PolarDB allows you to use Object Storage Service (OSS) foreign tables to directly query CSV-formatted data stored in OSS. This effectively reduces the storage costs. This topic describes how to use OSS foreign tables to access OSS data.
Prerequisites
Your PolarDB cluster meets one of the following requirements:
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is 8.0.1.1.25.4 or later.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is 8.0.2.2.1 or later.
For more information about how to check the cluster version, see Query the engine version.
How it works
You can use OSS foreign tables to store CSV-formatted cold data in an OSS bucket for query and analysis. Cold data refers to data that is infrequently accessed. The following figure shows the process.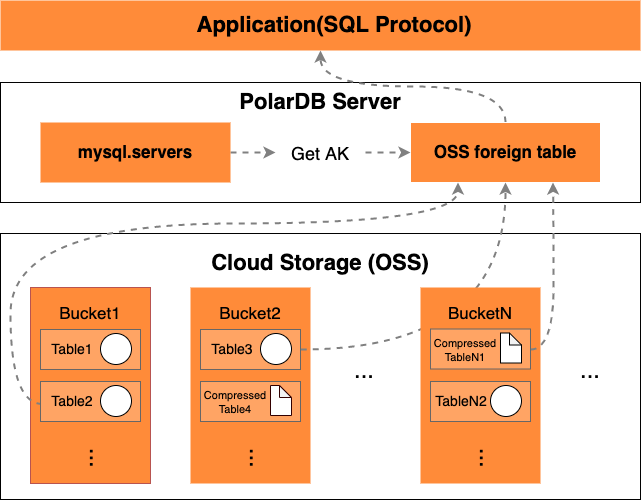
Limits
You can use OSS foreign tables to query only CSV-formatted data.
You can perform only the following operations on OSS foreign tables: CREATE, SELECT, and DROP.
NoteThe DROP operation deletes only the table information in PolarDB, without affecting the data files stored in OSS.
OSS foreign tables do not support indexing, partitioning, or transactions.
CSV-formatted data can contain numeric, date and time, and string values, as well as NULL values. The following tables describe the supported data types.
NoteGeospatial data types are not supported.
You cannot query compressed files in the CSV format.
NULL values are supported for clusters that meet one of the following requirements:
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is 8.0.1.1.28 or later.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is 8.0.2.2.5 or later.
Numeric types
Data type
Size
Data range (signed)
Data range (unsigned)
Description
TINYINT
1 Byte
-128~127
0~255
A small integer value
SMALLINT
2 Bytes
-32768~32767
0~65535
An integer value
MEDIUMINT
3 Bytes
-8388608~8388607
0~16777215
An integer value
INT or INTEGER
4 Bytes
-2147483648~2147483647
0~4294967295
An integer value
BIGINT
8 Bytes
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808~9223372036854775807
0~18446744073709551615
A big integer value
FLOAT
4 Bytes
-3.402823466 E+38~-1.175494351E-38; 0; 1.175494351E-38~3.402823466351E+38
0; 1.175494351E-38~3.402823466E+38
A single-precision floating-point value
DOUBLE
8 Bytes
-2.2250738585072014E-308~-1.7976931348623157E+308; 0; 1.7976931348623157E+308~2.2250738585072014E-308
0; 1.7976931348623157E+308~2.2250738585072014E-308
A double-precision floating-point value
DECIMAL
For DECIMAL(M,D), it is M+2 if M>D. Otherwise, it is D+2.
Depends on the values of M and D.
Depends on the values of M and D.
A decimal value
Date and time data types
Data type
Size
Data range
Format
Description
DATE
3 Bytes
1000-01-01~9999-12-31
YYYY-MM-DD
A date value
TIME
3 Bytes
-838:59:59~838:59:59
HH:MM:SS
A time value or duration
YEAR
1 Byte
1901~2155
YYYY
A year value
DATETIME
8 Bytes
1000-01-01 00:00:00~9999-12-31 23:59:59
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
A combined date and time value
NoteThe month and date of this type must have two digits. For example, January 1, 2020 must be written as 2020-01-01, instead of 2020-1-1. The query cannot be executed as expected if 2020-1-1 is pushed down to OSS.
