One hot encoding converts a feature with m possible values into m binary features, each being mutually exclusive. Only one feature is active at any given time, resulting in a sparse dataset post-encoding. The output is a sparse key-value structure.
Overview
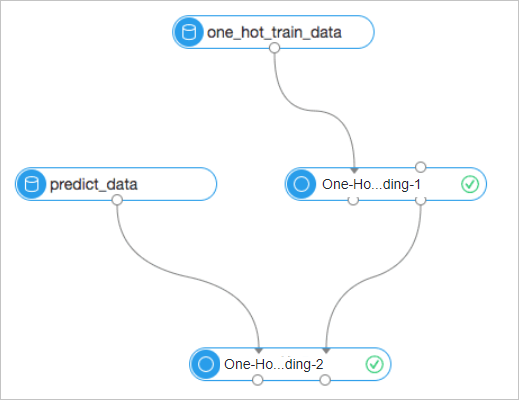
The One Hot Encoding component provides the training and prediction features:
Training:
Input node: The left input node (Input Table Name) is for training data. During training, the right input node is not required.
Output node: The component provides two output nodes. The left node is the encoded result table and the right node is the model table used for encoding new data of the same type.
Prediction:
The right input node (Input Model Table) is for model input. You can use existing one hot model to encode new data.
Configure the component
You can use one of the following methods to configure the One Hot Encoding component.
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
Configure the following parameters on the pipeline page.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Select Binary Column | Required. The fields that require binarization. |
Other Reserved Features | The features that are reserved and exported in the key-value format. The selected fields are exported as features in the key-value format. The fields must be of the DOUBLE type. They are not subject to one-hot encoding and are encoded from 0. | |
Appended Columns | Optional. The columns that are appended to the output table. | |
Parameters Setting | Lifecycle | The lifecycle of the output table. Default value: 7. |
Output table type | The type of the output table. Valid values: KV and Table. If the number of the features that require discretization is large, we recommend that you set this parameter to KV. If you set this parameter to Table, the output table can contain a maximum of 1,024 columns. | |
Cores | The number of cores. | |
Memory Size per Node | The memory size of each core. Unit: MB. | |
Delete Encoding of Last Enumeration | If you set to true, the linear independence of the encoded data is ensured. | |
Ignore Empty Elements | If you set to true, empty elements are not encoded. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
Configure the component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see SQL Script.
PAI -name one_hot
-project algo_public
-DinputTable=one_hot_test
-DbinaryCols=f0,f1,f2
-DmodelTable=one_hot_model
-DoutputTable=one_hot_output
-Dlifecycle=28;Parameter | Required | Description | Default value |
inputTable | Yes | The name of the input table. | None |
inputTablePartitions | No | The partitions that are selected from the input table for training. | All partitions of the input table |
binaryCols | Yes | The fields that require one-hot encoding. These fields must be enumeration features, and their data types are not limited. | None |
reserveCols | No | The selected fields that are exported as features in the key-value format. The fields must be of the DOUBLE type. They are not subject to one-hot encoding and are encoded from 0. | Empty string |
appendCols | No | The selected fields that are exported to the output table the same as they are in the input table. | None |
outputTable | Yes | The output table that is generated after one-hot encoding. The encoding result is stored in the key-value format. | None |
inputModelTable | No | The model table used for encoding. Note One of inputModelTable and outputModelTable must be a non-empty string. When inputModelTable is not empty, the corresponding table must be a non-empty model table. | Empty string |
outputModelTable | No | The output model table. Note One of inputModelTable and outputModelTable must be a non-empty string. | Empty string |
lifecycle | No | The lifecycle of the output table. | 7 |
dropLast | Yes | Specifies whether to delete the encoding result of the last enumerator. If this parameter is set to true, the linear independence of the encoded data is ensured. | false |
outputTableType | Yes | The type of the output table. Valid values: kv (sparse table) and table (dense table). If the number of the features that require discretization is large, we recommend that you set this parameter to kv. If you set this parameter to table, the output table can contain a maximum of 1,024 columns. If the number of the exported columns exceeds the value, an error is reported. | kv |
ignoreNull | Yes | Specifies whether to ignore empty elements in the data that requires encoding. If this parameter is set to true, empty elements are not encoded. | false |
coreNum | No | The number of cores. | Determined by the system |
memSizePerCore | No | The memory size of each core. Unit: MB. Valid values: [2048,64 × 1024]. | Determined by the system |
The encoding field column can support up to tens of millions of discrete values.
When using a trained model for subsequent encodings, the parameters dropLast, ignoreNull, and reserveCols are fixed within the model and cannot be modified. To change these parameters, you must train again.
By default, the kv table produced by One Hot Encoding uses zero-based numbering.
