TairRoaing is an implementation of Roaring bitmap in Tair. TairRoaring provides powerful and stable computing performance, which helps improve query speed while consuming only a small amount of memory.
TairRoaring is improved based on Roaring bitmaps in the following aspects:
TairRoaring can strike a balance between performance and space complexity in a large number of scenarios by using two-level indexes and dynamic containers.
TairRoaring uses optimization techniques such as single instruction, multiple data (SIMD), vectorization, and popcount algorithms to improve computing efficiency and deliver efficient time and space complexity.
TairRoaring takes advantage of the powerful computing performance and high stability provided by Tair to support business scenarios.
For more information about TairRoaring, see TairRoaring.
Test tool
The test tool provided by this topic is developed by using the Go programming language and is similar to the tool used by the redis-benchmark utility. This makes the test tool easy to use and modify. This test tool can generate two random values to help you create test examples and can also display results as histograms. For more information, see TairRoaring test tool.
Usage:
Usage of ./redis:
-a string Account password used to log on to the instance. Password format: <user>:<password>.
-batching int Pipeline mode. This parameter also sets the number of individual commands that each pipeline contains. The pipeline mode combines the MULTI and EXEC commands. For example, -batching 10 indicates that 10 commands exist between the MULTI and EXEC commands.
-c int Number of tests that are run. This parameter ignores the test duration (-d).
-command string Test command. You can add the __RAND__ and __RAND2__ fields to the suffix of a command or parameter. The fields take effect and become random values only when they are added to a command or parameter suffix. Default command: TR.GETBIT foo-__RAND__.
-d int Test duration. Unit: seconds. Default value: 30.
-h string Endpoint used to connect to the instance. Default value: 127.0.0.1.
-p int Number of tests that can be run concurrently. Default value: 4.
-port int Port number of the instance. Default value: 6379.
-r int Range of random value 1. Default value: 100000000.
-r2 int Range of random value 2. Default value: 100000000.Sample command:
# Run the TR.SETBIT command. Set the key to a random number that is less than 100000 and the fields to random numbers that are less than 10000000.
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.SETBIT foo-__RAND__ bar-__RAND2__" -p 20 -c 1Test methods and results for the standard architecture
The instance involved is a 16 GB Tair (Enterprise Edition) DRAM-based instance that uses the standard architecture. The network latency is less than 0.1 milliseconds.
Testing for a single key
Performance testing
Write data to a single key concurrently to obtain the maximum queries per second (QPS) value.
Read command testing
Run the following commands: TR.GETBIT, TR.GETBITS, TR.RANGE, TR.SCAN, and TR.RANK. Sample command:
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.GETBIT foo-__RAND__ bar-__RAND2__" -p 20 -c 1Test results:
Command
Number of keys involved
Number of data records involved
Parameter range
QPS reference value
Average latency (ms)
TR.GETBIT
1
1
1~10000000
255000
0.21
TR.GETBITS
1
100
1~10000000
54000
0.97
TR.RANK
1
1
1~10000000
161000
0.24
TR.RANGE
1
100
0~100
129000
0.46
TR.SCAN
1
100
1~10000000
130000
0.38
Write command testing
Run the following commands: TR.SETBIT, TR.SETBITS, TR.APPENDBITARRAY, TR.SETRANGE, and TR.FLIPRANGE. Sample command:
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.SETBIT foo-__RAND__ bar-__RAND2__" -p 20 -c 1Test results:
Command
Number of keys involved
Number of data records involved
Parameter range
QPS reference value
Average latency (ms)
TR.SETBIT
1
1
1~10000000
145000
0.37
TR.SETBITS
1
100
1~10000000
22000
0.71
TR.SETBITS (ordered)
1
100 (The maximum offset value of bits is 2^32.)
1~6000
28000
0.66
TR.APPENDBITARRAY
1
1000 (Half of the bits have a value of 1.)
1~10000000
10000
0.38
TR.SETRANGE
1
-
1000
130000
0.3
TR.FLIPRANGE
1
-
1~10000000
100000
0.46
Pipeline testing
Use different batch sizes to test the performance of commands in pipeline mode.