TIMESTAMP
4 Bytes
1970-01-01 00:00:00~2038-01-19 03:14:07
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
A timestamp (combined date and time) value
NoteThe month and date of this type must have two digits. For example, January 1, 2020 must be written as 2020-01-01, instead of 2020-1-1. The query cannot be executed as expected if 2020-1-1 is pushed down to OSS.
String types
Data type
Size
Description
CHAR
0~255 Bytes
A fixed-length string
VARCHAR
0~65535 Bytes
A variable-length string
TINYBLOB
0~255 Bytes
A small binary large object up to 255 characters
TINYTEXT
0~255 Bytes
A short string
BLOB
0~65535 Bytes
A standard binary large object
TEXT
0~65535 Bytes
A standard string
MEDIUMBLOB
0~16777215 Bytes
A medium binary large object
MEDIUMTEXT
0~16777215 Bytes
A medium string
LONGBLOB
0~4294967295 Bytes
A long binary large object
LONGTEXT
0~4294967295 Bytes
A long string
NULL values
Insert a NULL value
Insert the NULL value into an OSS foreign table.
To insert the NULL value into an OSS foreign table, you must set
NULL_MARKERwhen you create the table. The default value ofNULL_MARKERis NULL for an OSS foreign table. You can execute theSHOW CREATE TABLEstatement to check the value of NULL_MARKER.SHOW CREATE TABLE t1;Sample result:
+-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t1 | CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=CSV DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci /*!99990 800020204 NULL_MARKER='NULL' */ CONNECTION='server_name' | +-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)Insert a NULL value into a CSV file.
If you insert a value of
NULL_MARKERfor a field in a CSV file without enclosing the value in double quotation marks ("), PolarDB identifies the value as NULL.NoteIf you enclose the value of
NULL_MARKERin double quotation marks ("), PolarDB identifies the value as a string. This means that theis_nullstatement cannot identify the value as NULL. If the data type of a field to which a NULL value is assigned in the CSV file does not match that of the corresponding field in the OSS foreign table, an error is reported.The
NULL_MARKERvalue cannot contain only digits or be left empty. In addition, it cannot contain the following four characters:",\n,\r, or,
Example
Execute the following statement to create an OSS foreign table:
CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=CSV NULL_MARKER='NULL' CONNECTION='server_name';In this example, the data file contains the following data:
1,"xiaohong","2022-01-01 00:00:00" NULL,"xiaoming","2022-02-01 00:00:00" 3,NULL,"2022-03-01 00:00:00" 4,"xiaowang",NULLThe following OSS data is obtained if you query the OSS foreign table:
SELECT * FROM t1; +------+----------+---------------------+ | id | name | time | +------+----------+---------------------+ | 1 | xiaohong | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 | | NULL | xiaoming | 2022-02-01 00:00:00 | | 3 | NULL | 2022-03-01 00:00:00 | | 4 | xiaowang | NULL | +------+----------+---------------------+
Read a NULL value
When data is read from a CSV file, if the value of a field in the CSV file is NULL and the corresponding value in the OSS foreign table can be set to NULL, the field is directly set to NULL.
When data is read from a CSV file, if the value of a field in the CSV file is NULL but the corresponding value in the OSS foreign table is set to NOT NULL, the data in the CSV file conflicts with the data specified in the OSS foreign table. In this case, different results are returned depending on the specified syntax verification rule.
If you set
sql_modetoSTRICT_TRANS_TABLES, an error is reported.If you set
sql_modeto a value other thanSTRICT_TRANS_TABLESand the current field has a default value, the value of the current field is set to the default value. If the current field does not have a default value, the current field is assigned to the default value of MySQL based on the field type. For more information, see Data Type Default Values. If a warning message appears, you can execute theSHOW WARNINGS;statement to view the details of the warning message.
