To optimize the performance of PolarDB for MySQL, PolarDB offers the thread pool feature. This feature decouples threads from sessions. Instead of assigning one thread per session, the feature uses a pool of threads to execute tasks across active sessions.
Benefits
By default, MySQL uses a session exclusive mode for threads, where each session creates an exclusive thread. When many sessions exist, significant resource competition occurs and degrades performance. A high volume of thread scheduling and cache invalidation also causes a sharp drop in performance.
The PolarDB thread pool implements a priority and concurrency control mechanism for different types of SQL operations and keeps the number of connections close to the optimal number. This allows the PolarDB database to maintain high performance under high-connection and high-concurrency conditions. The benefits of the thread pool are as follows:
When many threads run concurrently, the thread pool automatically adjusts the number of concurrent threads to an optimal range. This helps avoid excessive thread scheduling and frequent cache invalidation.
When many transactions run concurrently, the thread pool assigns different priorities to statements and transactions. It separately controls the concurrency of statements and transactions to reduce resource competition.
The thread pool assigns a higher priority to administration-related SQL statements to ensure these statements are executed first. This ensures that operations such as creating new connections, management, and monitoring can run stably even when the system load is high.
The thread pool assigns a relatively lower priority to complex SQL statements and limits their maximum concurrency. This prevents too many complex SQL statements from exhausting system resources and making the entire database service unavailable.
Use the thread pool
The thread pool feature involves the following parameters. You can modify them in the console as needed. For more information, see Set cluster and node parameters.
Cluster parameters in the PolarDB console use the loose_ prefix to ensure compatibility with MySQL configuration files. To modify these parameters in the PolarDB console, select the parameter with the loose_ prefix.
Parameter | Description |
loose_thread_pool_enabled | Specifies whether to enable the thread pool feature. Valid values:
Note
|
loose_thread_pool_size | The number of thread groups in the thread pool. The value range is related to the number of CPU cores of the primary node in the cluster. Value range: DBNodeClassCPU to DBNodeClassCPU × 10. Default value: DBNodeClassCPU × 2. Note
Examples:
|
loose_thread_pool_high_prio_mode | The mode for the high-priority queue of the thread pool. Valid values:
Note Scope:
|
loose_thread_pool_high_prio_tickets | The number of tickets for the high-priority queue. Value range: 0 to 4294967295. Default value: 4294967295. Note Scope:
|
loose_thread_pool_idle_timeout | The time threshold for releasing idle threads in the thread pool. An idle thread that has not served any requests is released after this time. Value range: 0 to 31536000. Default value: 60. Unit: seconds. Note Applies to:
|
loose_thread_pool_oversubscribe | The number of active threads allowed in each thread group. An active thread is a thread that is executing an SQL statement, but does not include threads in the following two situations:
Value range: 1 to 1000. Default value: 20. |
loose_thread_pool_stall_limit | The time threshold to determine that the thread pool is stalled. When the thread pool is stalled, the system creates a new thread to serve SQL statements. Value range: 1 to 18446744073709551615. Default value: 10. Unit: milliseconds. Note For MySQL 5.6, the default value is 30 milliseconds. |
loose_bypass_thread_pool_ips | Specifies the client IP addresses that are not restricted by the thread pool. Even when the thread pool is full, clients with these IP addresses can execute SQL statements for management operations. Example: Note Applicable versions: MySQL 8.0.1 with a revision version of 8.0.1.1.19 or later. |
loose_bypass_thread_pool_check_ignore_proxy | Specifies whether to ignore client IP addresses that connect through a proxy when checking the
Note Applicable versions: MySQL 8.0.1 with a revision version of 8.0.1.1.19 or later. |
loose_thread_pool_high_priority_users | Specifies the high-priority database accounts. After configuration, requests from these accounts are placed in the high-priority queue of the thread pool and processed first. Example: Note
|
loose_thread_pool_mark_ddl_thread_timeout_sec | Specifies the timeout threshold for DDL threads in the thread pool. After this time, the DDL thread is marked as timed out, and the system creates a new thread to process the request. Value range: 0 to 864000. Default value: 600. Unit: seconds. Note Applicable versions: MySQL 8.0.1 with a revision version of 8.0.1.1.19 or later. |
loose_thread_pool_mark_ddl_thread_timeout_immediately | Specifies whether to immediately mark a DDL thread as timed out when the thread pool is under high load and the lower-priority queue is stacked. If a DDL thread is marked as timed out, the system creates a new thread to process the request. This parameter is suitable for business scenarios that require frequent batch DDL operations. Valid values:
Note Applicable versions: MySQL 8.0.1 with a revision version of 8.0.1.1.19 or later. |
Query the thread pool status
You can execute the following command to query the thread pool status:
select * from information_schema.THREAD_POOL_STATUS;The following sample output is returned.
