This topic describes how to verify read/write splitting on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that runs RDS High-availability Edition. In this topic, an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance is connected to the RDS instance over an internal network.
Prerequisites
A primary RDS instance that runs RDS High-availability Edition is created.
A read-only RDS instance is created for the primary RDS instance.
At least one database that contains at least one table is created on the RDS instance. A test account is created for the RDS instance. The test account can be a standard account or a privileged account. For more information, see Create accounts and databases.
NoteIf you create a standard account, you must grant the standard account the Read/Write (DDL + DML) permissions on the required database.
In this example, a database named testdb01, a table named products, and a test account named cxx1 are created.
An IP address whitelist is configured for the RDS instance.
The ECS instance that you connected to the RDS instance resides in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the RDS instance. The MySQL client is installed on the ECS instance.
The database proxy feature is enabled for the RDS instance.
The SQL Explorer and Audit feature is enabled for the RDS instance.
Background information
The read/write splitting capability of the database proxy feature helps forward write requests to the primary RDS instance and read requests to the read-only RDS instance to implement automatic read/write splitting. This offloads read requests from the primary RDS instance. After you enable and configure the database proxy feature, you can perform the operations provided in this topic to check whether read and write requests are forwarded based on the read weights that you specified.
Verification process
In this example, an ECS instance is connected to the RDS instance over an internal network to verify the effectiveness of read/write splitting. You can perform the following steps:
In the ApsaraDB RDS console, set the weight of the read-only RDS instance to a multiple of 100 and the weight of the primary RDS instance to 0. The settings ensure that all read requests are forwarded to the read-only RDS instance. In this example, the weight of the read-only RDS instance is set to 10000, and the weight of the primary RDS instance is set to 0.
Use the test account to connect the ECS instance to the RDS instance by using the database proxy endpoint, and then perform read and write operations.
On the SQL Explorer and Audit page of the ApsaraDB RDS console, view the records of SQL statements that are executed on the primary RDS instance and read-only RDS instance.
Check whether the read requests are processed by the read-only RDS instance and whether the write requests are processed by the primary RDS instance based on the execution records of SQL statements to determine whether read/write splitting is implemented.
Procedure
Specify read weights.
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the primary RDS instance resides. Then, find the primary RDS instance and click the ID of the RDS instance.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Database Proxy. In the Connection Information section of the page that appears, find the required proxy endpoint, which is formerly known as terminal.
Click Modify Configuration in the Actions column of the proxy endpoint.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the following parameters:
Read/Write Attributes: Set this parameter to Read/Write (Read/Write Splitting).
Read Weight Allocation: Set this parameter to Custom. Then, set the weight of the read-only RDS instance to 10000 and the weight of the primary RDS instance to 0. Click OK.
In the Connection Information section, obtain the VPC-type proxy endpoint of the required proxy endpoint.
Use the cxx1 test account to connect the ECS instance to the database and perform read operations.
Log on to the ECS instance that you want to connect to the RDS instance.
NoteFor more information about how to log on to an ECS instance, see Connect to an instance.
Run the following command to connect the ECS instance to the RDS instance:
mysql -hProxy endpoint -PPort number -uUsername -pPasswordThe following table describes the parameters that are used in the preceding command.
Parameter
Description
Configuration
Proxy Endpoint
The VPC-type proxy endpoint that you obtained from Step 1.
If you use a client to connect to the RDS instance, you must use a public proxy endpoint.
P
The port number. Enter the port number after the uppercase letter P.
N/A.
-u
The username. Enter the username after the letter u.
N/A.
p
The password. Enter the password after the lowercase letter p.
Enter the password after
-p. No spaces are allowed.You can also enter the password after you run the command instead of entering the password following
-pbefore you run the command. This helps prevent the password from being displayed in plaintext.Run the following command to access the database testdb01:
USE testdb01;Execute the SQL statements for read operations six times. Sample statement:
SELECT * FROM products LIMIT 20;
Execute the SQL statements for write operations in the testdb01 database three times. Sample statement:
NoteIn the preceding step, you have connected the ECS instance to the RDS instance and accessed the testdb01 database. For more information, see Step 2.
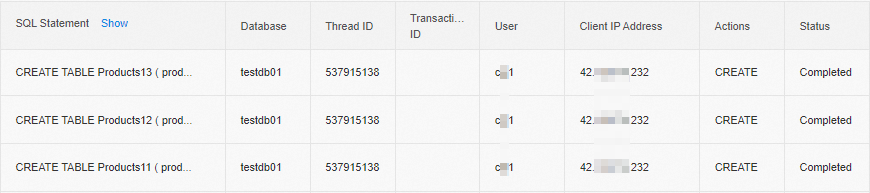
CREATE TABLE Products11 ( prod_id CHAR(10) NOT NULL, vend_id CHAR(10) NOT NULL, prod_name CHAR(254) NOT NULL, prod_price DECIMAL(8,2) NOT NULL, prod_desc VARCHAR(1000) NULL );View the records of SQL statements that are executed on the primary RDS instance and the read-only RDS instance.
The records show that all SELECT statements are executed on the read-only RDS instance. The records show that all CREATE statements are executed on the primary RDS instance.
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the primary RDS instance resides. Then, find the primary RDS instance and click the ID of the RDS instance.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page of the primary RDS instance, choose . On the page that appears, select a time range and click Query. No execution records of the SELECT statements are found.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page of the primary RDS instance, click Basic Information. In the Instance Distribution section of the page that appears, move the pointer over the number to the right of Read-only Instance. In the dialog box that appears, click the ID of the read-only RDS instance.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page of the read-only RDS instance, choose . On the page that appears, select a time range and click Query. The records of the SELECT statements that are executed six times are displayed.
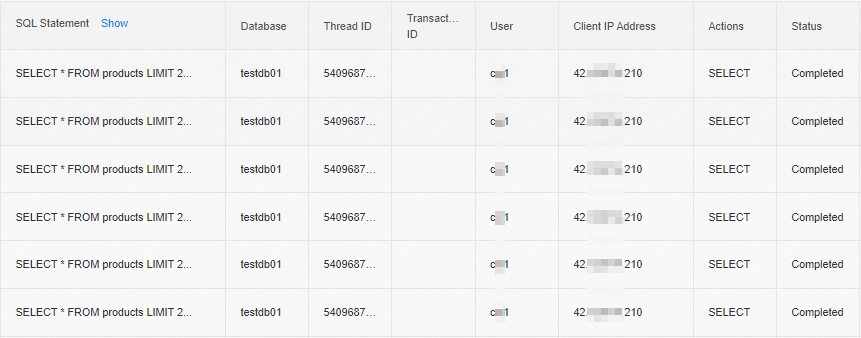
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page of the primary RDS instance, choose . On the page that appears, select a time range and click Query. The records of the SELECT statements that are executed six times are displayed.
Verification conclusion
If the weight of the read-only RDS instance is set to 10000 and the weight of the primary RDS instance is set to 0, all write requests are processed by the primary RDS instance, and all read requests are processed by the read-only RDS instance. This way, read/write splitting is implemented.