NoteYou can execute the
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "sql_mode";statement to view the current syntax verification rule. You can log on to the PolarDB console and go to to modify the value ofsql_modeto change the syntax verification rules. For more information, see Modify parameters.Example
Create an OSS foreign table named
t, and then set theidfield to NOT NULL and no default value.CREATE TABLE `t` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=CSV CONNECTION="server_name";In this example, the
t.csvfile contains the following data:NULL 2When you use an OSS foreign table to read data from the CSV file, one of the following scenarios occurs:
If
sql_modeis set toSTRICT_TRANS_TABLESand when you execute the following statement to query the data in the CSV file:SELECT * FROM t;The following error message is reported:
ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'id' doesn't have a default valueIf
sql_modeis set to a value other thanSTRICT_TRANS_TABLESand when you execute the following statement to query the data in the CSV file:SELECT * FROM t;Sample result:
+----+ | id | +----+ | 0 | | 2 | +----+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)0 is the default value of MySQL. Execute the following statement to view the details of the warning message:
SHOW WARNINGS;Sample result:
+---------+------+-----------------------------------------+ | Level | Code | Message | +---------+------+-----------------------------------------+ | Warning | 1364 | Field 'id' doesn't have a default value | +---------+------+-----------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Parameters
Log on to the PolarDB console. Find the cluster on the Clusters page and go to the page to modify the parameters.
Parameter | Level | Description |
loose_csv_oss_buff_size | Session | The size of memory occupied by an OSS thread. Default value: 134217728. Unit: byte. Valid values: 4096 to 134217728. |
loose_csv_max_oss_threads | Global | The number of OSS threads that are allowed to run. Default value: 1. Valid values: 1 to 100. |
The maximum memory for OSS is loose_csv_max_oss_threads * loose_csv_oss_buff_size.
When OSS is used, we recommend that you limit the total memory usage of OSS to 5% of the memory capacity of the current node. Otherwise, an out-of-memory issue may occur.
Procedure
Create an OSS server
Create an OSS server to add OSS connection information and connect to OSS.
Other methods to connect to OSS have been disabled due to security risks. You can only create an OSS server to add OSS connection information and connect to OSS.
Statements for clusters of later versions
If your cluster meets the following requirements, the creation syntax in this section applies:
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is 8.0.1.1.28 or later.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is 8.0.2.2.5 or later.
CREATE SERVER <server_name>
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER oss OPTIONS
(
[DATABASE '<my_database_name>',]
EXTRA_SERVER_INFO '{"oss_endpoint": "<my_oss_endpoint>","oss_bucket": "<my_oss_bucket>","oss_access_key_id": "<my_oss_access_key_id>","oss_access_key_secret": "<my_oss_access_key_secret>","oss_prefix":"<my_oss_prefix>","oss_sts_token":"<my_oss_sts_token>"}'
);The
DATABASEparameter is optional. This parameter works the same as theoss_prefixparameter. We recommend that you useoss_prefix.The
oss_sts_tokenparameter is supported for clusters that meet the following requirements:A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is 8.0.1.1.29 or later.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is 8.0.2.2.6 or later.
The following table describes the parameters in the syntax.
Parameter | Data type | Required | Description |
server_name | STRING | Yes | The OSS server name. Note The name must be globally unique. The name can be up to 64 characters in length and is case-insensitive. A name that contains more than 64 characters is automatically truncated. You can specify the OSS server name as a quoted string. |
my_database_name | String | No | The OSS directory for the CSV file. Note If both |
my_oss_endpoint | STRING | Yes | The endpoint of the OSS server. Note If you access your database from an Alibaba Cloud server, use an internal endpoint to prevent incurring Internet traffic. An internal endpoint contains the keyword "internal". For example, the internal endpoint of an OSS node in the China (Hangzhou) region is |
my_oss_bucket | STRING | Yes | The bucket where the data files are stored. Before you import data, you must create OSS buckets. Note We recommend that you deploy the bucket in the same zone as the PolarDB cluster to reduce network latency. |
my_oss_access_key_id | STRING | Yes | The AccessKey ID of the RAM user or Alibaba Cloud account. |
my_oss_access_key_secret | STRING | Yes | The AccessKey Secret of the RAM user or Alibaba Cloud account. |
my_oss_prefix | String | No | The OSS directory for the CSV file. |
my_oss_sts_token | String | No | The temporary access credentials provided by Security Token Service (STS) Note
|
Statements for clusters of earlier versions
If your cluster meets the following requirements, the creation syntax in this section applies:
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is from 8.0.1.1.25.4 to 8.0.1.1.28.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is from 8.0.2.2.1 to 8.0.2.2.5.
