PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) allows you to use the Elastic Parallel Query feature to run analytical queries so that you can use some hybrid transaction/analytical processing (HTAP) capabilities. This topic describes how to use the feature to improve the performance of analytical queries.
How the Elastic Parallel Query feature works
In Elastic Parallel Query, a query is run on multiple nodes in parallel. The node that coordinates how the query is run is called the query coordinator (QC) node, and the other nodes are called parallel execution (PX) nodes. After a query request is initiated, the QC node divides the execution plan of the query into shards and routes the shards to the PX nodes. Each PX node runs the assigned part of the execution plan and sends the query result to the QC node. Then, the QC node aggregates the query results.
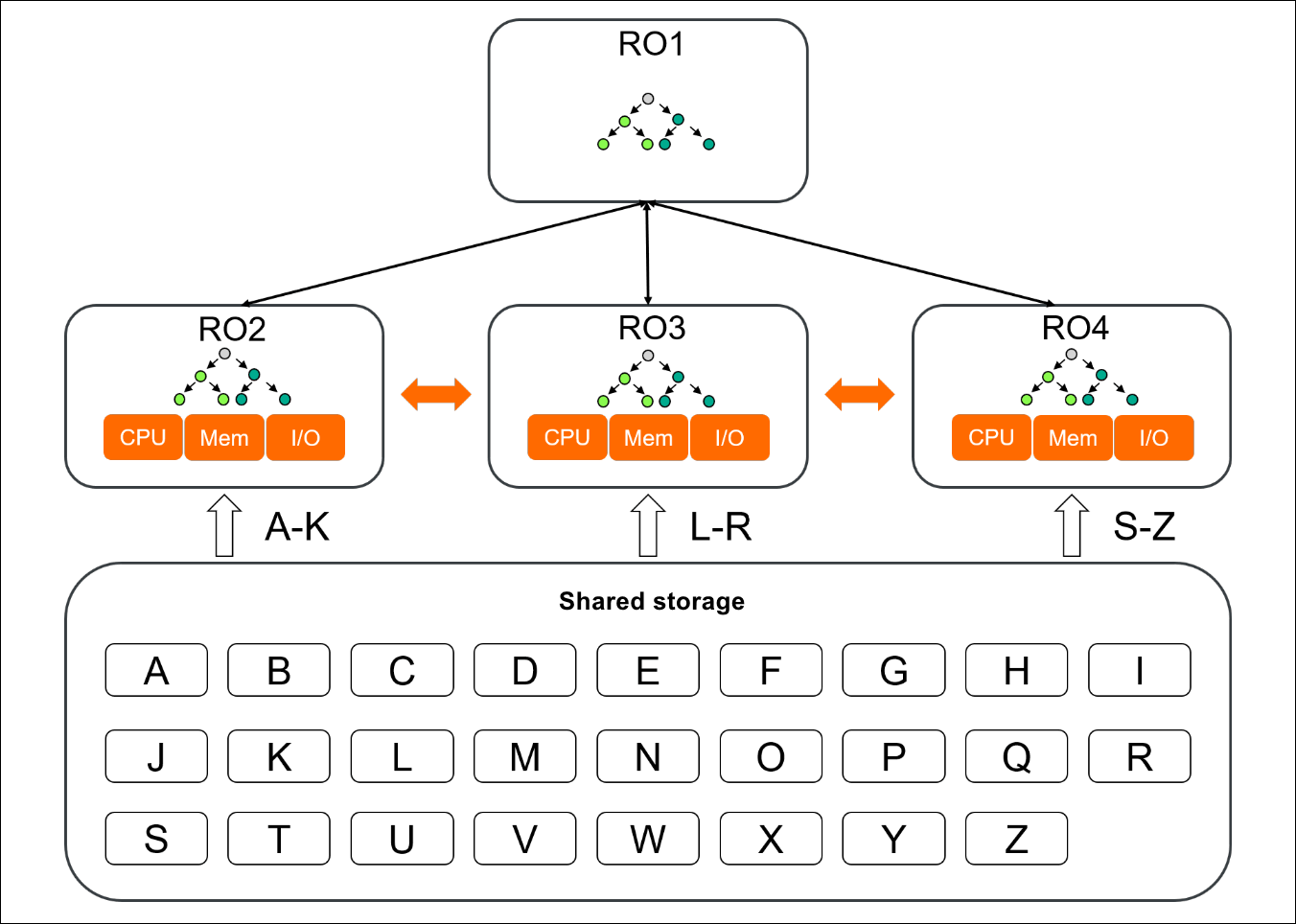
In the preceding figure, RO1 is the QC node and RO2, RO3, and RO4 are the PX nodes. After RO1 receives a query request, RO1 divides the execution plan of the query into three shards and routes the shards to RO2, RO3, and RO4. Each PX node runs its assigned part of the execution plan, obtains the required data blocks from the shared storage system Polar File System (PolarFS), and then sends the query results to the QC node. Then, the QC node combines the query results and returns the final result.