mysql> select * from information_schema.THREAD_POOL_STATUS;
+----+--------------+---------------------+----------------------+-------------------+---------------------------+------------------+-----------------+------------------+
| ID | THREAD_COUNT | ACTIVE_THREAD_COUNT | WAITING_THREAD_COUNT | DUMP_THREAD_COUNT | SLOW_THREAD_TIMEOUT_COUNT | CONNECTION_COUNT | LOW_QUEUE_COUNT | HIGH_QUEUE_COUNT |
+----+--------------+---------------------+----------------------+-------------------+---------------------------+------------------+-----------------+------------------+
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 19 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 21 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 22 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 23 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 27 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 29 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 31 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 32 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 33 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 34 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 35 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 36 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 38 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 39 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 41 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 42 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 43 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 44 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 45 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 46 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 47 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 48 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 49 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 51 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 52 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 53 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 54 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 55 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 56 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 57 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 58 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 59 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 61 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 62 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 63 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
+----+--------------+---------------------+----------------------+-------------------+---------------------------+------------------+-----------------+------------------+
64 rows in set (0.00 sec)The parameters are described as follows.
Parameter | Description |
ID | The ID of the thread group. |
THREAD_COUNT | The number of threads in the thread group. |
ACTIVE_THREAD_COUNT | The number of active threads in the thread group. |
WAITING_THREAD_COUNT | The number of threads in the thread group that are waiting for disk I/O or transaction commits. |
DUMP_THREAD_COUNT | The number of persistent connections of the DUMP class in the thread group. |
SLOW_THREAD_TIMEOUT_COUNT | The number of threads in the thread group that are marked as timed out. |
CONNECTION_COUNT | The number of user connections established in the thread group. |
LOW_QUEUE_COUNT | The number of requests waiting in the lower-priority queue of the thread group. |
HIGH_QUEUE_COUNT | The number of requests waiting in the high-priority queue of the thread group. |
Sysbench tests
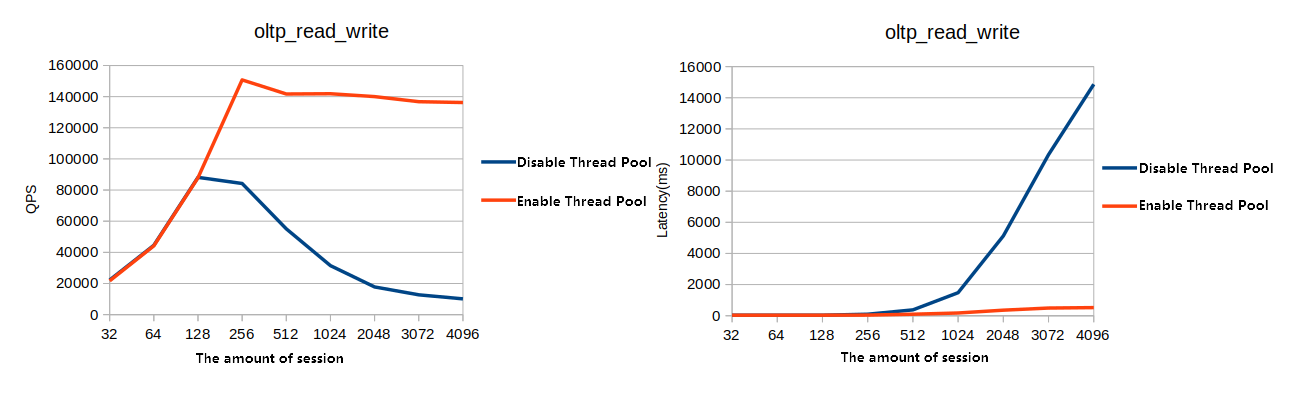
This section compares the database performance with the thread pool feature enabled and disabled. Test results indicate that the database provides significantly higher performance under high concurrency conditions when the thread pool feature is enabled.
