of the RAM role.
ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN: the ARN of the OIDC identity provider (IdP).
ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_TOKEN_FILE: the path of the OIDC token file.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "oidc_role_arn",
// The ARN of the RAM role. You can set RoleArn using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN environment variable.
RoleArn = "<RoleArn>",
// The ARN of the OIDC provider. You can set OidcProviderArn using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN environment variable.
OIDCProviderArn = "<OidcProviderArn>",
// The path to the OIDC token file. You can set OidcTokenFilePath using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_TOKEN_FILE environment variable.
OIDCTokenFilePath = "<OidcTokenFilePath>",
// The role session name. You can set RoleSessionName using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_SESSION_NAME environment variable.
RoleSessionName = "<RoleSessionName>",
// A smaller permission policy. This is optional. Example: {"Statement": [{"Action": ["*"],"Effect": "Allow","Resource": ["*"]}],"Version":"1"}
Policy = "<Policy>",
RoleSessionExpiration = 3600
};
var ecsCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
}
}
}API call example
Method 7: Use a credential URI
This method lets you encapsulate an STS token in your application and provide a custom URI to external resources. Other services can obtain the STS token only through the URI. This minimizes the risk of AccessKey exposure. The Credentials tool lets you obtain the STS token by calling the service URI to initialize the Credentials client.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "credentials_uri",
// The URI to get the credential, in the format http://local_or_remote_uri/. You can set CredentialsUri using the ALIBABA_CLOUD_CREDENTIALS_URI environment variable.
CredentialsURI = "<CredentialsURI>"
};
}
}
}API call example
Method 8: Use a bearer token
Currently, only Cloud Call Center (CCC) supports initializing credentials with a bearer token.
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
namespace credentials_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Config config = new Config()
{
Type = "bearer",
// Enter your Bearer Token.
BearerToken = "<BearerToken>"
};
var bearerCredential = new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
string bearerToken = bearerCredential.GetBearerToken();
string credentialType = bearerCredential.GetType();
}
}
}API call example
Default credential provider chain
If your development and production environments use different credential types, a common practice is to retrieve the current environment information in the code and write branch code to retrieve different credentials. With the default credential provider chain of the Credentials tool, you can use the same code and control how credentials are obtained in different environments through external configuration. When you initialize the credential client by calling new Client(config) and passing null without passing any parameters, the Alibaba Cloud SDK tries to find the relevant credential information in the following order.
1. Use environment variables
If no credential information is found in the system attributes, the Credentials continues to check the environment variables.
If both the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are specified, they are used as the default credential.
If ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID, ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET, and ALIBABA_CLOUD_SECURITY_TOKEN are specified, the STS token is used as the default credential.
2. Use an OIDC RAM role
If no credentials with a higher priority are found, the Credentials tool checks the following environment variables that are related to the RAM role of the OIDC IdP:
ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN: the ARN of the RAM role.
ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN: the ARN of the OIDC IdP.
ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_TOKEN_FILE: the file path of the OIDC token.
If the preceding three environment variables are specified and valid, the Credentials tool uses the environment variables to call the AssumeRoleWithOIDC operation of STS to obtain an STS token as the default credential.
3. Use the config.json configuration file
If no credentials with a higher priority are found, the Credentials tool attempts to load the config.json file. Default file path:
Linux/macOS:
~/.aliyun/config.jsonWindows:
C:\Users\USER_NAME\.aliyun\config.json
Do not change the preceding default paths. If you want to use this method to configure an access credential, manually create a config.json file in the corresponding path. Example:
{
"current": "<PROFILE_NAME>",
"profiles": [
{
"name": "<PROFILE_NAME>",
"mode": "AK",
"access_key_id": "<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID>",
"access_key_secret": "<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET>"
},
{
"name": "<PROFILE_NAME1>",
"mode": "StsToken",
"access_key_id": "<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID>",
"access_key_secret": "<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET>",
"sts_token": "<SECURITY_TOKEN>"
},
{
"name":"<PROFILE_NAME2>",
"mode":"RamRoleArn",
"access_key_id":"<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID>",
"access_key_secret":"<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET>",
"ram_role_arn":"<ROLE_ARN>",
"ram_session_name":"<ROLE_SESSION_NAME>",
"expired_seconds":3600
},
{
"name":"<PROFILE_NAME3>",
"mode":"EcsRamRole",
"ram_role_name":"<RAM_ROLE_ARN>"
},
{
"name":"<PROFILE_NAME4>",
"mode":"OIDC",
"oidc_provider_arn":"<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>",
"oidc_token_file":"<OIDC_TOKEN_FILE>",
"ram_role_arn":"<ROLE_ARN>",
"ram_session_name":"<ROLE_SESSION_NAME>",
"expired_seconds":3600
},
{
"name":"<PROFILE_NAME5>",
"mode":"ChainableRamRoleArn",
"source_profile":"<PROFILE_NAME>",
"ram_role_arn":"<ROLE_ARN>",
"ram_session_name":"<ROLE_SESSION_NAME>",
"expired_seconds":3600
}
]
}
In the config.json file, you can use mode to specify a type of credential:
AK: uses the AccessKey pair of a RAM user to obtain the credential information.