Precautions
Because multiple read-only nodes must be used to run each query in parallel, Elastic Parallel Query is suitable only for analytical queries that are run infrequency.
Use the Elastic Parallel Query feature to perform analytical queries at different levels
You can use the Elastic Parallel Query feature to perform analytical queries at the following three granularity levels:
System level: Configure the relevant parameters to specify whether to enable or disable the Elastic Parallel Query feature for all queries and all sessions.
Session level: Execute the ALTER SESSION statement or configure the session-level GUC parameters to specify whether to enable or disable the Elastic Parallel Query feature for the current session.
Query level: Use a hint to specify whether the Elastic Parallel Query feature is enabled or disabled for a specific query.
Parameters
By default, the Elastic Parallel Query feature is disabled in PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle). To use this feature, configure the parameters described in the following figure.
Parameter | Parameters |
polar_cluster_map | Queries the names of all the read-only nodes in PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle). You cannot configure this parameter. Each time you add a read-only node, the list of node names returned for the parameter is automatically updated. Note This parameter is available only for clusters that use the minor kernel version 1.1.20 (released in January 2022) or earlier. |
polar_px_nodes | Specifies the read-only nodes in which your query is run on multiple nodes. This parameter is empty by default, which indicates that all read-only nodes are used for parallel execution. If you want to use specific nodes for parallel execution, set the parameter to the names of the nodes that you want to use. Use commas (,) to separate the node names. Example: |
polar_px_enable_replay_wait | Specifies whether to enable strong consistency. Valid values: on and off. A delay exists between the primary node and read-only nodes in your PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster. For example, after the primary node executes a CREATE TABLE statement, this DDL statement is replayed on the read-only nodes so that the read-only nodes are synchronized with the primary node. This replay causes the delay. If you set the The default value is off, which indicates that strong consistency is disabled. If you set the parameter to off, a long delay exists between the primary node and read-only nodes due to log replay and the read-only nodes may fail to read the latest log records of DDL operations. If you set the You can also set this parameter to on for a specified database role. |
polar_px_max_workers_number | Specifies the maximum number of workers processes that can be run on a node for Elastic Parallel Query. The default value is 30. This parameter is used to limit the degree of parallelism on each node. The number of workers processes for each node in all sessions for Elastic Parallel Query cannot exceed the value of this parameter. |
polar_enable_px | Specifies whether to enable the Elastic Parallel Query feature. The default value is off, which indicates that the feature is disabled. |
polar_px_dop_per_node | Specifies the degree of parallelism for Elastic Parallel Query on the current session. The default value is 1. We recommend that you set the value to the number of cores in your operating system. If you set polar_px_dop_per_node to N, each node uses N px workers processes for a session to run your query in parallel. |
px_workers | Specifies whether the feature is applied to the specified tables. By default, the feature is applied to no tables. The feature is computing resource-consuming. To reduce the consumed computing resources, you can configure this parameter to specify the tables to which the feature applies. The following code provides an example to describe how to configure this parameter: |
synchronous_commit | Specifies whether a transaction needs to wait for WAL logs to be written to the disk before it returns a success message to the client when the database commits the transaction. Default value: on. Valid values:
Note The parameter is set to on in PX mode. |
Examples
The following section describes the effect of the Elastic Parallel Query feature. In the example, a single-table query is performed.
Background information
Execute the following statements to create a table named test and insert data into the table:
CREATE TABLE test(id int);
INSERT INTO test SELECT generate_series(1,1000000);
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM test;By default, the Elastic Parallel Query feature is disabled. The native execution plan for a single-table query is to perform a sequential scan (Seq Scan), as shown in the following code:
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on test (cost=0.00..35.50 rows=2550 width=4)
(1 row)To enable the Elastic Parallel Query feature, perform the following steps.
