This topic describes how to use Alibaba Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus to monitor a MySQL database.
Prerequisites
The information about the MySQL database that you want to monitor, such as the address, the port number, and the username and password that are used to connect to the MySQL database, is available.
Enable the MySQL component
In the left-side navigation pane, click Integration Center.
In the Database section of the Integration Center page, click MySQL.

On the Start Integration tab of the MySQL panel, set the parameters and click OK. Then, a Prometheus instance is created to monitor the database.
Parameter
Description
Select the environment type
Select the environment in which the database is deployed. Valid values:
Kubernetes Environment
ECS (VPC)
Cloud Services
Select Cluster
Select the ACK cluster in which the database is deployed. The parameter is available if the database is deployed in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster.
Select VPC
Select the ECS instance in which the database is deployed. The parameter is available if the database is deployed in an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Select Region for Storage
The parameter is available if the database is deployed in ApsaraDB RDS.
MySQL Address
The address of the MySQL database.
NoteThe MySQL database can be deployed in an ACK cluster, an ECS instance, or ApsaraDB RDS.
MySQL Service Port
The port number of the MySQL database. Example: 3306.
MySQL Username and MySQL Password
The username and password of the MySQL database.
ImportantTo prevent data breach risks, we recommend that you do not use an administrator account. Create a MySQL account for mysqld_exporter and grant minimum permissions to the account. For more information, see Create a MySQL user for Managed Service for Prometheus.
Configure alerting for the MySQL database
Log on to the Managed Service for Prometheus console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. Then, click the name of the Prometheus instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Alert Rules to view the alert rules of the database.
Managed Service for Prometheus provides multiple default alert rules for key MySQL metrics. You can also create alert rules based on your business requirements. For more information, see Create an alert rule for a Prometheus instance.
NoteFor information about the key MySQL metrics, see the Key metrics sections.
For more information about the alert rules that Managed Service for Prometheus presets for key MySQL metrics, see the Configure alerting for the database section.
View the dashboard
You can view monitoring data in the dashboard, such as the service availability, database queries, network traffic, connections, and memory usage.
Log on to the Managed Service for Prometheus console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Integration Management.
On the Integrated Environments tab of the Integration Management page, click the name of the environment in which the database is deployed.
In the Addon Type section of the Component Management tab, click MySQL. Then, click Dashboards to view all the dashboards.
Click the name of the dashboard.
Availability, queries per second (QPS), and database connections
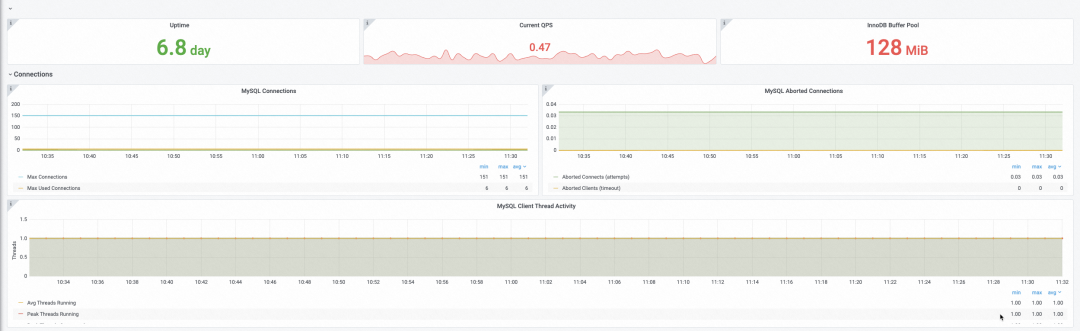
Database queries
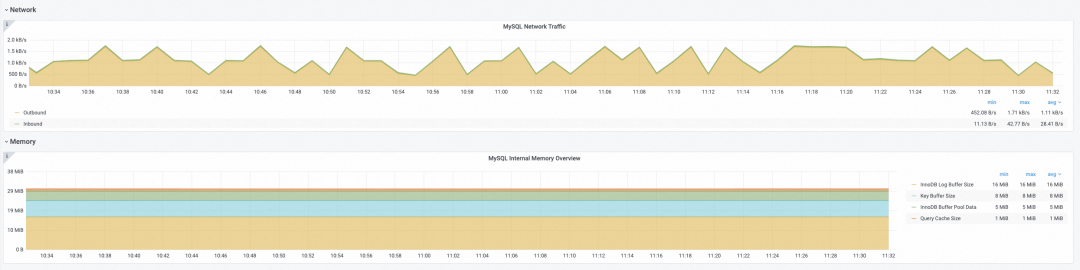
Traffic and memory usage
File monitoring data
Key metrics
Type | Metric | Description |
Availability | mysql_up | Indicates whether the MySQL database is available. |
mysql_global_status_uptime | Indicates the running duration of the MySQL database. You can create an alert rule for the metric to check whether the running duration is less than 30 minutes. | |
