PolarDB for MySQL uses the Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) technology to optimize log shipment and provides the RDMA-based log shipment solution. This solution uses RDMA as a replacement for the traditional shipment methods based on shared storage or TCP, which can improve the log shipment throughput by 100% and reduce the replication latency by more than 50%. This topic describes how RDMA-based log shipment works, how to enable this feature, and how it performs in standard scenarios.
How RDMA-based log shipment works
By default, PolarDB synchronizes logs by using methods based on shared storage or TCP. To accelerate log synchronization and reduce overhead, PolarDB introduces the RDMA-based log shipment technology. This is how RDMA-based log shipment works:
The redo log buffer of a read-only node is considered the remote image of the redo log buffer of a primary node.
Before the log buffer is written to the disk, the primary node asynchronously writes the redo log to the log buffer of the remote read-only node, and then synchronizes the offset to the read-only node.
The read-only node reads the local log buffer instead of the redo log in the shared storage, which speeds up replication and synchronization.
Compared with the two-sided operation of the traditional methods, the one-sided operation of RDMA-based log shipment uses READ/WRITE verbs and does not involve the receiver CPU. Logs are written to the memory of the remote read-only node by using the remote address and key.
Limits
The cluster is of PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.1 and the revision version is 8.0.1.1.33 or later.
You cannot enable the RDMA-based log shipment feature for a secondary cluster in a global database network (GDN).
Usage
You can configure the loose_innodb_polar_log_rdma_transfer parameter to enable RDMA-based log shipment.
Parameter | Level | Description |
loose_innodb_polar_log_rdma_transfer | Global | Specifies whether to enable the RDMA-based log shipment feature. Valid values:
|
Performance test
Reduces replication latency
In various write scenarios, RDMA-based log shipment can greatly reduce the replication latency of read-only nodes.
The following example describes the replication latency test of a PolarDB for MySQL 8.0 cluster with 32 CPU cores and 128 GB of memory. The test uses 20 tables, each of which contains 2 million rows of data. The test compares the replication latency of the read-only node when RDMA-based log shipment is enabled or disabled and at different redo write rates.
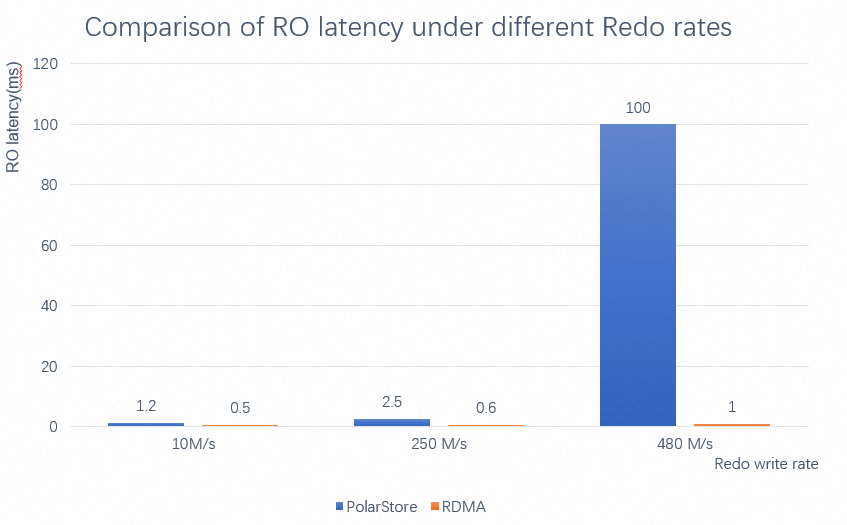
As shown in the preceding figure, when RDMA-based log shipment is enabled, the replication latency of the read-only node is greatly reduced as the redo write rate increases.
Improves the SCC performance of PolarDB
When global consistency (high-performance mode) is enabled, the replication latency of the read-only node significantly affects the performance of PolarDB for MySQL. RDMA-based log shipment can effectively improve the Strict Consistency Cluster (SCC) performance.
The following example describes the SCC performance test of a PolarDB for MySQL 8.0 cluster with 8 CPU cores and 32 GB of memory. The test uses 20 tables, each of which contains 2 million rows of data. The test compares the SCC performance of the read-only node when RDMA-based log shipment is enabled or disabled and with different numbers of threads.
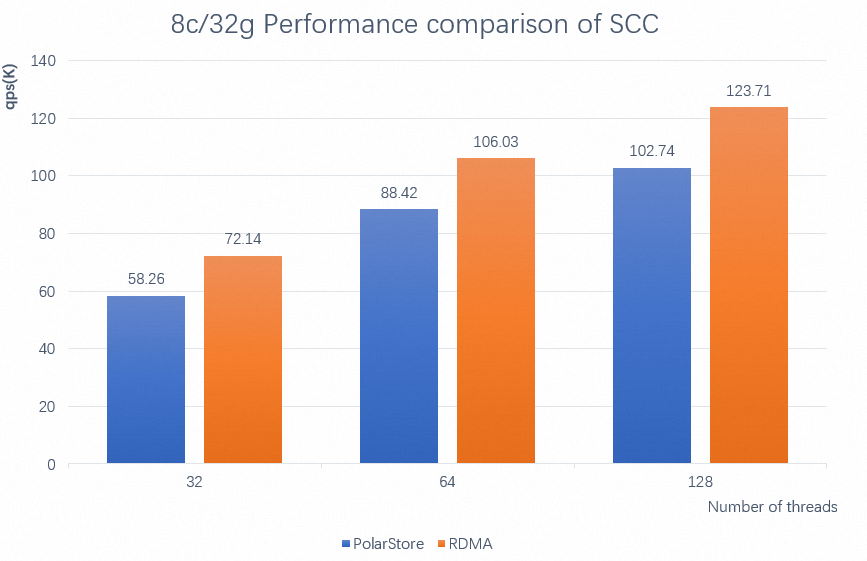
As shown in the preceding figure, when RDMA-based log shipment is enabled, the SCC performance of the read-only node is improved by about 20%.