Enable this feature for the table named test:
ALTER TABLE test SET (px_workers=1); SET polar_enable_px=on; EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM test;The following query result is returned:
QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 2:1 (slice1; segments: 2) (cost=0.00..431.00 rows=1 width=4) -> Seq Scan on test (scan partial) (cost=0.00..431.00 rows=1 width=4) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (3 rows)Query the names of all the read-only nodes.
Execute the following statement:
SHOW polar_cluster_map;The following query result is returned:
polar_cluster_map ------------------- node1,node2,node3 (1 row)In this example, the cluster has three read-only nodes: node1, node2, and node3.
Specify node1 and node2 for Elastic Parallel Query.
Execute the following statement:
SET polar_px_nodes='node1,node2';Query the nodes that are specified for Elastic Parallel Query:
SHOW polar_px_nodes ;The following query result is returned:
polar_px_nodes ---------------- node1,node2 (1 row)
Performance data
The following performance data is obtained from a test in which five read-only nodes are used for parallel execution.
When
SELECT COUNT(*)is executed for a full table scan, Elastic Parallel Query is 60 times faster than single-node parallel execution.In TPC-H queries, Elastic Parallel Query is 30 times faster than single-node parallel execution.
Note In this example, a test based on the TPC-H benchmark is implemented, but it does not meet all the requirements of a TPC-H benchmark test. Therefore, the test results may be incomparable with the published results of the TPC-H benchmark test.
Specify a level for Elastic Parallel Query
This section describes how to use the Elastic Parallel Query feature to perform analytical queries at different granularity levels:
System level
If you want to use the Elastic Parallel Query feature at the system level, configure global Grand Unified Configuration (GUC) parameters to enable the feature and to specify the degree of parallelism.
Examples
postgres=# alter system set polar_enable_px=1; ALTER SYSTEM postgres=# alter system set polar_px_dop_per_node=1; ALTER SYSTEM postgres=# select pg_reload_conf(); pg_reload_conf ---------------- t (1 row) postgres=# \c postgres You are now connected to database "postgres" as user "postgres". postgres=# drop table if exists t1; DROP TABLE postgres=# select id into t1 from generate_series(1, 1000) as id order by id desc; SELECT 1000 postgres=# alter table t1 set (px_workers=1); ALTER TABLE postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 2:1 (slice1; segments: 2) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows)Session level
If you want to use the Elastic Parallel Query feature at the session level, execute the ALTER SESSION statement or configure session-level GUC parameters.
ALTER SESSION syntax
ALTER SESSION ENABLE PARALLEL QUERY ALTER SESSION DISABLE PARALLEL QUERY ALTER SESSION FORCE PARALLEL QUERY [PARALLEL integer]NoteALTER SESSION ENABLE PARALLEL QUERYspecifies that you can use a hint or the corresponding syntax to enable Elastic Parallel Query for the current session.ALTER SESSION DISABLE PARALLEL QUERYspecifies that the current session does not support Elastic Parallel Query even if a hint or the corresponding syntax is specified.ALTER SESSION FORCE PARALLEL QUERY <PARALLEL integer>specifies that the Elastic Parallel Query feature is forcefully enabled for the current session. <PARALLEL integer> specifies the degree of parallelism. If you do not specify <PARALLEL integer>, the default value of your database is used as the degree of parallelism. The default value is the value specified by the polar_px_dop_per_node parameter.You can use different methods to specify degrees of parallelism. The degrees of parallelism have different priorities based on the method. The degree of parallelism specified in a hint has the highest priority, the degree of parallelism specified in the FORCE PARALLEL statement has the medium priority, and the degree of parallelism specified by the polar_px_dop_per_node parameter has the lowest priority.
If you execute the ALTER SESSION statement, the configuration of Elastic Parallel Query for the current session is modified. After the current session is reconnected, Elastic Parallel Query is enabled for the session by default.
