A reliable backup feature can effectively prevent data loss. PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) clusters support scheduled backup and manual backup. When you delete a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster, you can choose to retain the backup data.
Data backup
Storage type: Enterprise Edition PolarStore Level 4 (PSL4) or PSL 5. Data backups are categorized into two levels based on their storage location: level-1 backup and level-2 backup.
Data backup feature
Enabled by default
Retention period
Description
How to view backup size
Level-1 backup
Yes
3 to 14 days
The level-1 backup feature creates snapshots by using the Redirect-on-Write (ROW) method. The snapshots are directly stored in the distributed storage system of the PolarDB cluster. The level-1 backup feature does not duplicate data. When a data block is modified, the system saves the original version of the data block to a snapshot and redirects the writes to a new data block. In this case, you can back up data within a few seconds regardless of the size of your database storage.
PolarDB clusters use multi-threaded parallel processing and other technical innovations to enhance data backup and restoration and can restore data from a backup set to a new cluster within 10 minutes.
NoteBy default, the level-1 backup feature is enabled, and you cannot disable this feature.
Level-1 backups can be retained for up to 30 days. If you want to use this feature, contact us for admission to the whitelist.
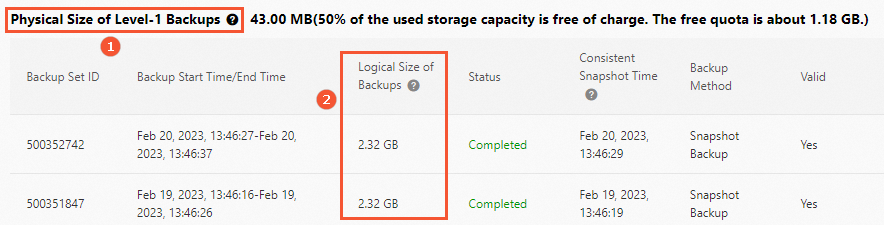
The physical size of level-1 backups is shown in the following figure.
 Note
NoteTotal Physical Size of Level-1 Backups (Snapshots) of a PolarDB cluster: the total physical storage space occupied by all level-1 backups (callout 1 in the figure). The data of a PolarDB cluster and multiple level-1 backups (snapshots) use the same physical data blocks. You are charged based on data blocks. For more information about data backup, see FAQ.
Level-2 backup
No
30 to 7,300 days
To permanently retain level-2 backups, enable the Permanently Retain Backups before Cluster Deletion feature.
The level-2 backup feature compresses and then stores level-1 backups in on-premises storage. Level-2 backup is slower compared with level-1 backup. However, level-2 backup is more cost-effective than level-1 backup.
If you enable this feature, expired level-1 backups are transferred to on-premises storage and stored as level-2 backups. The backups are transferred at a rate of approximately 150 MB/s.
You can implement level-2 backup across different zones in the same region or across different regions. For more information, see Intra-region and cross-region backups.
NoteIf a level-1 backup expires before the previous level-1 backup is transferred to a level-2 backup, the level-1 backup is deleted and is not transferred to a level-2 backup. For example, a PolarDB cluster creates a level-1 backup at 01:00 every day and retains the backup for 24 hours. If the PolarDB cluster creates Level-1 Backup A at 01:00 on January 1 and creates Level-1 Backup B at 01:00 on January 2. Level-1 Backup A expires at 01:00 on January 2 and starts to be transferred to a level-2 backup. However, Level-1 Backup A stores a large amount of data, and the transfer task is not complete by 01:00 on January 3. In this case, Level-1 Backup B is deleted after it expires at 01:00 on January 3 and is not transferred to a level-2 backup.
