Model Gallery lets you evaluate large language models (LLMs) using custom or public datasets, helping you identify models that meet your business requirements.
Overview
Model evaluation lets you assess LLMs using custom or public datasets.
Custom dataset-based evaluation includes:
Rule-based evaluation uses Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation (ROUGE) and Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) metrics to calculate the difference between the predicted results of a model and the actual results.
Judge model-based evaluation uses a judge model provided by PAI to score each question-response pair. The scores are used to judge model performance.
Public dataset-based evaluation loads multiple public datasets, performs model predictions, and provides an industry-standard evaluation reference based on the evaluation framework specific to each dataset.
Model evaluation supports all AutoModelForCausalLM models in Hugging Face.
Latest feature:
Use a judge model based on Qwen2 to score model responses in open-ended and complex scenarios. This feature is free for a limited time. Try it in .
Scenarios
Model evaluation supports various business needs:
Model benchmark test: Evaluate model capabilities using public datasets and compare results against industry benchmarks.
Domain evaluation: Compare pre-trained and fine-tuned model results to assess domain-specific knowledge.
Regression test: Verify model performance against a test set to ensure it meets deployment standards.
Prerequisites
An Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket is created. For more information, see Get started with the OSS console.
Billing
When you use the model evaluation feature, you are charged for OSS storage and Deep Learning Containers (DLC) evaluation jobs. For more information, see Billing overview and Billing of Deep Learning Containers (DLC).
Data preparations
Model evaluation supports both custom and public datasets (such as C-Eval).
Public dataset: Pre-uploaded datasets maintained by PAI, ready for direct use.
The public datasets include MMLU, TriviaQA, HellaSwag, GSM8K, C-Eval, and TruthfulQA. More public datasets will be integrated in the future.
Custom dataset: Upload a JSONL file to OSS and create a custom dataset. For details, see Upload objects and Create and manage datasets. Example format:
The
questionfield identifies the question column;answeridentifies the answer column. You can also select columns on the evaluation page. For judge model evaluation, the answer column is optional.[{"question": "Is it correct that Chinese invented papermaking?", "answer": "Yes"}] [{"question": "Is it correct that Chinese invented gunpowder?", "answer": "Yes"}]Sample file: eval.jsonl. Note that the file is in Chinese.