Database connection | mysql_global_status_connection_errors_total | Indicates connection errors, which are one of the major database errors. You can use this metric to view the information about a specific error and the number of connection errors. |
mysql_global_status_threads_connected | Indicates the number of threads on which connections to the MySQL database are established. | |
mysql_global_status_threads_running | Indicates the number of threads on which the requests to connect to the MySQL database are sent but do not succeed yet. | |
mysql_global_status_max_used_connections | Indicates the maximum number of connections to the MySQL database. | |
mysql_global_variables_max_connections | Indicates the upper limit on the connections to the MySQL database. When the number of connections reaches the upper limit, requests to establish connections are denied. | |
mysql_global_status_aborted_connects | Indicates the failed connection attempts. | |
mysql_global_status_aborted_clients | Indicates the connections that timed out. | |
Query | mysql_global_status_slow_queries | Indicates the slow queries of the MySQL database. |
mysql_global_status_queries | Indicates the QPS of the MySQL database. | |
Network traffic | mysql_global_status_bytes_received | Indicates inbound traffic. |
mysql_global_status_bytes_sent | Indicates outbound traffic. | |
File monitoring data | mysql_global_status_opened_files | Indicates the files that are opened in the MySQL database. |
mysql_global_status_open_files | Indicates the files that are being opened. | |
mysql_global_variables_open_files_limit | Indicates the files that can be opened. | |
mysql_global_status_innodb_num_open_files | Indicates the files that are opened by InnoDB. |
Configure alerting for the database
Using a self-managed Prometheus system to monitor a MySQL database is complex. You must install a MySQL exporter, enter information about the connections to the database, configure service discovery, and build dashboards. Managed Service for Prometheus provides built-in MySQL exporter, out-of-the-box dashboards, and alerting in the visualized console. This simplifies service deployment and reduces workloads.
Managed Service for Prometheus provides default alert rules for MySQL databases to help you efficiently build the dashboards and alerting system. The following alert rules are preset:
Availability: If the metric value is 0, the MySQL database is unavailable. If the metric value is 1, the MySQL database is running as expected. You can replace the
${instance}variable with the MySQL database that you want to monitor.mysql_up{${instance}} != 1Slow queries: You can use this metric to identify SQL statements that can be improved in the database.
rate(mysql_global_status_slow_queries{${instance}}[5m]) > 0Connection errors: Connection errors are one of the major database errors. When an alert is triggered, you can receive a notification that contains error details, including the error type and QPS.
rate(mysql_global_status_connection_errors_total{${instance}}[5m]) > 0Connection usage: Most connection errors are caused by insufficient number of connections. You can troubleshoot connection errors based on this metric.
100 * mysql_global_status_threads_connected{${instance}} / mysql_global_variables_max_connections{${instance}} > 90When the connection usage reaches the upper limit, the MySQL database denies connection requests. To resolve this issue, you can increase the upper limit. Before you increase the upper limit on connections, you must run the following command to check the upper limit on the files that can be opened.
mysql_global_variables_open_files_limit - mysql_global_variables_innodb_open_filesInnoDB log wait time: You can specify a period of time during which a log write must wait for the undo log to be flushed.
rate(mysql_global_status_innodb_log_waits{${instance}}[5m])