StsToken: uses the STS token as the credential information.
RamRoleArn: uses the ARN of a RAM role to obtain the credential information.
EcsRamRole: uses the RAM role attached to an ECS instance to obtain the credential information.
OIDC: uses the ARN of an OIDC IdP and the OIDC token file to obtain the credential information.
ChainableRamRoleArn: utilizes a role chaining mechanism. It allows you to assume a new RAM role and acquire a new, temporary credential by referencing another credential profile, which is specified by the
source_profileparameter.
After you complete the configurations, the Credentials tool selects the credential specified by the current parameter in the configuration file and initialize the client. You can also specify the ALIBABA_CLOUD_PROFILE environment variable to specify the credential information. For example, you can set the ALIBABA_CLOUD_PROFILE environment variable to client1.
4. Use the RAM role of an ECS instance
ECS instances and elastic container instances can be assigned RAM roles. Programs that run on the instances can use the Credentials tool to automatically obtain an STS token for the RAM role. The STS token can be used to initialize the Credentials client.
If the value is
false(default), the system tries to switch to normal mode to continue retrieving the credential.If the value is
true, the credential can only be obtained in security hardening mode. If access in security hardening mode fails, an exception is thrown.
The configurations for the metadata server determine whether the server supports the security hardening mode (IMDSv2).
In addition, you can specify ALIBABA_CLOUD_ECS_METADATA_DISABLED=true to disable access from the Credentials tool to the metadata server of ECS.
For more information about ECS instance metadata, see Obtain instance metadata.
For more information about how to attach a RAM role to an ECS instance, see the "Create an instance RAM role and attach the instance RAM role to an ECS instance" section of the Instance RAM roles topic. For more information about how to attach a RAM role to an elastic container instance, see the "Assign the instance RAM role to an elastic container instance" section of the Use an instance RAM role by calling API operations topic.
5. Use a Credentials tool URI
If no valid credential is obtained using the preceding methods, the Credentials tool checks the ALIBABA_CLOUD_CREDENTIALS_URI environment variable. If this environment variable exists and specifies a valid URI, the Credentials tool initiates an HTTP requests to obtain an STS token as the default credential.
Auto-refresh mechanism for session-type credentials
Session credentials include ARNs of RAM roles (RamRoleArn), RAM roles of ECS instances, RAM roles of OIDC IdPs (OIDCRoleArn), and credential URIs. The Credentials tool provides a built-in automatic update mechanism for session credentials. After a credential is obtained from the first call, the Credentials tool stores the credential in the cache. In subsequent calls, the credential is read from the cache as long as the credential is not expired. Otherwise, the Credentials tool makes a call to obtain the credential again, and updates the credential in the cache.
For RAM roles of ECS instances, the Credentials tool updates the credential 15 minutes before the cache time-to-live (TTL) ends.
In the following example, the Credentials client is created in single-instance mode and is used to initialize the cloud service client. Then, an API operation is called during different time periods to check whether internal cache is used and whether the credential is refreshed after the cache expires.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Aliyun.Credentials.Models;
using AlibabaCloud.SDK.Ecs20140526;
using AlibabaCloud.OpenApiClient.Models;
using AlibabaCloud.TeaUtil.Models;
namespace Example
{
/// <summary>
/// The Credential class is used to manage Alibaba Cloud credential instances. It uses the static singleton pattern.
/// </summary>
public static class Credential
{
private static readonly Lazy<Aliyun.Credentials.Client> _instance = new(() =>
{
try
{
var config = new Aliyun.Credentials.Models.Config
{
Type = "ram_role_arn",
AccessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
AccessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"),
RoleArn = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN"),
RoleSessionName = "RamRoleArnTest",
RoleSessionExpiration = 3600
};
return new Aliyun.Credentials.Client(config);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Credential initialization failed: " + ex.Message, ex);
}
});
public static Aliyun.Credentials.Client Instance => _instance.Value;
}
/// <summary>
/// The EcsClient class is used to manage ECS client instances. It uses the static singleton pattern.
/// You must set the endpoint and credential using Initialize.
/// </summary>
public static class EcsClient
{
private static string _endpoint = string.Empty; // Explicit initialization. Cannot be null.
private static Aliyun.Credentials.Client _credential = null!; // Explicit initialization. Cannot be null.
private static readonly Lazy<AlibabaCloud.SDK.Ecs20140526.Client> _instance = new(() =>
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(_endpoint))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Endpoint must be set before initializing the ECS client.");
}
if (_credential == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Credential must be set before initializing the ECS client.");
}
try
{
var ecsConfig = new AlibabaCloud.OpenApiClient.Models.Config
{
Endpoint = _endpoint,
Credential = _credential
};
return new AlibabaCloud.SDK.Ecs20140526.Client(ecsConfig);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("ECS client initialization failed: " + ex.Message, ex);
}
});
public static void Initialize(string endpoint, Aliyun.Credentials.Client credential)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(endpoint))
{
throw new ArgumentException("Endpoint cannot be null or empty.", nameof(endpoint));
}
if (credential == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(credential), "Credential cannot be null.");
}
_endpoint = endpoint;
_credential = credential;
}
public static AlibabaCloud.SDK.Ecs20140526.Client Instance => _instance.Value;
}
public class Program
{
public static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Initialize EcsClient.