CREATE SERVER <server_name>
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER oss OPTIONS
(
[DATABASE '<my_database_name>',]
EXTRA_SERVER_INFO '{"oss_endpoint": "<my_oss_endpoint>","oss_bucket": "<my_oss_bucket>","oss_access_key_id":"<my_oss_access_key_id>","oss_access_key_secret":"<my_oss_access_key_secret>"}'
); The oss_prefix and oss_sts_token parameters are not supported.
The following table describes the parameters in the syntax.
Parameter | Data type | Required | Components |
server_name | STRING | Yes | The OSS server name. Note The name must be globally unique. The name can be up to 64 characters in length and is case-insensitive. A name that contains more than 64 characters is automatically truncated. You can specify the OSS server name as a quoted string. |
my_database_name | String | No | The name of the OSS directory for the CSV file. |
my_oss_endpoint | STRING | Yes | The endpoint of the OSS server. Note If you access your database from an Alibaba Cloud server, use an internal endpoint to prevent incurring Internet traffic. An internal endpoint contains the keyword "internal". Example: |
my_oss_bucket | STRING | Yes | The bucket where the data files are stored. Before you import data, you must create OSS buckets. |
my_oss_access_key_id | STRING | Yes | The AccessKey ID of the RAM user or Alibaba Cloud account. |
my_oss_access_key_secret | STRING | Yes | The AccessKey Secret of the RAM user or Alibaba Cloud account. |
The SERVERS_ADMIN permissions are required when you create an OSS server. You can execute the SHOW GRANTS FOR username; statement to check whether the current user has the SERVERS_ADMIN permissions. A privileged account has the SERVERS_ADMIN permissions by default, and can grant the SERVERS_ADMIN permissions to standard accounts.
If you do not have the
SERVERS_ADMINpermissions, the error messageAccess denied; you need (at least one of) the SERVERS_ADMIN OR SUPER privilege(s) for this operationappears.If you use a standard account that does not have the
SERVERS_ADMINpermissions, you can use a privileged account to execute the following statement:GRANT SERVERS_ADMIN ON *.* TO `users`@`%` WITH GRANT OPTION.If you use a privileged account that does not have the
SERVERS_ADMINpermissions, you can reset the permissions of the account. To do so, find the cluster in the PolarDB console and click the cluster ID or name to go to the cluster details page. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the User Account tab, find the privileged account that you want to manage and click Reset Permissions in the Actions column. Wait until the permissions are reset. Then, the privileged account has theSERVERS_ADMINpermissions.If you are using a privileged account, you can execute the
SELECT Server_name, Extra_server_info FROM mysql.servers;statement to view the information of the OSS server that you create. The values of theoss_access_key_idandoss_access_key_secretparameters are encrypted for security reasons.
Upload data
You can use the ossutil tool to upload a local CSV file to a remote OSS bucket.
The OSS directory for CSV files must be the
DATABASEoross_prefixdirectory on the OSS server.The CSV file name must be
OSS foreign table name.CSVand the CSV extension must be in uppercase. For example, if the OSS foreign table name ist1, the CSV file name must bet1.CSV.The data fields in the CSV file must match the fields of the OSS foreign table. For example, if the OSS foreign table
t1has only the fieldidof theINTtype, the CSV file can have only one field of theINTtype.We recommend that you directly upload the local MySQL data file and create an OSS foreign table based on the table definitions.
Create an OSS foreign table
After you define an OSS server, you can create an OSS foreign table on PolarDB to connect to OSS. Example:
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (create_definition,...) engine=csv connection="<connection_string>";The value of connection_string consists of the following items that are separated by forward slashes (/):
The OSS server name.
Optional. The path of the data file in OSS.
NoteYou can configure the path of the data file in OSS if your cluster meets the following requirements:
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.1 whose revision version is 8.0.1.1.28 or later.
A cluster of MySQL 8.0.2 whose revision version is 8.0.2.2.5 or later.
(Optional) The data file name.
NoteThe data file name cannot contain the
.CSVextension.If you do not specify a data file name, the OSS file corresponding to the current table is
Name of the current table.CSV. If you specify a data file name, the OSS file corresponding to the current table isSpecified data file name.CSV.If you configure the path of the data file in OSS, you must specify the file name. Otherwise, the last segment of the path is considered as the file name when the system searches for the data file.