When encoding new data using the model, if the data contains discrete values not present in the mapping table of the model, these values are ignored and not encoded. To encode these values, the model mapping table must be retrained.
Example
Sample input data.
f0(BIGINT)
f1(STRING)
f2(DATETIME)
f3(DOUBLE)
f4(BOOLEAN)
12
prefix1
1970-09-15 12:50:22
0.1
true
12
prefix3
1971-01-22 03:15:33
0.4
false
NULL
prefix3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
0.2
NULL
3
NULL
1970-01-01 08:00:00
0.3
false
34
NULL
1970-09-15 12:50:22
0.4
NULL
3
prefix1
1970-09-15 12:50:22
0.2
true
3
prefix1
1970-09-15 12:50:22
0.3
false
3
prefix3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
0.2
true
3
prefix3
1971-01-22 03:15:33
0.1
false
NULL
prefix3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
0.3
false
Configure the One Hot Encoding parameters in the SQL script component as follows.
PAI -project algo_public -name one_hot --Default component parameters, no modification needed -DinputTable=one_hot -DbinaryCols=f0,f2,f4 -DoutputModelTable=one_hot_model_8 -DoutputTable=one_hot_in_table_1_output_8 -DdropLast=false -DappendCols=f0,f2,f4 -DignoreNull=false -DoutputTableType=table -DreserveCols=f3 -DcoreNum=4 -DmemSizePerCore=2048;After successful execution, view the output results.
The output model table from One Hot Encoding is as follows.
col_name
col_value
mapping
_reserve_
f3
0
f0
12
1
f0
3
2
f0
34
3
f0
null
4
f2
0
5
f2
22222222000
6
f2
33333333000
7
f4
0
8
f4
1
9
f4
null
10
The top row in the model mapping table is the reserve row, and the column name is fixed to reserve. This row stores reserve information. The remaining rows correspond to the mapping information of the encoding.
The encoded result table
Table
f0
f2
f4
_reserve__f3_0
f0_12_1
f0_3_2
f0_34_3
f0_null_4
f2_0_5
f2_22222222_6
f2_33333333_7
f4_0_8
f4_1_9
f4_null_10
12
1970-09-15 12:50:22
true
0.1
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
12
1971-01-22 03:15:33
false
0.4
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
NULL
1970-01-01 08:00:00
NULL
0.2
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
false
0.3
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
34
1970-09-15 12:50:22
NULL
0.4
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
3
1970-09-15 12:50:22
true
0.2
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
3
1970-09-15 12:50:22
false
0.3
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
true
0.2
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
3
1971-01-22 03:15:33
false
0.1
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
NULL
1970-01-01 08:00:00
false
0.3
0.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
0.0
KV
f0
f2
f4
kv
12
1970-09-15 12:50:22
true
0:0.1,1:1,6:1,9:1
12
1971-01-22 03:15:33
false
0:0.4,1:1,7:1,8:1
NULL
1970-01-01 08:00:00
NULL
0:0.2,4:1,5:1,10:1
3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
false
0:0.3,2:1,5:1,8:1
34
1970-09-15 12:50:22
NULL
0:0.4,3:1,6:1,10:1
3
1970-09-15 12:50:22
true
0:0.2,2:1,6:1,9:1
3
1970-09-15 12:50:22
false
0:0.3,2:1,6:1,8:1
3
1970-01-01 08:00:00
true
0:0.2,2:1,5:1,9:1
3
1971-01-22 03:15:33
false
0:0.1,2:1,7:1,8:1
NULL
1970-01-01 08:00:00
false
0:0.3,4:1,5:1,8:1
Scalability test
Test data: The number of samples is 200 million, and the number of enumerators is 100,000. The test data is listed in the following table.
f0 | f1 |
94 | prefix3689 |
9664 | prefix5682 |
2062 | prefix5530 |
9075 | prefix9854 |
9836 | prefix1764 |
5140 | prefix1149 |
3455 | prefix7272 |
2508 | prefix7139 |
7993 | prefix1551 |
5602 | prefix4606 |
3132 | prefix5767 |
The test result is listed in the following table.
core num | train time | predict time | Acceleration ratio |
5 | 84s | 181s | 1/1 |
10 | 60s | 93s | 1.4/1.95 |
20 | 46s | 56s | 1.8/3.23 |
Uses notes for the console
Directly use component for encoding.
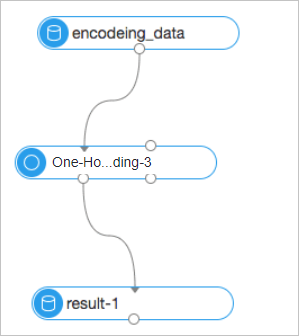
Use the component to train a model. Then, use the model to encode data.