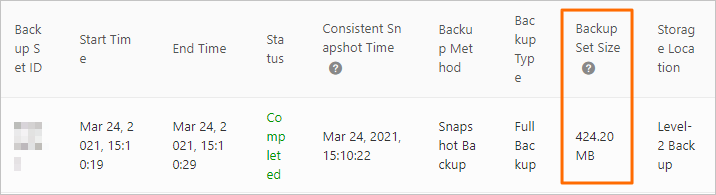
The following figure shows the total size of level-2 backups. The total size of level-2 backups is the sum of the data sizes of all level-2 backups.
Physical log backup
Benefits
The log backup feature allows you to create backups by uploading real-time redo logs to Object Storage Service (OSS) in parallel. The feature is enabled by default, and log backups are retained for 3 to 7,300 days. You can permanently save log backups by enabling the Permanently Retain Backups before Cluster Deletion feature.
NoteBy default, the log backup feature is enabled, and you cannot disable this feature.
Based on a full backup set and the log backups generated after the backup set is created, you can perform point-in-time recovery for a PolarDB cluster. This prevents data loss and ensures data security. If you perform PITR, you must consider the amount of time that is required to query redo logs, which is affected by the amount and workload of your business data. In most cases, redo logs are queried at a rate of 1 GB every 20 seconds to 180 seconds. The total restoration duration is the sum of the time required to restore backup sets and the time required to query redo logs.
View backup size
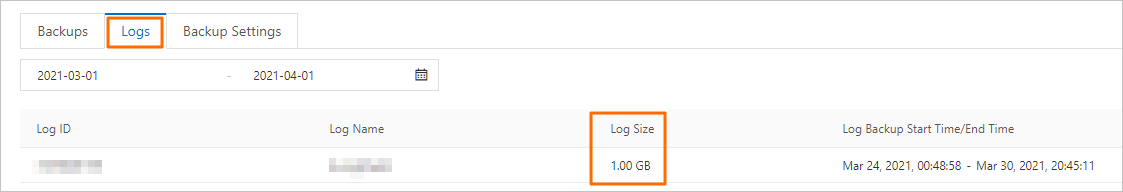
The following figure shows the total size of log backups.
Intra-region backup and cross-region backup
Differences
Backup type
Description
Enabled by default
Scenario
Benefits
Intra-region backup
Backup files are stored across different zones in the same region.
Yes
NoteBy default, this storage method is enabled when you enable level-2 backup.
Long-term archiving
Allows you to reduce costs by dumping data at a low backup frequency.
Cross-region backup feature
Backup files are stored across regions.
Disabled. You must manually enable cross-region backup.
Geo-redundancy and MLPS level 3
Allows you to reduce recovery point objective (RPO). This backup storage method is suitable for private network environments that are encrypted and highly secure. You can reduce costs by dumping data at a low backup frequency.
NoteLow-frequency level-2 backup: The backup frequency of level-2 backup is lower than that of level-1 backup.
Alibaba Cloud regions in which the cross-region backup feature is supported
Source region
Destination region
China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), and China (Hong Kong).
China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), and China (Hong Kong).
NoteCross-region backup files are replicated to a region that is different from the source region.
US (Virginia)
US (Silicon Valley)
Backup data protection
Tamper proofing:
Data backups of PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) are categorized into level-1 and level-2 backups based on the storage location. The level-1 backup feature creates snapshots that are directly stored in the distributed storage system of PolarDB. Level-2 backups and log backups are stored in OSS. Both storage methods used by the backup system supports the Write Once Read Many (WORM) feature, which prevents data tampering.
Malicious or accidental deletion prevention:
Manual deletion: You can delete only manual backups, not automatic backups.
Automatic deletion upon expiration: When automatic backup data exceeds the configured retention period, the system automatically deletes the data. However, the automatic backup feature cannot be disabled. The minimum retention period in backup policy settings is 3 days. The default retention period is 7 days. The minimum backup frequency is twice a week. Therefore, the backup data of automatic full backups and log backups cannot be completely deleted.
Pricing
You can use the backup and restoration feature free of charge. However, backup files consume storage space. For information about the billing rules for the backup storage space, see Billing rules for backup storage that exceeds the free quota.