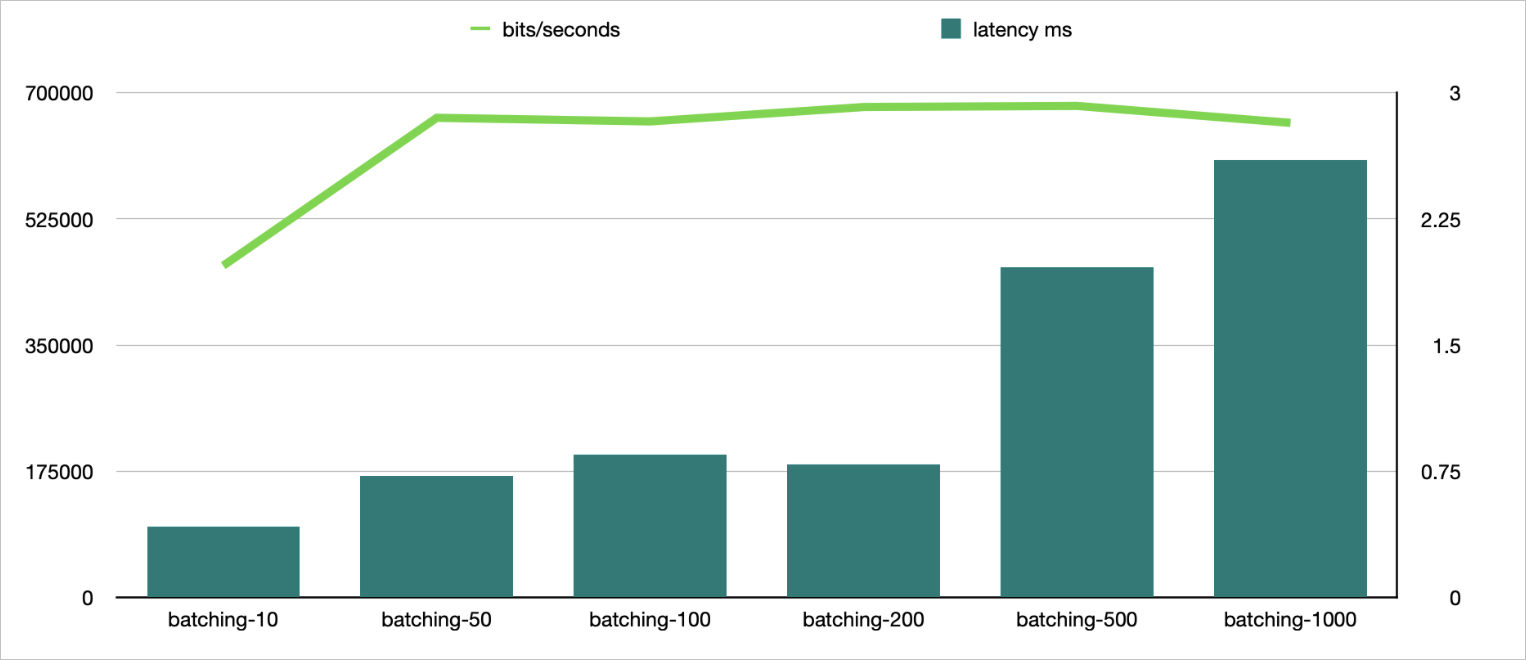
TR.SETBIT
Sample command:
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 10000000 -command "TR.SETBIT foo-__RAND__ 1" -batching 10 -p 20 -c 1parallel
batching
Bits per second
Average latency (ms)
20
10
460000
0.42
10
50
665000
0.72
6
100
660000
0.85
3
200
680000
0.79
3
500
681500
1.96
2
100
658000
2.6
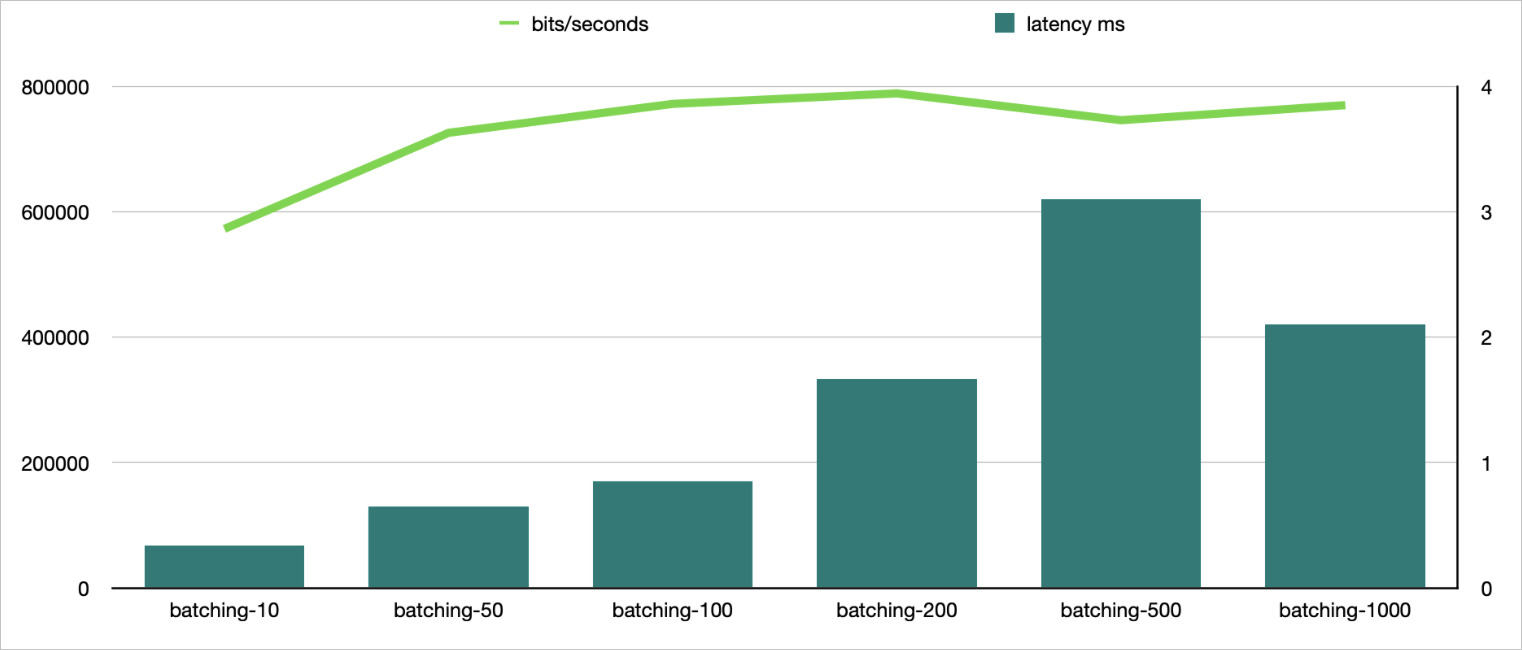
TR.GETBIT
Sample command:
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.GETBIT foo-__RAND__ __RAND2__" -batching 10 -p 20 -c 1NoteIf the key specified by foo-__RAND__ does not exist, the key is handled as an empty key. Therefore, you must write data to keys first for testing purposes.
parallel
batching
Bits per second
Average latency (ms)
20
10
572700
0.34
10
50
725900
0.65
7
100
772000
0.85
7
200
788800
1.67
5
500
746000
3.1
2
100
770000
2.1
Memory testing
Run the TR.STAT command for several times to analyze the distribution of bits in a key. Different key capacities are used. Sample command:
TR.STAT foo JSONScenarios that involve sparse data
Sparse data indicates bits that are sparsely distributed with a density less than 6.25%. In these scenarios, the key mostly contains array containers. The capacity of the key can be calculated by using the following formula: Key capacity = Key cardinality × 2 bytes.
cardinality
rle-c
array-c
bitset-c
heap mem (byte)
37700484
-
65536
-
75400968
75011384
-
65536
-
150022768
100403264
-
65536
-
200806528
163090592
-
65536
-
326181184
Scenarios that involve random data
In these scenarios, the key mostly contains bitset containers. To follow algorithmic logic, the system converts an array container into a bitset container when the array container has more than 4,096 elements.
cardinality
rle-c
array-c
bitset-c
heap mem (byte)
253104088
-
65534
2
506208102
261169659
-
63273
2263
522227634
267974804
-
35932
29604
533159296
273694253
-
6607
58929
536491922
343504134
-
0
65536
536870912
535589835
-
0
65536
536870912
Scenarios that involve consecutive random bits
In these scenarios, the storage capacity is closely linked to the distribution of bits. As a result, the tests performed in these scenarios have little value.
