This topic presents the OLTP workload performance test results for PolarDB for PostgreSQL version 16.
Introduction
Compared with open source PostgreSQL 16, PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16 delivers improved overall performance through the following optimizations:
Adopts leading hardware technologies, such as Optane storage cards based on 3DXpoint storage medium, NVMe SSDs, and RoCE RDMA networking.
Implements a full I/O and network protocol stack running in user mode, leveraging new hardware to achieve higher performance and lower latency.
Replaces native PostgreSQL xid transactions with a monotonically incrementing 64-bit integer using Polar CSN (Commit Sequence Number) technology to enhance OLTP performance under high concurrency.
Reduces I/O operations and improves performance using techniques such as prefetching, pre-extension, and rel_size_cache.
For detailed testing steps, see Performance testing methodology (OLTP).
Test environment and specifications
The environments and specifications for PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16 and open source PostgreSQL 16 are shown in the table below. The open source PostgreSQL 16 tests were deployed on Alibaba Cloud ECS instances:
Parameter | PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16 | Open source PostgreSQL 16 |
CPU cores + memory | 8 cores, 64 GB | 8 cores, 64 GB |
Load-generating ECS instance type | ecs.u1-c1m2.8xlarge | ecs.u1-c1m2.8xlarge |
Concurrency | 256 | 256 |
PostgreSQL version | 16.10 | 16.10 |
Disk performance level | PSL5 | cloud_essd+PL3 |
Reserved disk space | Auto-scaling, unlimited | Auto-scaling, unlimited |
Kernel parameters for PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16 were aligned with those of open source PostgreSQL 16 for performance testing. All other parameters used default values.
