Standardization is a data preprocessing technique that converts feature data to a unified dimension. The Standardization component unifies the dimensions of different features by setting the mean to 0 and the standard deviation to 1. Standardization can enhance the convergence and performance of the models, especially models that use the gradient descent optimization algorithm.
Algorithm description
You can standardize one or more columns in a table and save the generated data to a new table.
The following formula is used for standardization: (X - Mean)/(Standard deviation).
Mean: the mean of samples.
Standard deviation: the standard deviation of samples. The standard deviation is used when samples are used to calculate the total deviation. To make the value obtained after standardization closer to the mean, you must moderately increase the calculated standard deviation by using the formula
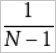 .
.The formula used to calculate the standard deviation of samples is
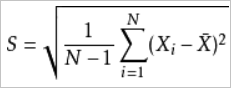 .
.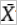 represents the mean of samples X1, X2, ..., and Xn.
represents the mean of samples X1, X2, ..., and Xn.
Configure the component
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
Add the Standardization component on the pipeline page of Machine Learning Designer and configure the component parameters described in the following table on the right side of the page.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | All Selected by Default | Default select all. Extra columns do not affect the prediction results. |
Reserve Original Columns | Processed columns are prefixed with "stdized_". Supports DOUBLE and BIGINT types. | |
Input Sparse Matrix | Specifies whether to support the input data in the sparse format. If you enable this feature, configure the following parameters:
| |
Tuning | Cores | The number of cores. The system automatically allocates cores used for training based on the volume of input data. |
Memory Size per Core | The memory size of each core. The system automatically allocates the memory based on the volume of input data. Unit: MB. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
Configure the Standardization component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see Scenario 4: Execute PAI commands within the SQL script component.
Command for dense data
PAI -name Standardize -project algo_public -DkeepOriginal="false" -DoutputTableName="test_5" -DinputTablePartitions="pt=20150501" -DinputTableName="bank_data_partition" -DselectedColNames="euribor3m,pdays"Command for sparse data
PAI -name Standardize -project projectxlib4 -DkeepOriginal="true" -DoutputTableName="kv_standard_output" -DinputTableName=kv_standard_test -DselectedColNames="f0,f1,f2" -DenableSparse=true -DoutputParaTableName=kv_standard_model -DkvIndices=1,2,8,6 -DitemDelimiter=",";
Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
inputTableName | Yes | None | The name of the input table. |
selectedColNames | No | All columns | The columns that are selected from the input table for training. The column names must be separated by commas (,). Columns of the INT and DOUBLE types are supported. If the input data is in the sparse format, columns of the STRING type are supported. |
inputTablePartitions | No | All partitions | The partitions that are selected from the input table for training. The following formats are supported:
Note If you specify multiple partitions, separate them with commas (,). |
outputTableName | Yes | None | The name of the output table. |
outputParaTableName | Yes | None | The name of the output parameter table. |
inputParaTableName | No | None | The name of the input parameter table. |
keepOriginal | No | false | Specifies whether to reserve original columns. Valid values:
|
lifecycle | No | None | The lifecycle of the output table. |
coreNum | No | Automatically assigned by the system | The number of cores. |
memSizePerCore | No | Automatically assigned by the system | The memory size of each core. |
enableSparse | No | false | Specifies whether to support the input data in the sparse format. Valid values:
