In actual stress testing scenarios, you can extract output parameters from the response of a request and use the extracted information as the input of the next request. You can define multiple output parameters in a single API. This topic describes how to extract output parameters.
Configure output parameters
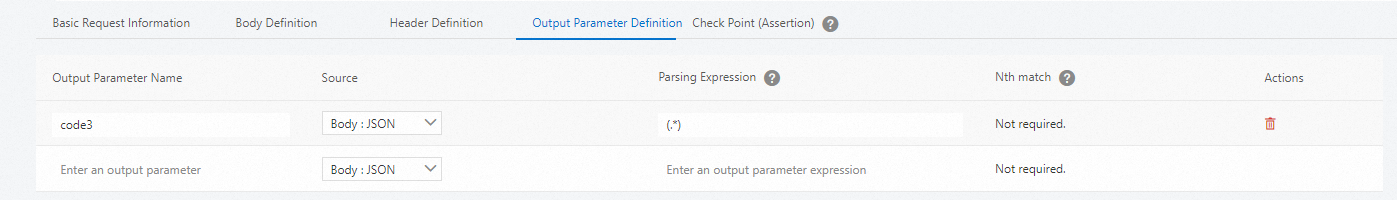 The following table describes the elements in an output parameter.
The following table describes the elements in an output parameter.
Element | Description |
Output Parameter Name | The name of the output parameter. The name can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). The name must start with a letter. |
Source | The parsing method of the response. You can select one of the following parsing methods:
|
Parsing Expression | The parsing expression that is used to extract the content that you want to use as the output parameter from the response. |
Nth match | This parameter is available only when you set the Source parameter to Body : TEXT. If the specified parsing expression has more than one match in the response, use this parameter to specify the ordinal number of the string that you want to use as the output parameter. The ordinal numbers start from 0. A negative value specifies the Nth string from the end. Valid values: -99 to 99. If you want to use a random string as the output parameter, enter random. |
Body : JSON parsing method
The following types of responses are supported: application/json and text/json.
PTS supports both the new and old versions of the JSONPath syntax. To highlight the differences between the new and old versions of JSONPath expressions, the following sections provide the sample JSONPath structure and the syntax and descriptions of JSONPath expressions for both versions.
We recommend that you use the new version of the JSONPath syntax.
JSONPath expressions (new version)
The following sample code provides an example of the new version of the JSONPath structure. The following table describes the syntax and descriptions of the new version of JSONPath expressions.
JSONPath syntax | Description |
$ | The root object. For example, if you specify the |
[num] | Retrieval of an element in an array. The num variable specifies a number. For example, if you specify the |
[num0,num1,num2...] | Retrieval of multiple elements in an array. The num variable specifies a number. In this case, multiple elements in the array are returned. For example, if you specify the |
[start:end] | Retrieval of a range of elements defined by a start element and an end element in an array. For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key)] | Retrieval of non-empty object attributes. For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key > 123)] | Retrieval of numeric-type object attributes by a comparison operation. The supported comparison operators include equal to (=), not equal to (!=), greater than (>), greater than or equal to (>=), less than (<), and less than and equal to (<=). For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key = '123')] | Retrieval of string-type object attributes by a comparison operation. The supported comparison operators include equal to (=), not equal to (!=), greater than (>), greater than or equal to (>=), less than (<), and less than and equal to (<=). For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key like 'aa%')] | Retrieval of string-type object attributes by a like clause. You can use only a percentage sign (%) as the wildcard. The not like clauses are supported. For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key rlike 'regexpr')] | Retrieval of string-type object attributes by a regular expression. The Java Development Kit (JDK) syntax is used and the not rlike clauses are supported. For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key in ('v0', 'v1'))] | Retrieval of object attributes by an in clause. String- and numeric-type objects are supported. The not in clauses are supported. For example, if you specify the |
[?(@.key between 234 and 456)] | Retrieval of object attributes by a between clause. Numeric-type objects are supported. The not between clauses are supported. For example, if you specify the |
length() or size() | Retrieval of the number of elements in an array. For example, if you specify the |
.. | Retrieval of a specific attribute. For example, if you specify the |
* | Retrieval of all attributes in an object. For example, if you specify the |
randomIndex() | Retrieval of a random element in an array. For example, if you specify the |
['key'] | Retrieval of an attribute. For example, if you specify the |
['key0','key1'] | Retrieval of multiple attributes. For example, if you specify the |
The semantics of the $.store.book[0].title and $['store']['book'][0]['title'] expressions are the same.
JSONPath expressions (old version)
The following sample code provides an example of the old version of the JSONPath structure. The following table describes the syntax and descriptions of the old version of JSONPath expressions.
{
"info": "success",
"message": "Succeeded.",
"data": {
"id":13509, "code":0,
"items": [
{"name": "name1", "value": "1234"},
{"name": "name2", "value": "8448"},
{"name": "name3", "value": "1298"},
{"name": "name4", "value": "3049"},
{"name": "name5", "value": "7648"}
]
}
}
Output parameter value | Old version of the parsing expression | New version of the parsing expression (for comparison) |
The value of the info object. |
|
|
The ID value in the data array. |
|
|
The value of the first element in the items array. Relative position is supported. |
|
|
The value of the second to last element in the items array. Relative position is supported. |
| Not supported |
The entire items array. |
|
|
A random element in the items array. |
|
|
Body : TEXT parsing method
All text formats are supported. You can use regular expressions to extract information. If a regular expression has multiple matches, you can specify which match is used. By default, 0 indicates the first match.
