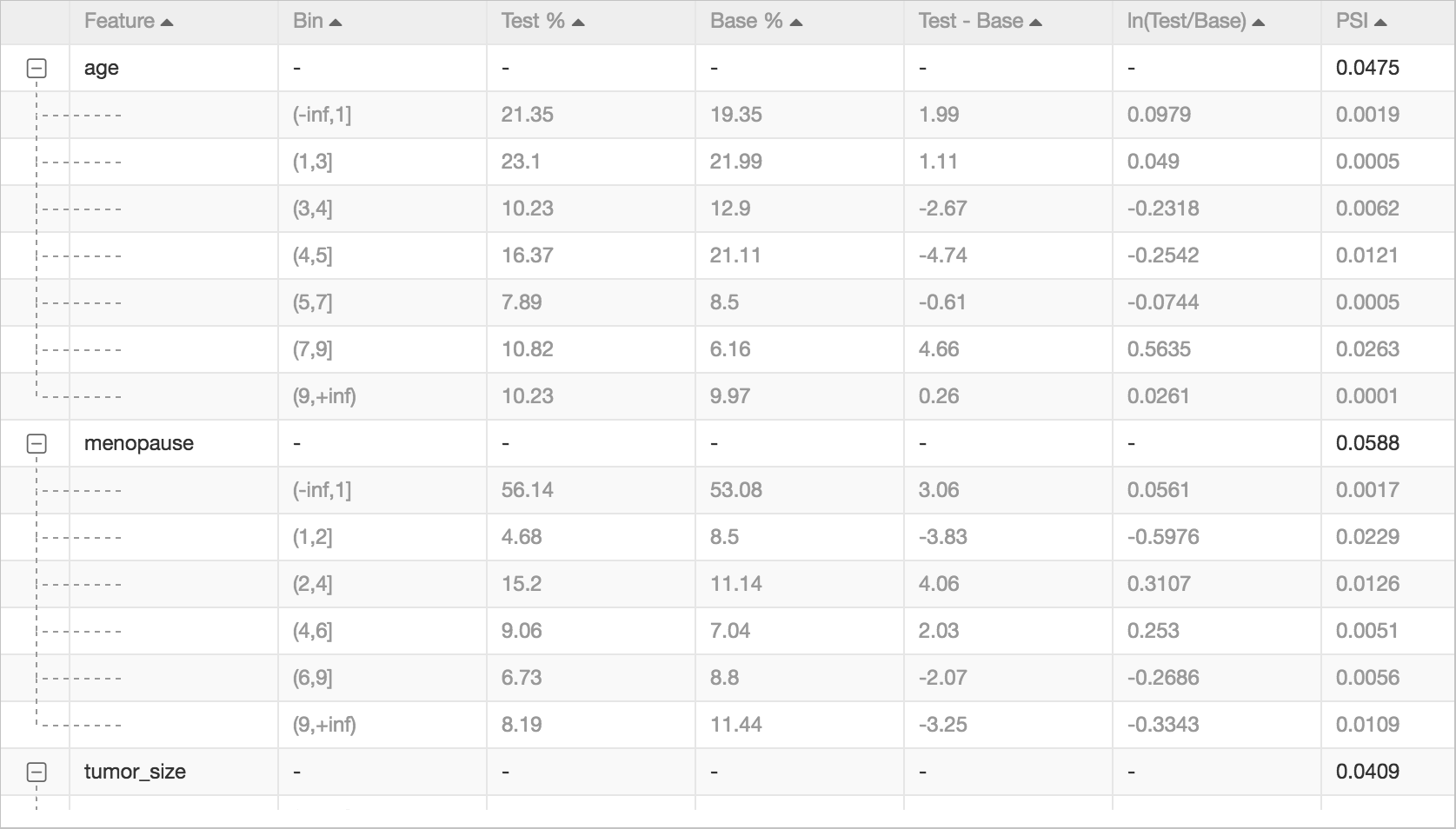
The Population Stability Index (PSI) is a statistical metric used to assess the degree of difference between two sample distributions. It is commonly utilized to monitor a model's performance stability across different times or environments. By measuring the distribution differences between two samples, PSI can help identify potential data shifts or drifts, thus providing a basis for model maintenance and updating.
Background information
PSI is a common metric that is used to measure the stability of samples. For example, you can use it to measure whether the changes in the population within two months are stable. A PSI value less than 0.1 indicates insignificant changes. A PSI value from 0.1 to 0.25 indicates minor changes. A PSI value greater than 0.25 indicates major changes.