View an OSS foreign table
After an OSS foreign table is created, you can execute the show create table statement to view the OSS foreign table. Check whether the engine of the created table is CSV (ENGINE=CSV ). If not, the version of your PolarDB cluster is outdated and does not support OSS. For more information, see Prerequisites.
Example
CREATE TABLE t1 (id int) engine=csv connection="server_name/a/b/c/d/t1";In the preceding sampel code, connection_string consists of the following elements:
The OSS server Name:
server_name.The path of the data file in OSS:
oss_prefix/a/b/c/d/.The data file:
t1. The actual data file ist1.CSV. The.CSVsuffix is omitted based on parameter requirements.
You can use only the data file name to specify the data file corresponding to the OSS foreign table. For example, the following statement queries the t2.CSV file in the oss_prefix path of OSS.
CREATE TABLE t1 (id int) engine=csv connection="server_name/t2";Query data
The t1 table is used in the following examples.
# Query the number of data records in the t1 table.
SELECT count(*) FROM t1;
# Query records in a specified range.
SELECT id FROM t1 WHERE id < 10 AND id > 1;
# Query a specified record.
SELECT id FROM t1 where id = 3;
# Query records by joining multiple tables.
SELECT id FROM t1 left join t2 on t1.id = t2.id WHERE t2.name like "%er%";The following table describes common error messages and causes when you query data.
If no error message is reported but a warning message appears when you query data, you must execute the SHOW WARNINGS; statement to view the message.
Error message | Cause | Solution |
OSS error: No corresponding data file on the OSS engine. | The specified data file is not found in OSS. | Check whether the data file exists in the specified path in OSS based on the preceding rules.
|
There is not enough memory space for OSS transmission. Currently requested memory %d. | Insufficient memory for OSS queries. | You can use one of the following methods to fix this error:
|
ERROR 8054 (HY000): OSS error: error message : Couldn't connect to server. Failed connect to aliyun-mysql-oss.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com:80; | The current cluster cannot connect to the OSS server. | Check whether the current cluster is in the same zone as the OSS bucket.
|
Query optimization
During the query process, the query engine can push queries with specific conditions down to a remote OSS bucket to enhance query efficiency. This optimization is called engine condition pushdown. The engine condition pushdown feature is subject to the following limits:
Only UTF-8 encoded CSV files are supported.
Only the following types of operators are supported in SQL statements:
Comparison operators:
>,<,>=,<=, and==Logical operators:
LIKE,IN,AND, andORArithmetic operators:
+,-,*, and/
Only a single file can be queried when you use an SQL statement. The following clauses are not supported: JOIN, ORDER BY, GROUP BY, and HAVING.
The WHERE clause cannot contain aggregation conditions. For example,
WHERE max(age) > 100is not allowed.A maximum of 1,000 columns can be specified for an SQL statement. The column name in an SQL statement can be a maximum of 1,024 bytes in length.
A maximum of five wildcards (
%) are supported in a LIKE clause.A maximum of 1,024 constants are supported in an IN clause.
The maximum column size and row size for a CSV object are 256 KB.
The maximum size of an SQL statement is 16 KB. A maximum of 20 expressions can be added after a WHERE clause. Each statement supports up to 100 aggregation operations.
By default, the engine condition pushdown feature is disabled. To enable this feature, execute the SET SESSION optimizer_switch='engine_condition_pushdown=on'; statement.
Queries that meet the preceding conditions are pushed down to a remote OSS bucket. You can use the execution plan of an OSS foreign table to view the queries that are pushed down to a remote OSS bucket.