The following sample code provides an example API response:
<input name="id" value="34729XXXX">
<input name="token" value="acdfo4dfopasdf44dXXXX">
...
<script>
var planId=4587;
var planId=5689;
var planId=8906;
</script>
Output parameter value | Parsing expression | Nth match |
The value whose name is id. |
| 0 |
The value whose name is token. |
| 0 |
The value of the third PlanID element. |
| 2 |
The value of a random PlanID element. |
| random |
Format conventions:
Order matching principle: matches the parsing expression against the response body based on the text sequence in the response body. If a match is found, the matching text is assigned to the output parameter and the subsequent text is ignored. You must make sure that the parsing expression that you use can precisely match the desired text. If you need to select only the first match from multiple matches, you do not need to specify which match is used.
The matching text cannot contain special characters, such as braces ({}) and parentheses (()).
When you use a regular expression to extract information from a JSON response, you do not need to add a space after the colon between the key and value in a key-value pair. You can add a space after the colon between the key and value in each key-value pair to optimize the visual effects of JSON data.
Cookie : K/V and Header : K/V parsing methods
The Cookie : K/V and Header : K/V parsing methods are used to extract the Cookie field and Header field, respectively. You can specify the keys that you want to extract in the parsing expression. For example, if the Cookie field contains token=1234;path=/ and you want to extract the value of the token, enter token in the parsing expression.
Status Code parsing method
You can use the Status Code parsing method to extract the response status codes of requests. In most cases, use this parsing method for check points or conditional jumps. Different page information is returned for different status codes.
Output parameters of JDBC nodes
To extract output parameters from SQL query results, you must select the Body : JSON parsing method that is described in the preceding section. The following sample code provides an example of the JSON data structure:
{
"data": [
{
"Column 1": "value",
"Column 2": "value"
},
{
"Column 1": "value",
"Column 2": "value"
}
...
]
}For example, the following table describes the SQL query results. Assume that you want to parse the value (name1) in the name column of the first row as the output parameter.
id | name |
1 | name1 |
2 | name2 |
Use the following parsing expression:
$.data[0].nameDebug output parameters
If you cannot determine whether a parsing expression is correct, you can debug the parsing expression and the associated output parameter in scenario debugging. Perform the following steps:
In the lower part of the PTS Scenario page, click Debug. In the Debug Scenario dialog box, click the name of the scenario. The details of the scenario are displayed on the right side of the dialog box. Select an API from the details of the scenario and click Click to test the output parameter regular expression.
In the dialog box that appears, select a source format, enter a regular expression, specify a value for the Nth match parameter, enter a name for the output parameter, and then click Test Expression. The matching result is obtained based on the response details, which predicts whether the extracted content meets expectations.
If you want to reset the output parameter, click Sync Output Parameter to synchronize the regular expression to the output parameter list of the API.
NoteAfter the scenario debugging is complete, you must go back to the Scenario Settings tab if the scenario has synchronized output parameters. On the Output Parameter Definition tab of the corresponding API, specify a name for each synchronized output parameter.
Example: Configure output parameters
In the financial management business, you want to recommend appropriate services based on the consumption capability of customers. In this case, you must extract the consumption capability level of each customer as the output parameter and use the output parameter to recommend services.
Perform the following steps:
Log on to the PTS console, choose , and then click PTS.
On the PTS Scenario page, add the APIs named Consumption Capability (including the output parameter) and Product Recommendation and enter the corresponding URLs.
In the API named Consumption Capability (including the output parameter), information about the consumption capability is extracted as the output parameter based on the response details of the request. Enter the output parameter name such as output and the parsing expression such as
data.items[0].value.In the lower-left corner of the PTS Scenario page, click Parameters. On the Custom Parameters tab of the panel that appears, view the created output parameter. Click the name of the output parameter, such as output, or click the
 icon that corresponds to the output parameter. The system automatically copies the parameter content.
icon that corresponds to the output parameter. The system automatically copies the parameter content. In the body of the API named Product Recommendation, specify the extracted output parameter. In the text editor of the Body Definition tab, paste the parameter content.
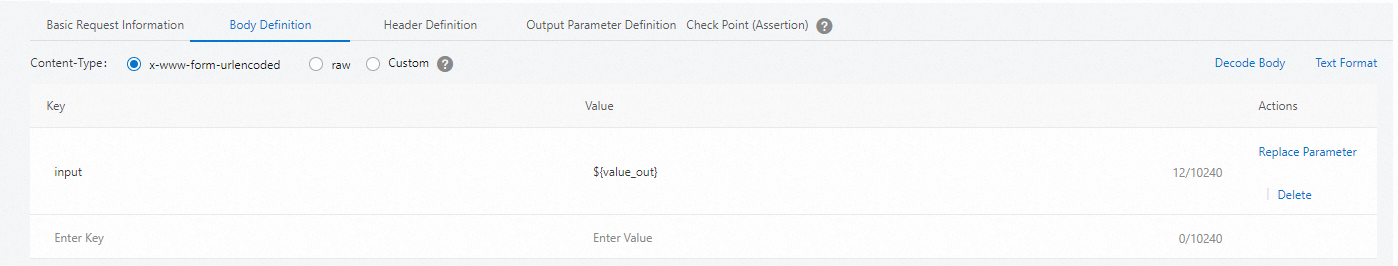
You can also edit the body content, such as combining strings, parameters, or functions.