If the changes in a population over time are unstable, you can use charts to identify the changes. You can perform binning for variables, calculate the number and proportion of the samples in each bin, and then present the statistics in a column chart. The following figure shows a sample chart. 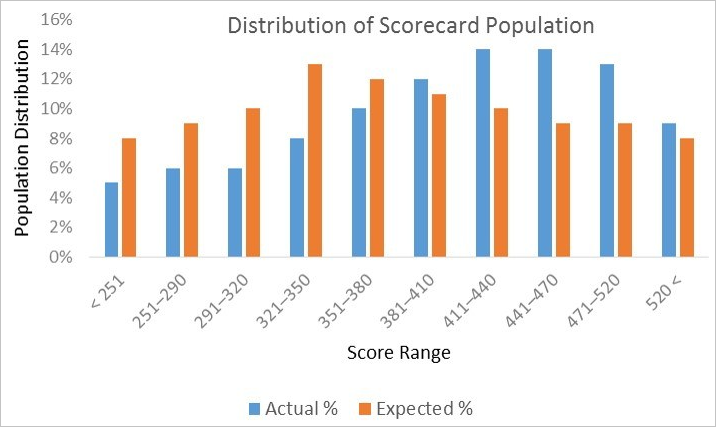 The preceding method can directly show whether a variable in two samples changes significantly. However, the shift in these changes cannot be measured by using this method. Therefore, the population stability cannot be automatically monitored. To resolve this issue, you can use the Population Stability Index component. The following figure shows the formula that is used to calculate PSI values.
The preceding method can directly show whether a variable in two samples changes significantly. However, the shift in these changes cannot be measured by using this method. Therefore, the population stability cannot be automatically monitored. To resolve this issue, you can use the Population Stability Index component. The following figure shows the formula that is used to calculate PSI values. 
Configure the component
You can use one of the following methods to configure the Population Stability Index component.
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
You can configure the parameters of the Population Stability Index component on the pipeline page of Machine Learning Designer of Machine Learning Platform for AI (PAI). Machine Learning Designer is formerly known as Machine Learning Studio. The following table describes the parameters.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Features for PSI Calculation | The feature columns that are required for PSI value calculation. |
Tuning | Cores | The number of CPU cores that are required. By default, the system determines the value. |
Memory Size | The memory size of each CPU core. By default, the system determines the value. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
Configure the component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see SQL Script.
PAI -name psi
-project algo_public
-DinputBaseTableName=psi_base_table
-DinputTestTableName=psi_test_table
-DoutputTableName=psi_bin_table
-DinputBinTableName=pai_index_table
-DfeatureColNames=fea1,fea2,fea3
-Dlifecycle=7Parameter | Description | Required | Default value |
inputBaseTableName | The name of the base table. The shift of the population is calculated based on the samples in the base and test tables. | Yes | No default value |
inputBaseTablePartitions | The partitions that are selected from the base table. | No | Full table |
inputTestTableName | The name of the test table. The shift of the population is calculated based on the samples in the base and test tables. | Yes | No default value |
inputTestTablePartitions | The partitions that are selected from the test table. | No | Full table |
inputBinTableName | The name of the binning result table. | Yes | No default value |
featureColNames | The feature columns that are required for PSI value calculation. | No | Full table |
outputTableName | The name of the output table. | Yes | No default value |
lifecycle | The lifecycle of the output table. | No | No default value |
coreNum | The number of CPU cores that are required. | No | Determined by the system |
memSizePerCore | The memory size of each CPU core. Unit: MB. | No | Determined by the system |
Example
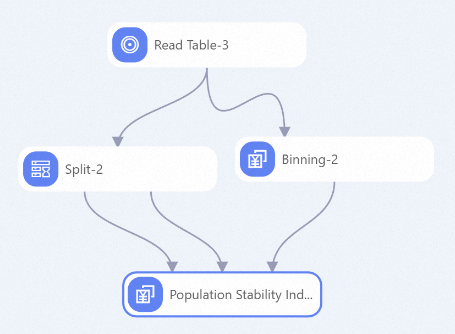
Use the Binning component to perform binning for features. Then, connect the Population Stability Index component to the two sample datasets that you want to compare and the Binning component, as shown in the following figure. Specify the Features for PSI Calculation parameter.
The following figure shows the calculation results of the Population Stability Index component.