EcsClient.Initialize("ecs.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com", Credential.Instance);
Action task = () =>
{
try
{
var credential = Credential.Instance.GetCredential();
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine($"AK ID: {credential.AccessKeyId}, AK Secret: {credential.AccessKeySecret}, STS Token: {credential.SecurityToken}");
var ecsClient = EcsClient.Instance;
var request = new AlibabaCloud.SDK.Ecs20140526.Models.DescribeRegionsRequest();
var runtime = new AlibabaCloud.TeaUtil.Models.RuntimeOptions();
var response = ecsClient.DescribeRegionsWithOptions(request, runtime);
Console.WriteLine($"Invoke result: {response.StatusCode}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"ECS client execution failed: {ex.Message}");
}
};
// Execute once immediately.
task();
// Start asynchronous tasks concurrently.
var tasks = new[]
{
ScheduleTaskAsync(task, 600),
ScheduleTaskAsync(task, 4200),
ScheduleTaskAsync(task, 4300)
};
await Task.WhenAll(tasks);
Console.WriteLine("All tasks completed.");
}
private static async Task ScheduleTaskAsync(Action task, int delaySeconds)
{
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(delaySeconds));
task();
}
}
}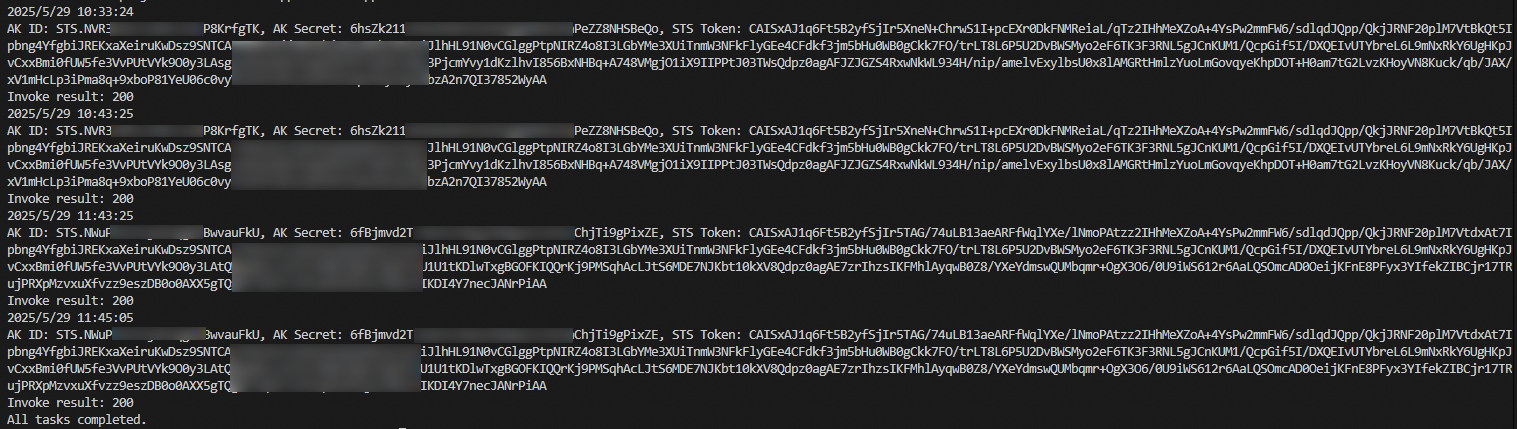
Log analysis:
In the first call, the system obtains the credential based on the configurations because the credential is not cached. After the system obtains the credential, the credential is stored in the cache.
The second call uses the same credential as the first call, which indicates that the credential is obtained from the cache.
In the third call, the credential has expired because the third call is 4,200 seconds later than the first call while the credential TTL (RoleSessionExpiration) is set to 3,600 seconds. The SDK obtains the credential again based on the automatic update mechanism and stored the credential in the cache.
The fourth call uses the same credential as the third call, which indicates that the credential is updated after cache expiration.
References
For more information about RAM, see Terms.
For more information about how to create an AccessKey pair, see Create an AccessKey pair.
For more information about how to create a RAM user, an AccessKey pair, a RAM role, and a policy and grant permissions to a RAM user, see RAM SDK overview.
For more information about how to assume a role using a program, see STS SDK overview.
For more information about RAM and STS-related API operations, see API reference.
Best practices for using an access credential to call API operations