Testing for multiple keys
Write testing
Test the engine performance when data is written to multiple keys concurrently. TR.SETBITS creates 100 random bits each time. Sample command:
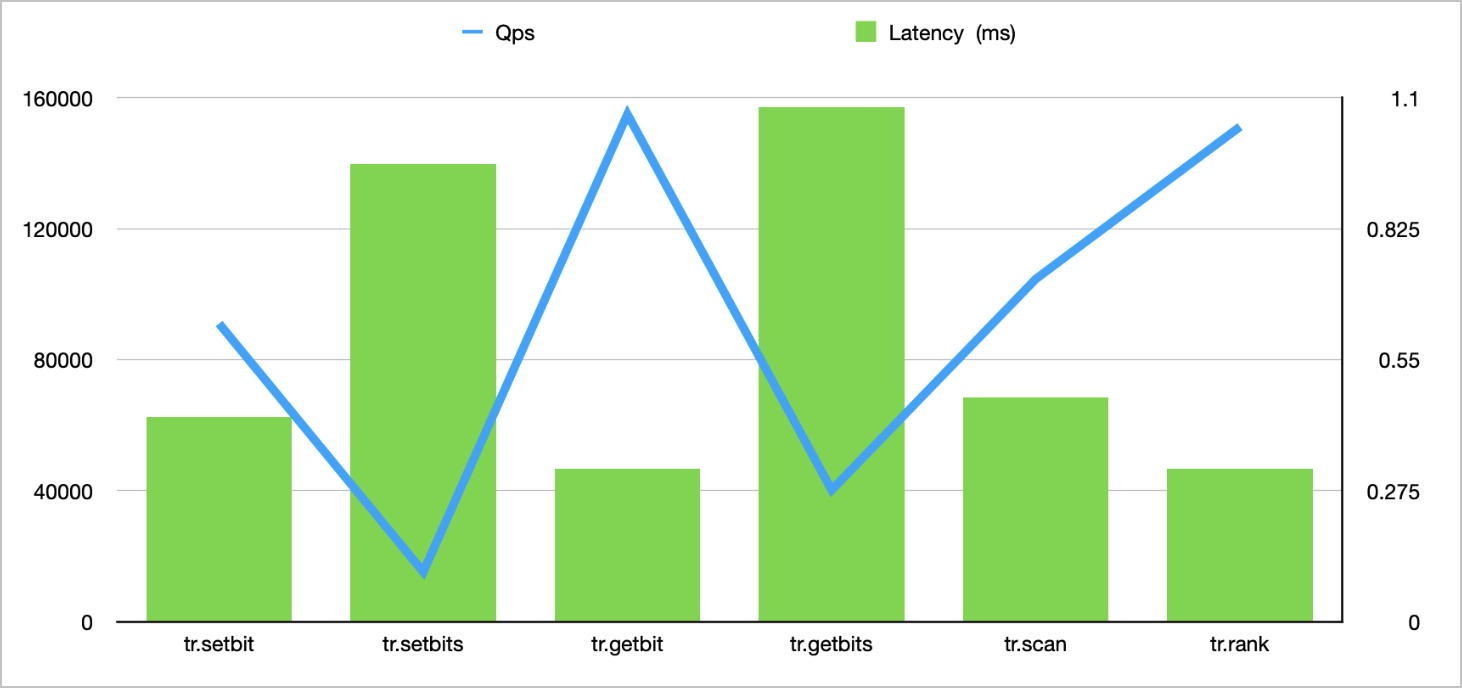
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 10000000 -r2 100000 -command "TR.SETBITS foo-__RAND2__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__ __RAND__" -p 20Command
FIELDS/RANGE
QPS reference value
Average latency (ms)
TR.SETBIT
1
91003
0.43
TR.SETBITS
100
15127
0.96
TR.GETBIT
1
154941
0.32
TR.GETBITS
100
40166
1.08
TR.SCAN
100
104637
0.47
TR.RANK
-
151161
0.32
Testing for bitwise operations
TR.BITOP
This command performs bitwise operations on multiple keys and stores the results in a new key. The AND, OR, NOT, DIFF, and XOR bitwise operations are supported.