Procedure
Select a model
To find a suitable model:
Go to the Model Gallery page.
Log on to the PAI console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Workspaces. Find and click your workspace name to open the Workspace Details page.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose to go to the Model Gallery page.
Find a model that is suitable for your business.
On the Model Gallery page, click a model to go to the Overview tab of the model details page.
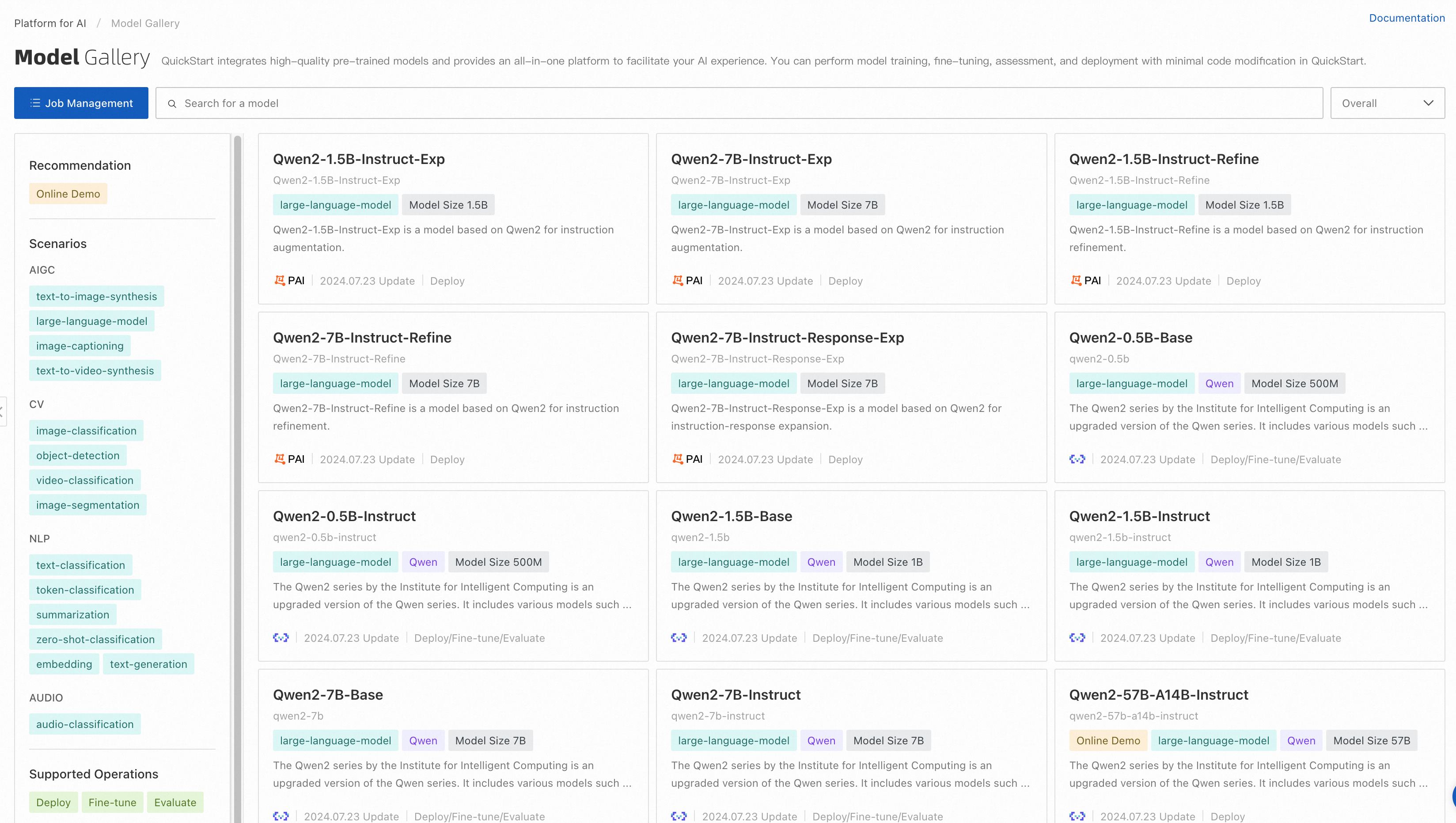
On the Overview tab of the model details page, click Evaluate in the upper-right corner. The Evaluate button is displayed only for models that can be evaluated.
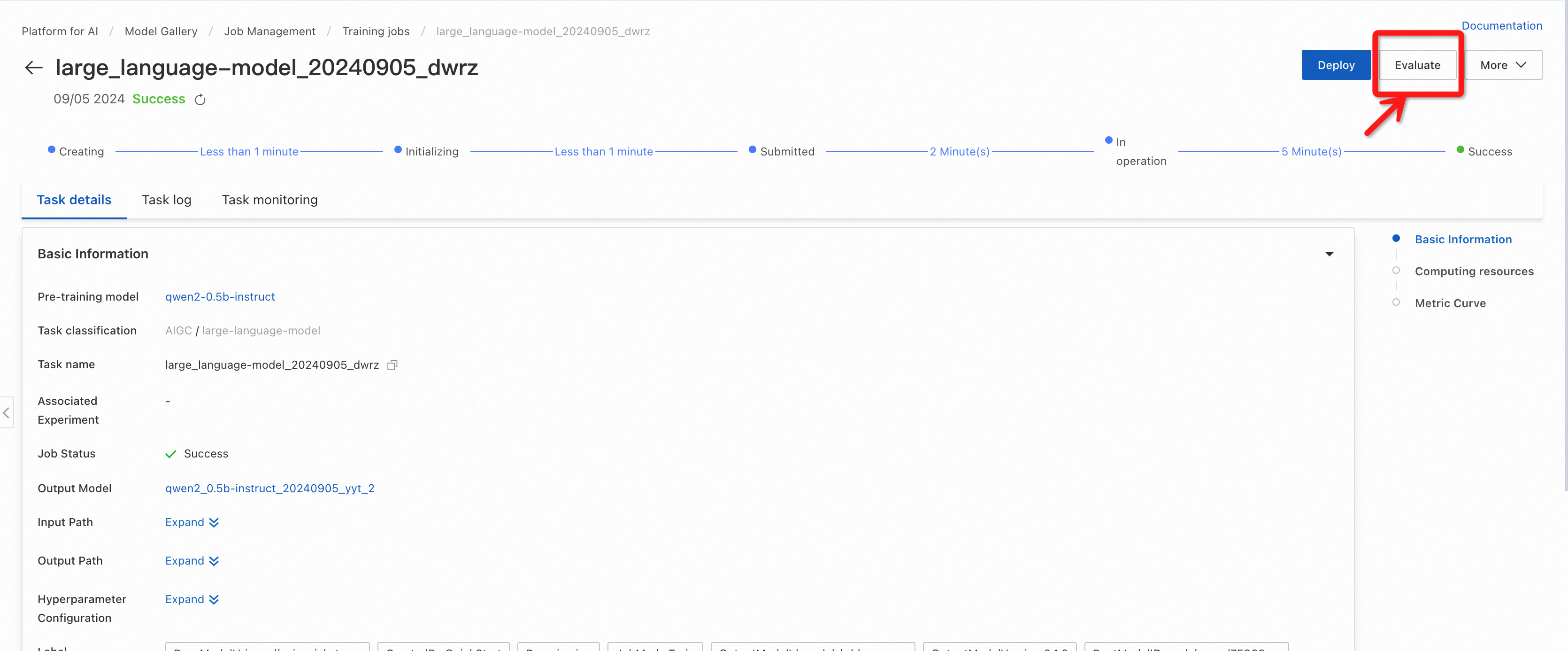
Click Job Management and click the training task. If a model can be evaluated, any fine-tuned model based on that model can also be evaluated.
Evaluate a model
Choose between Simple mode and Professional mode to evaluate your model.
Simple mode
Select a public or custom dataset for evaluation. To use the judge model, switch to Professional mode.

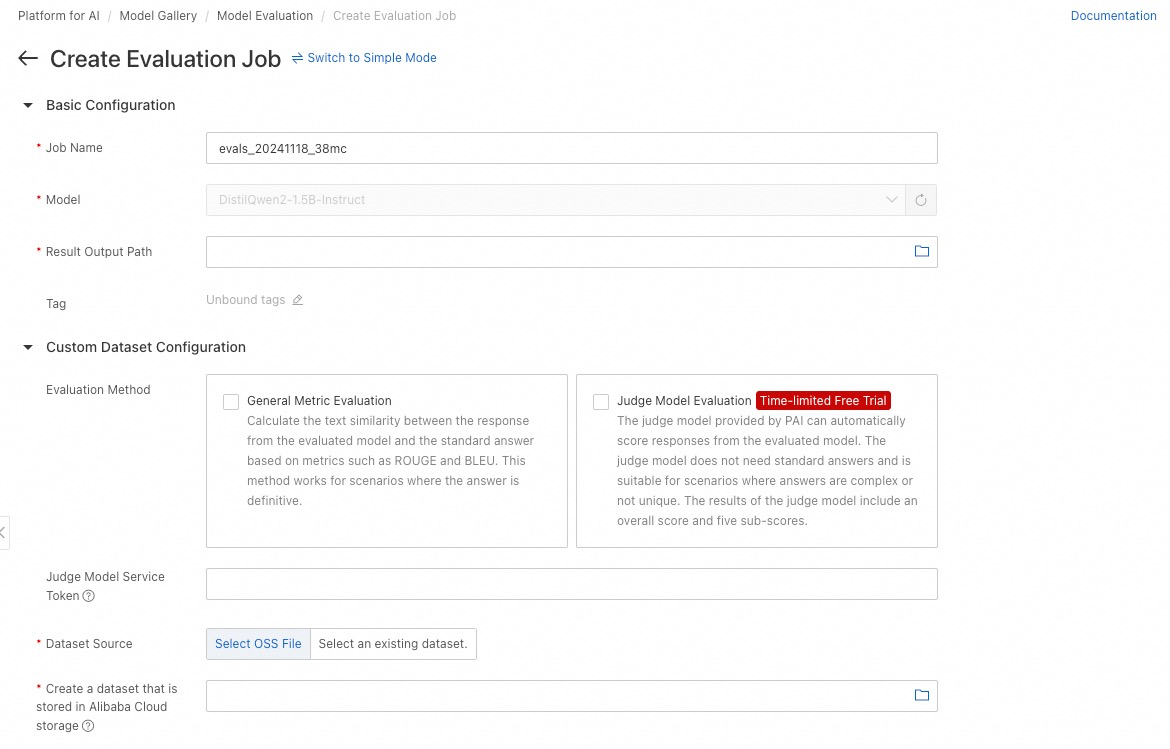
On the Create Evaluation Job page, configure the Job Name parameter.