View the execution plan of an OSS foreign table by executing the
EXPLAINstatement. Example:EXPLAIN SELECT count(*) FROM `t1` WHERE `id` > 5 AND `id` < 100 AND `name` LIKE "%1%%%%%" GROUP BY `id` ORDER BY `id` DESC; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 15000 | 1.23 | Using where; With pushed engine condition ((`test`.`t1`.`id` > 5) and (`test`.`t1`.`id` < 100)); Using temporary; Using filesort | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Queries with the conditions after
With pushed engine conditioncan be pushed down to a remote OSS bucket. Queries with the conditions`name` LIKE "%1%%%%%"andGROUP BY `id` ORDER BY `id` DESCcan be performed only on the local OSS server.View the execution plan of an OSS foreign table in the
treeformat. Example:EXPLAIN FORMAT=tree SELECT SELECT count(*) FROM `t1` WHERE `id` > 5 AND `id` < 100 AND `name` LIKE "%1%%%%%" Y `id` ORDER BY `id` DESC; +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | EXPLAIN | +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | -> Sort: <temporary>.id DESC -> Table scan on <temporary> -> Aggregate using temporary table -> Filter: (t1.`name` like '%1%%%%%') (cost=1690.00 rows=185) -> Table scan on t1, extra ( engine conditions: ((t1.id > 5) and (t1.id < 100)) ) (cost=1690.00 rows=15000) | +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)Queries with the conditions after
engine conditions:can be pushed down to a remote OSS bucket. Queries with the conditions`name` LIKE "%1%%%%%"andGROUP BY `id` ORDER BY `id` DESCcan be performed only on the local OSS server.NoteYou must use a PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2 cluster to query data. You can query the version number to check the cluster version.
View the execution plan of an OSS foreign table in the
JSONformat. Example:EXPLAIN FORMAT=json SELECT count(*) FROM `t1` WHERE `id` > 5 AND `id` < 100 AND `name` LIKE "%1%%%%%" GROUP BY `id` ORDER BY `id` DESC; +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | EXPLAIN | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | { "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "cost_info": { "query_cost": "1875.13" }, "ordering_operation": { "using_filesort": false, "grouping_operation": { "using_temporary_table": true, "using_filesort": true, "cost_info": { "sort_cost": "185.13" }, "table": { "table_name": "t1", "access_type": "ALL", "rows_examined_per_scan": 15000, "rows_produced_per_join": 185, "filtered": "1.23", "engine_condition": "((`test`.`t1`.`id` > 5) and (`test`.`t1`.`id` < 100))", "cost_info": { "read_cost": "1671.49", "eval_cost": "18.51", "prefix_cost": "1690.00", "data_read_per_join": "146K" }, "used_columns": [ "id", "name" ], "attached_condition": "(`test`.`t1`.`name` like '%1%%%%%')" } } } } } | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Queries with the conditions after
engine conditions:can be pushed down to a remote OSS bucket. Queries with the conditions`name` LIKE "%1%%%%%"andGROUP BY `id` ORDER BY `id` DESCcan be performed only on the local OSS server.
If the following error occurs, some characters in the current OSS data file do not meet the requirements for engine condition pushdown.
OSS error: The current query does not support engine condition pushdown. You need to use NO_ECP() hint or set optimizer_switch = 'engine_condition_pushdown=OFF' to turn off the condition push down function.You can use hints or the optimizer_switch variable to manually disable the engine condition pushdown feature.
hints
Use a hint to disable the engine condition pushdown feature for a query. In the following example, the engine condition pushdown feature is disabled for the
t1table:SELECT /*+ NO_ECP(t1) */ `j` FROM `t1` WHERE `j` LIKE "%c%" LIMIT 10;optimizer_switch
Use the optimizer_switch variable to disable the engine condition pushdown feature for all queries in the current session.
SET SESSION optimizer_switch='engine_condition_pushdown=off'; # Set the engine_condition_pushdown parameter to off. In this case, the engine condition pushdown feature is disabled for all queries in the current session.You can execute the following statement to determine whether the engine condition pushdown feature is enabled for all queries in the current session based on the value of the optimizer_switch variable:
select @@optimizer_switch;
Synchronize OSS server information between multiple nodes
The primary and read-only nodes of a PolarDB cluster share the same OSS server. This ensures that these nodes can access OSS data. The synchronization of OSS server information between these nodes is lock-free to ensure that operations on these nodes are independent.
After you modify the OSS server information, the modifications are synchronized to read-only nodes in a lock-free manner. If a thread on a read-only node holds the lock for the OSS server, the synchronization of OSS server information may be delayed. In this case, you can execute the /*force_node='pi-bpxxxxxxxx'*/ flush privileges; or /*force_node='pi-bpxxxxxxxx'*/flush table oss_foreign_table; statement to manually update the OSS server information of read-only nodes.