Sample command:
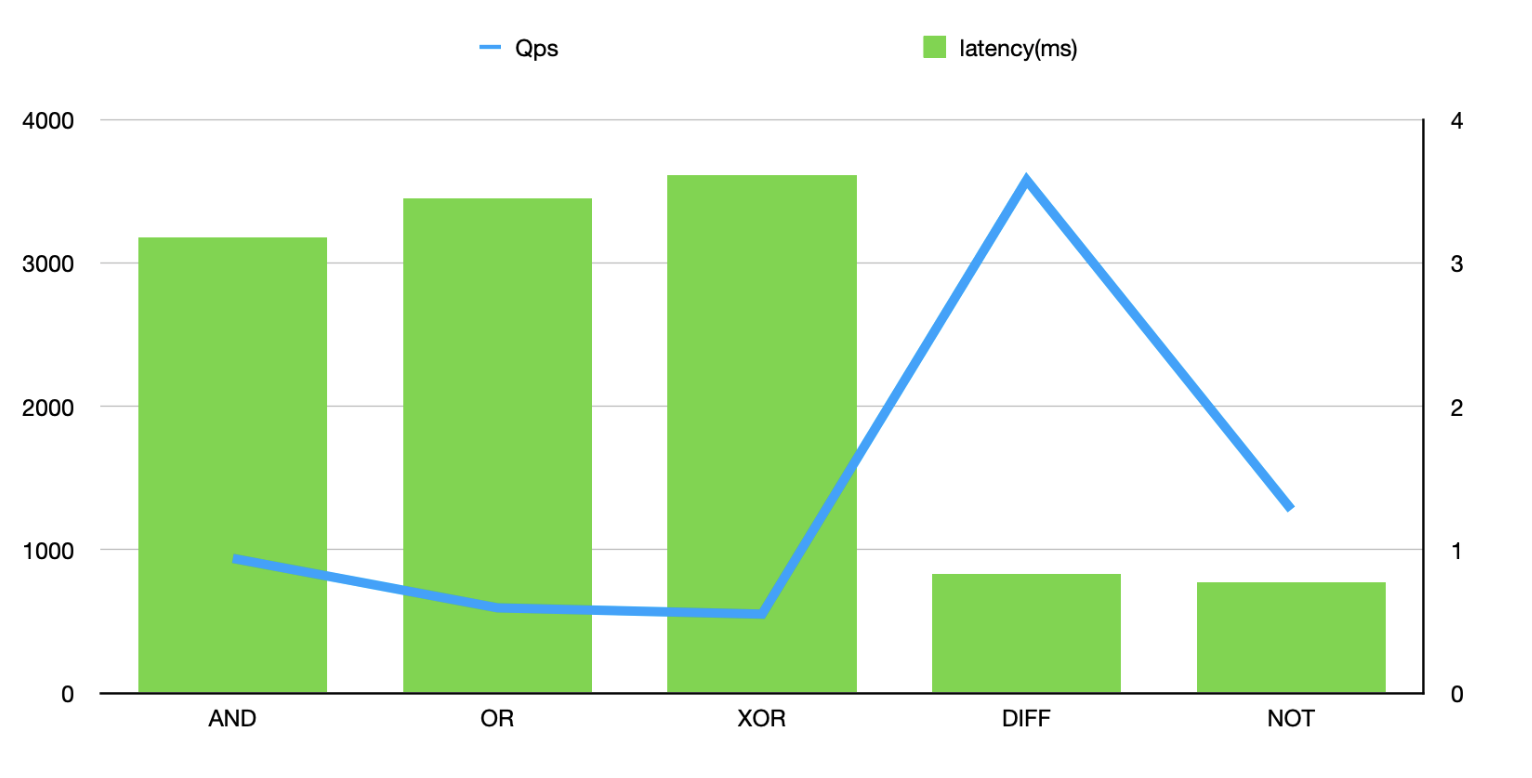
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.BITOP dest-__RAND__ AND foo-__RAND__ foo-__RAND__" -p 3 -c 1Bitwise operation
parallel
QPS reference value
Average latency (ms)
AND
3
940
3.18
OR
2
595
3.45
XOR
2
551
3.61
DIFF
3
3577
0.83
NOT
1
1281
0.77
TR.BITOPCARD
This command performs bitwise operations on multiple keys and returns the number of bits that have a value of 1. The AND, OR, NOT, DIFF, and XOR bitwise operations are supported.