Test workload description
Sysbench includes seven workload types: oltp_insert, oltp_point_select, oltp_read_only, oltp_read_write, oltp_update_index, oltp_update_non_index, and oltp_write_only. The test content for each scenario is described below:
Parameter | Scenario | Test content |
Write scenarios | oltp_insert | You can insert a table. |
oltp_update_index | Update indexed tables. | |
oltp_update_non_index | Update non-indexed tables. | |
oltp_write_only | Mixed insert, update, and delete operations. | |
Read scenarios | oltp_point_select | Point query. |
oltp_read_only | Point query + range query. | |
Read-write mixed | oltp_read_write | Mixed oltp_write_only and oltp_read_only workload. |
Metrics
TPS (Transactions Per Second): The number of transactions the database executes per second, measured by successful COMMIT operations.
Test data volume
The test data volume used in this experiment is shown in the table below:
Parameter | Description |
Number of tables | 8 |
Number of rows | 64,000,000 |
Total data volume | 128 GB |
Performance results
Write scenarios
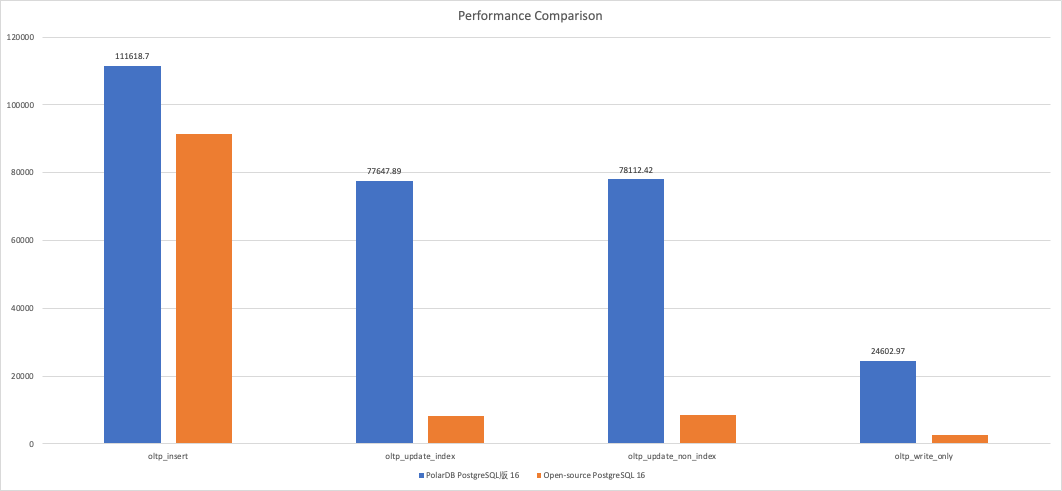
Stress testing scenario
PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16
Open source PostgreSQL 16 database
oltp_insert
111618.70
91512.15
oltp_update_index
77647.89
8129.04
oltp_update_non_index
78112.42
8420.75
oltp_write_only
24602.97
2658.71
Read scenarios
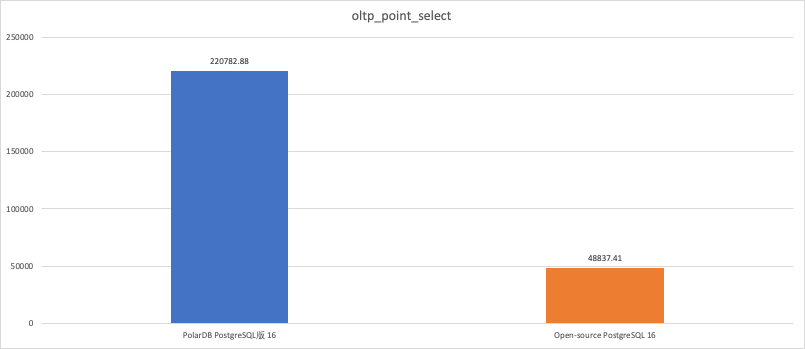
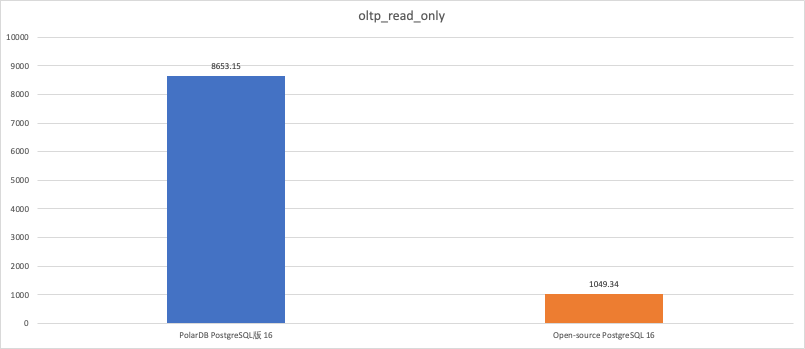
Stress testing scenario
PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16
Open source PostgreSQL 16 database
oltp_point_select
220782.88
48837.41
oltp_read_only
8653.15
1049.34
Read-write mixed scenario
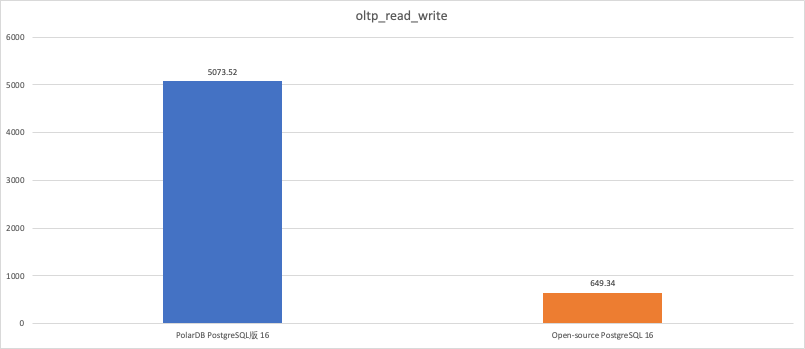
Stress testing scenario
PolarDB for PostgreSQL 16
Open source PostgreSQL 16 database
oltp_read_write
5073.52
649.34