|
itemDelimiter | No | "," | The delimiter used between key-value pairs. |
kvDelimiter | No | ":" | The delimiter used between keys and values. |
kvIndices | No | None | The feature indexes that require standardization in the table that contains data in the key-value format. |
Examples
Generate input data
drop table if exists standardize_test_input; create table standardize_test_input( col_string string, col_bigint bigint, col_double double, col_boolean boolean, col_datetime datetime); insert overwrite table standardize_test_input select * from ( select '01' as col_string, 10 as col_bigint, 10.1 as col_double, True as col_boolean, cast('2016-07-01 10:00:00' as datetime) as col_datetime union all select cast(null as string) as col_string, 11 as col_bigint, 10.2 as col_double, False as col_boolean, cast('2016-07-02 10:00:00' as datetime) as col_datetime union all select '02' as col_string, cast(null as bigint) as col_bigint, 10.3 as col_double, True as col_boolean, cast('2016-07-03 10:00:00' as datetime) as col_datetime union all select '03' as col_string, 12 as col_bigint, cast(null as double) as col_double, False as col_boolean, cast('2016-07-04 10:00:00' as datetime) as col_datetime union all select '04' as col_string, 13 as col_bigint, 10.4 as col_double, cast(null as boolean) as col_boolean, cast('2016-07-05 10:00:00' as datetime) as col_datetime union all select '05' as col_string, 14 as col_bigint, 10.5 as col_double, True as col_boolean, cast(null as datetime) as col_datetime ) tmp;
Run PAI commands
drop table if exists standardize_test_input_output; drop table if exists standardize_test_input_model_output; PAI -name Standardize -project algo_public -DoutputParaTableName="standardize_test_input_model_output" -Dlifecycle="28" -DoutputTableName="standardize_test_input_output" -DinputTableName="standardize_test_input" -DselectedColNames="col_double,col_bigint" -DkeepOriginal="true"; drop table if exists standardize_test_input_output_using_model; drop table if exists standardize_test_input_output_using_model_model_output; PAI -name Standardize -project algo_public -DoutputParaTableName="standardize_test_input_output_using_model_model_output" -DinputParaTableName="standardize_test_input_model_output" -Dlifecycle="28" -DoutputTableName="standardize_test_input_output_using_model" -DinputTableName="standardize_test_input";Input
standardize_test_input
col_string
col_bigint
col_double
col_boolean
col_datetime
01
10
10.1
true
2016-07-01 10:00:00
NULL
11
10.2
false
2016-07-02 10:00:00
02
NULL
10.3
true
2016-07-03 10:00:00
03
12
NULL
false
2016-07-04 10:00:00
04
13
10.4
NULL
2016-07-05 10:00:00
05
14
10.5
true
NULL
Output
standardize_test_input_output
col_string
col_bigint
col_double
col_boolean
col_datetime
stdized_col_bigint
stdized_col_double
01
10
10.1
true
2016-07-01 10:00:00
-1.2649110640673518
-1.2649110640683832
NULL
11
10.2
false
2016-07-02 10:00:00
-0.6324555320336759
-0.6324555320341972
02
NULL
10.3
true
2016-07-03 10:00:00
NULL
0.0
03
12
NULL
false
2016-07-04 10:00:00
0.0
NULL
04
13
10.4
NULL
2016-07-05 10:00:00
0.6324555320336759
0.6324555320341859
05
14
10.5
true
NULL
1.2649110640673518
1.2649110640683718
standardize_test_input_model_output
feature
json
col_bigint
{“name”: “standardize”, “type”:”bigint”, “paras”:{“mean”:12, “std”: 1.58113883008419}}
col_double
{“name”: “standardize”, “type”:”double”, “paras”:{“mean”:10.3, “std”: 0.1581138830082909}}
standardize_test_input_output_using_model
col_string
col_bigint
col_double
col_boolean
col_datetime
01
-1.2649110640673515
-1.264911064068383
true
2016-07-01 10:00:00
NULL
-0.6324555320336758
-0.6324555320341971
false
2016-07-02 10:00:00
02
NULL
0.0
true
2016-07-03 10:00:00
03
0.0
NULL
false
2016-07-04 10:00:00
04
0.6324555320336758
0.6324555320341858
NULL
2016-07-05 10:00:00
05
1.2649110640673515
1.2649110640683716
true
NULL
standardize_test_input_output_using_model_model_output
feature
json
col_bigint
{“name”: “standardize”, “type”:”bigint”, “paras”:{“mean”:12, “std”: 1.58113883008419}}
col_double
{“name”: “standardize”, “type”:”double”, “paras”:{“mean”:10.3, “std”: 0.1581138830082909}}