Sample command:
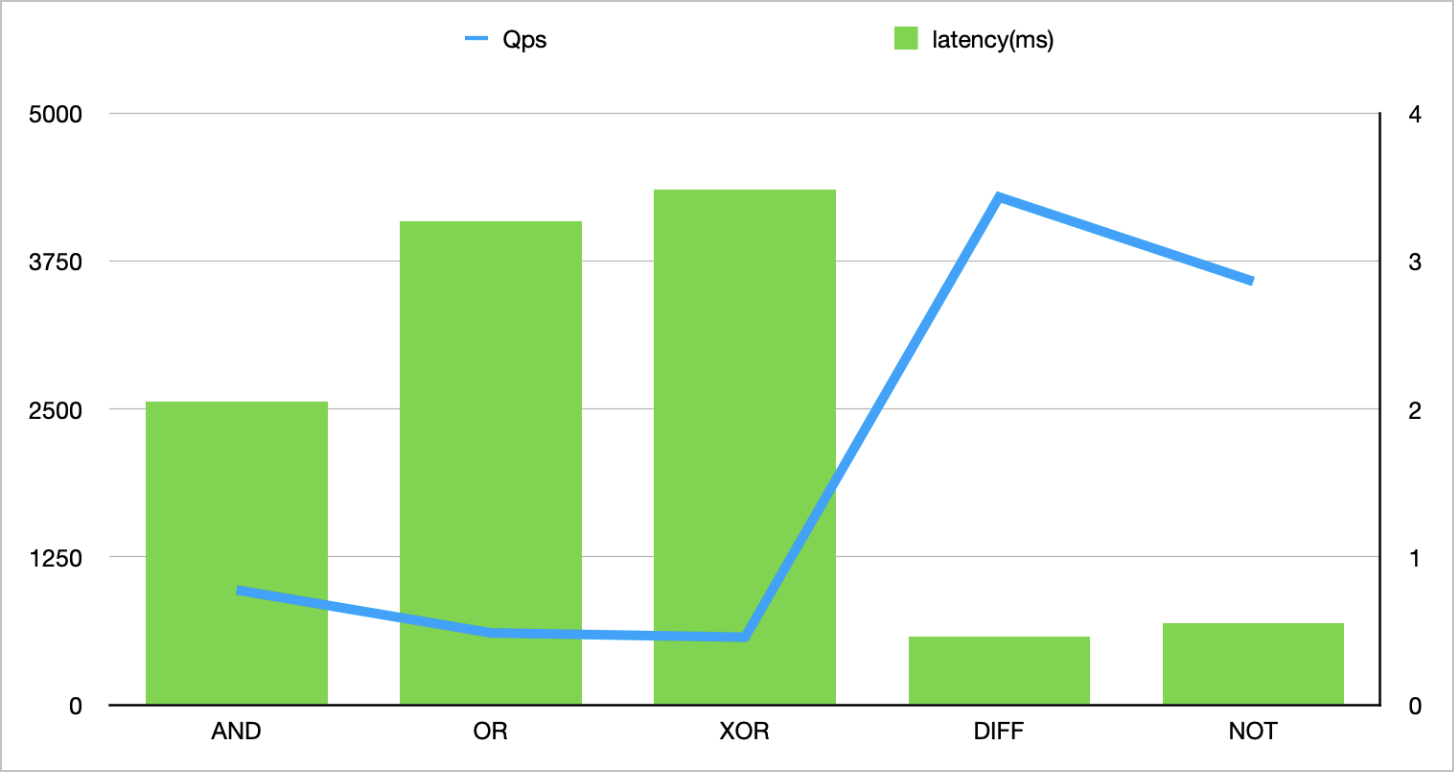
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.BITOPCARD AND foo-__RAND__ foo-__RAND__" -p 2 -c 1Bitwise operation
parallel
QPS reference value
Average latency (ms)
AND
2
971
2.05
OR
2
609
3.27
XOR
2
572
3.48
DIFF
2
4290
0.46
NOT
2
3577
0.55
Test methods and results for the cluster architecture
Test the performance of four DRAM-based instances that use the cluster architecture. The instances have different numbers of shards. Each shard is 4 GB in size. The following items list the specifications of the instances:
8 GB cluster instance (2 shards)
16 GB cluster instance (4 shards)
32 GB cluster instance (8 shards)
64 GB cluster instance (16 shards)
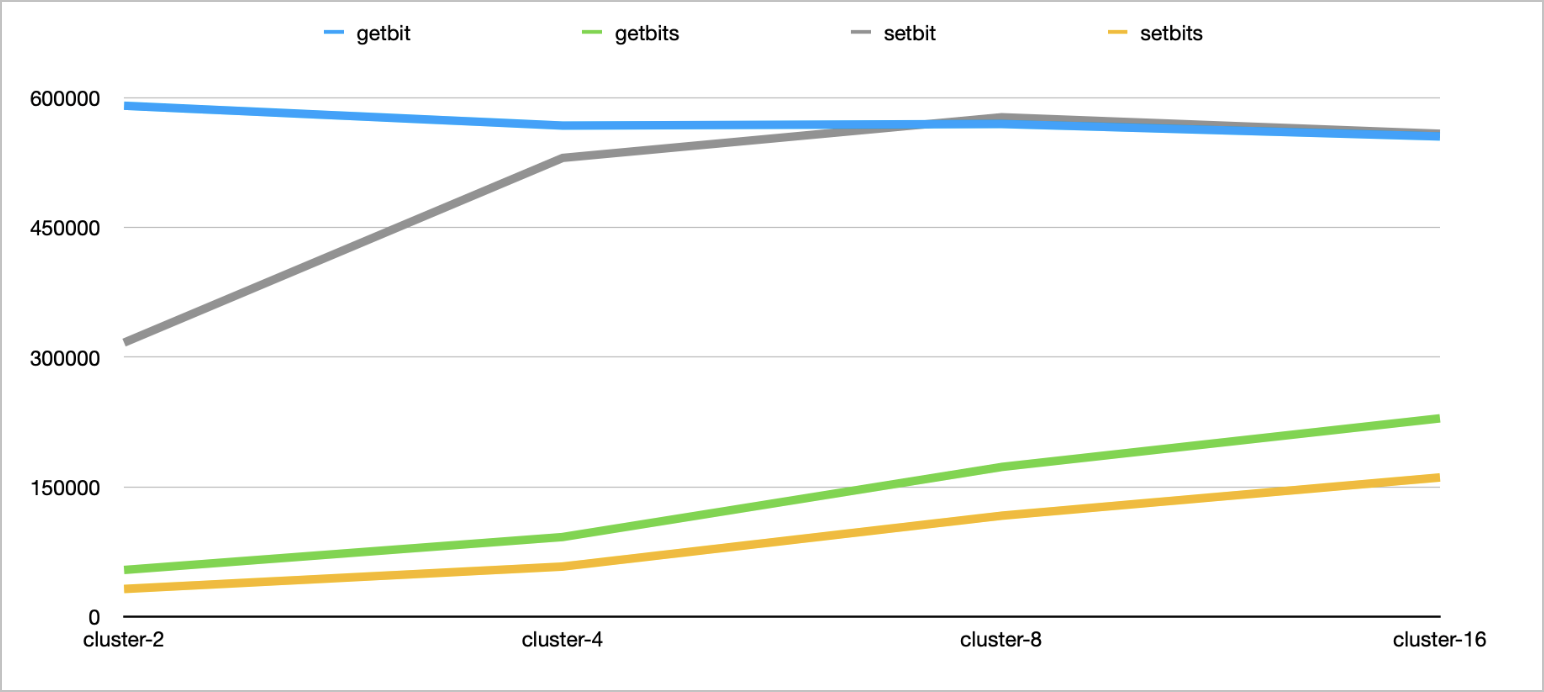
To prevent network interruptions, increase the bandwidths of all the instances to the maximum of 2,048 Mbit/s. Deploy the client used in tests in the zone where the instances reside and use proxy endpoints to access the instances. Run different commands that involve a single key to obtain the average QPS value of the instances.
Run the following commands: TR.GITBIT, TR.GITBITS, TR.SETBIT, and TR.SETBITS. Sample command:
./redis -h r-**********0d7f.redis.zhangbei.rds.aliyuncs.com -a user:password -d 30 -r 100000 -r2 10000000 -command "TR.SETBIT foo-__RAND__ bar-__RAND2__" -p 20 -c 1Test results:
Command | QPS value (DRAM-based cluster instance that has two shards) | QPS value (DRAM-based cluster instance that has four shards) | QPS value (DRAM-based cluster instance that has eight shards) | QPS value (DRAM-based cluster instance that has 16 shards) |
TR.GITBIT | 590742 | 567738 | 569610 | 555178 |
TR.GITBITS | 53900 | 91991 | 172969 | 229214 |
TR.SETBIT | 316753 | 530367 | 577406 | 558301 |
TR.SETBITS | 31917 | 57843 | 116614 | 160891 |