Figure 1. Online transactional processing (OLTP) update test on tables without an index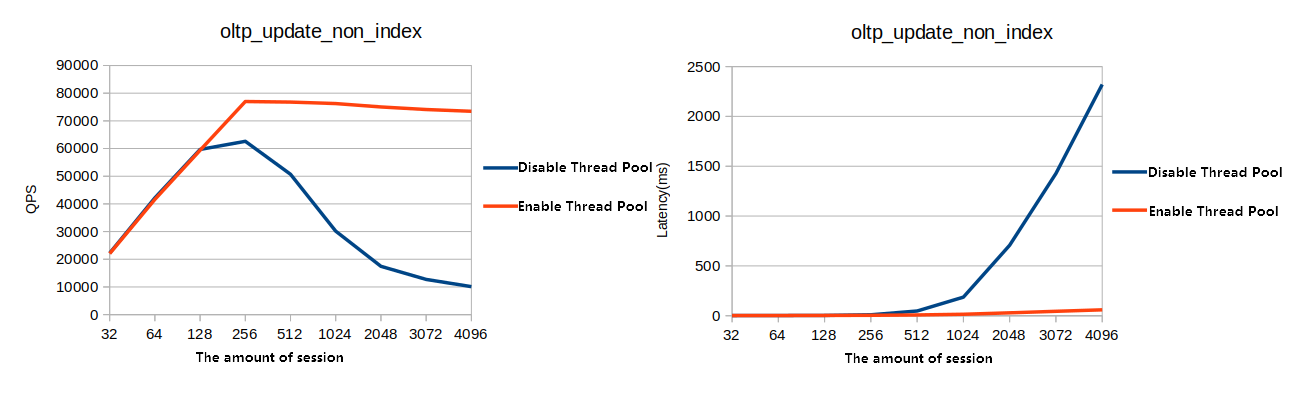
Figure 2. OLTP write-only test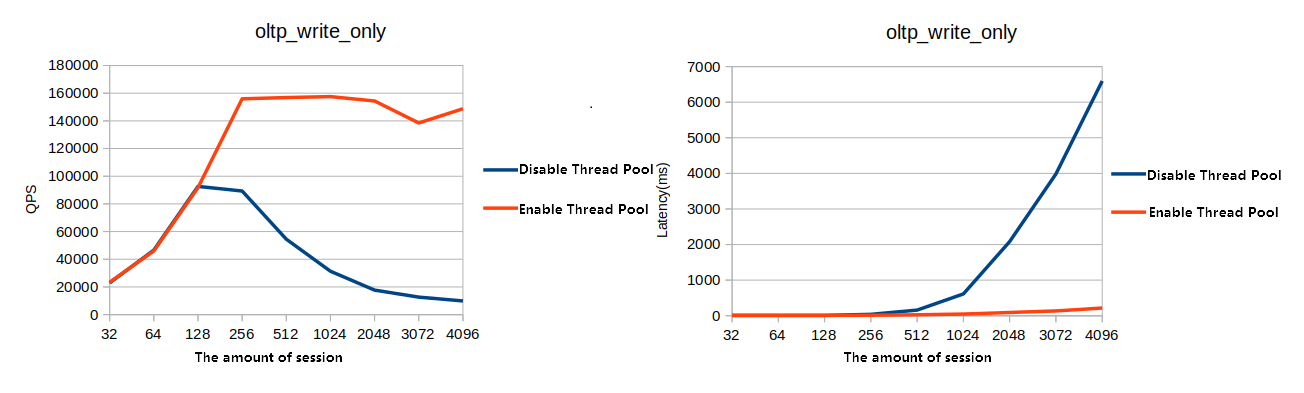
Figure 3. OLTP read-only test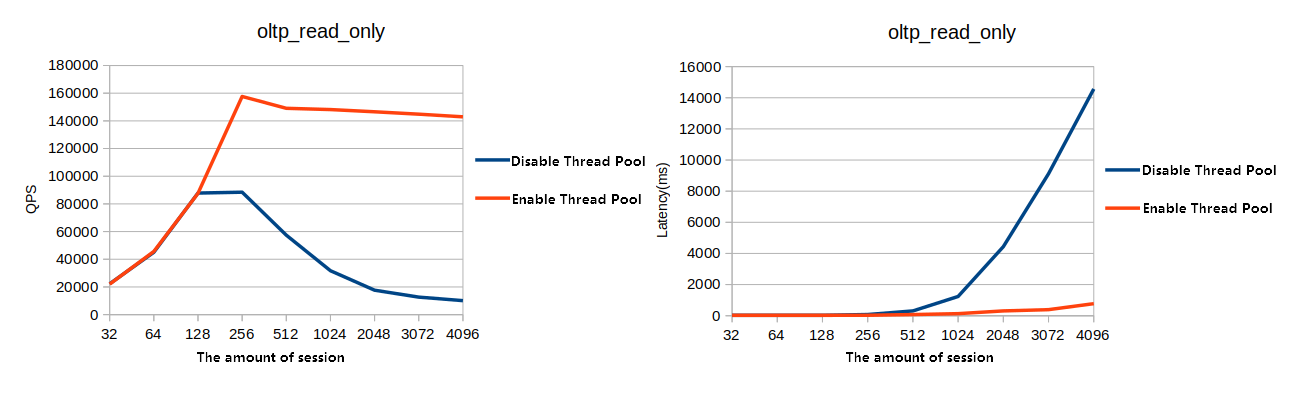
Figure 4. OLTP read/write test