Example
--enable postgres=# set polar_enable_px = false; SET postgres=# set polar_px_enable_hint = true; SET postgres=# alter session enable parallel query; ALTER SESSION postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ PARALLEL(4)*/ * from t1 where id < 10; INFO: [HINTS] PX PARALLEL(4) accepted. QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 8:1 (slice1; segments: 8) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows)--disable postgres=# set polar_enable_px = false; SET postgres=# set polar_px_enable_hint = true; SET postgres=# alter session disable parallel query; ALTER SESSION postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ PARALLEL(4)*/ * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------ Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) (3 rows)--force postgres=# set polar_enable_px = false; SET postgres=# set polar_px_enable_hint = false; SET postgres=# alter session force parallel query; ALTER SESSION postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 2:1 (slice1; segments: 2) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows) postgres=# alter session force parallel query parallel 2; ALTER SESSION postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 4:1 (slice1; segments: 4) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows)Configure GUC parameters
GUC parameters can be configured at the system or session level. You can configure the GUC parameters to specify whether to enable or disable the Elastic Parallel Query feature for the current session.
Example
postgres=# set polar_enable_px = true; SET postgres=# set polar_px_dop_per_node = 1; SET postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 2:1 (slice1; segments: 2) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows)
Query level
If you want to use the Elastic Parallel Query feature at the query level, use SQL hints to enable the feature and specify the degree of parallelism. Use the following hint syntax:
/*+ PARALLEL(DEFAULT) */ /*+ PARALLEL(integer) */ /*+ NO_PARALLEL(tablename) */NotePARALLEL(DEFAULT)specifies that Elastic Parallel Query is enabled and that the default degree of parallelism is used. The default degree of parallelism is specified by the polar_px_dop_per_node parameter.PARALLEL(integer)specifies that the Elastic Parallel Query feature is enabled and the degree of parallelism specified by the integer parameter is used.NO_PARALLEL(tablename)specifies that Elastic Parallel Query is disabled for the specified table. For queries that involve this table, Elastic Parallel Query is disabled.These hints are compatible with the hints provided by Oracle. If more than one PARALLEL hint is used, take note of the following items:
If multiple hint blocks such as /*+.A.*/ /*+.B.*/ /*+.C.*/ are used together, only the first hint block takes effect.
If multiple PARALLEL hints exist in a single hint block, such as /*+ parallel(A) parallel(B)*/, the execution result varies based on the degrees of parallelism specified in these hints. If the degrees of parallelism specified in these hints are the same, one of these hints takes effect. Otherwise, none of the hints take effect.
If a PARALLEL hint and a NO_PARALLEL hint exist in the same hint block, such as /*+ parallel(A) no_parallel(t1)*/, the NO_PARALLEL hint does not take effect.
Elastic Parallel Query supports only PARALLEL and NO_PARALLEL hints.
Configure the polar_px_enable_hint GUC parameter to enable or disable Elastic Parallel Query. The default value of this parameter is false.
Example
postgres=# set polar_enable_px = false; SET postgres=# set polar_px_dop_per_node = 1; SET postgres=# set polar_px_enable_hint = true; SET postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------ Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) (3 rows) postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ PARALLEL(DEFAULT) */ * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 2:1 (slice1; segments: 2) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows) postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ PARALLEL(4) */ * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- PX Coordinator 8:1 (slice1; segments: 8) Output: id -> Partial Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) Optimizer: PolarDB PX Optimizer (6 rows) postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ PARALLEL(0) */ * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------ Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) (3 rows) postgres=# explain (verbose, costs off) select /*+ NO_PARALLEL(t1) */ * from t1 where id < 10; QUERY PLAN ------------------------ Seq Scan on public.t1 Output: id Filter: (t1.id < 10) (3 rows)Results of specifying different settings for the three levels of Elastic Parallel Query
The following table describes the rules that are applied to the results of your queries when you specify different settings for the three levels of Elastic Parallel Query.
System level
Session level
Query level
Result
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
No hint specified
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism X
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
PARALLEL(Y)
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Y
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
No hint specified
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
PARALLEL(Y)
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
No hint specified
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Z
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
PARALLEL(Y)
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Y
polar_enable_px=on
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
No hint specified
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
PARALLEL(Y)
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Y
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
enable
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
No hint specified
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
PARALLEL(Y)
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
disable
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
No hint specified
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Z
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
PARALLEL(Y)
Parallel execution with a degree of parallelism Y
polar_enable_px=off
polar_px_dop_per_node=X
FORCE PARALLEL Z
NO_PARALLEL
Serial execution