Configure the Result Output Path. Ensure the directory is used only for this evaluation job to avoid results being overwritten.
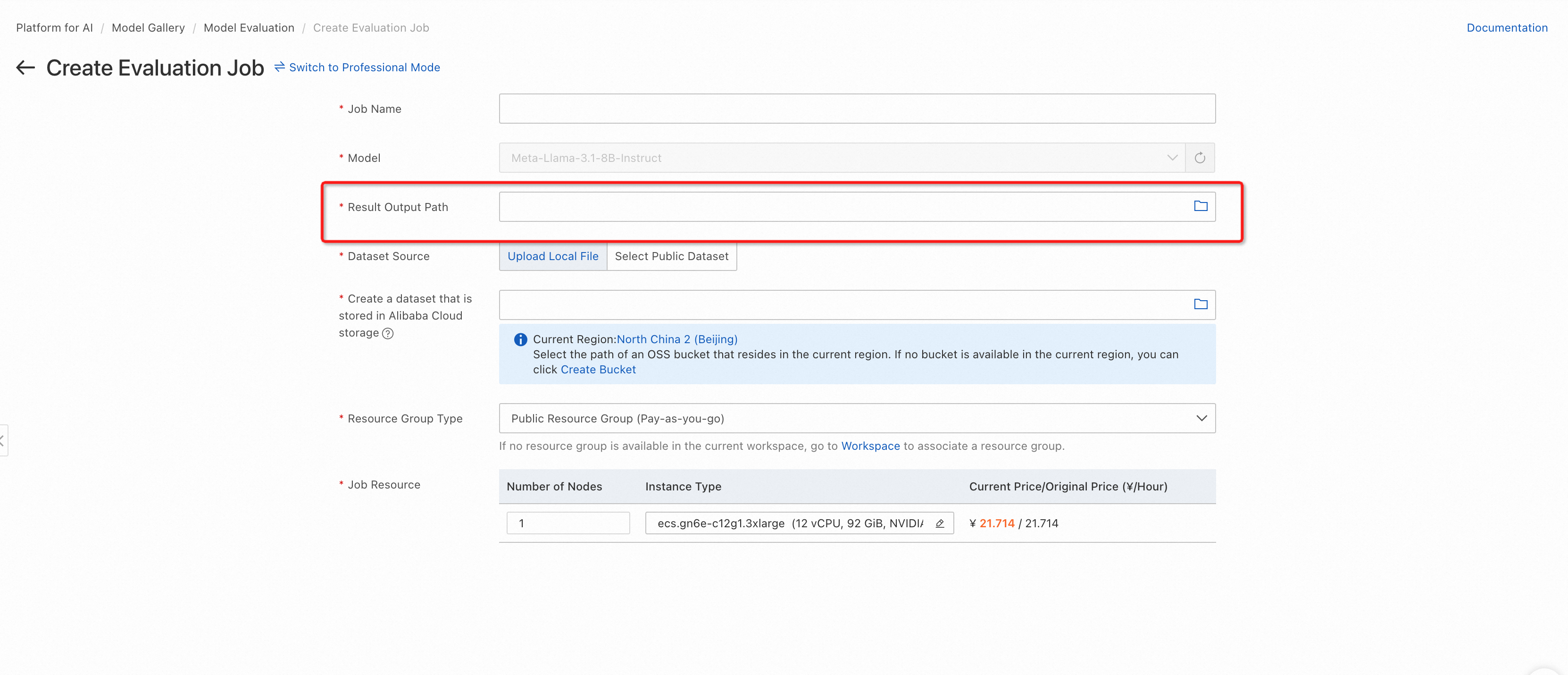
Select a dataset. You can use a custom dataset (following the format in Data preparations) or a PAI-provided public dataset.
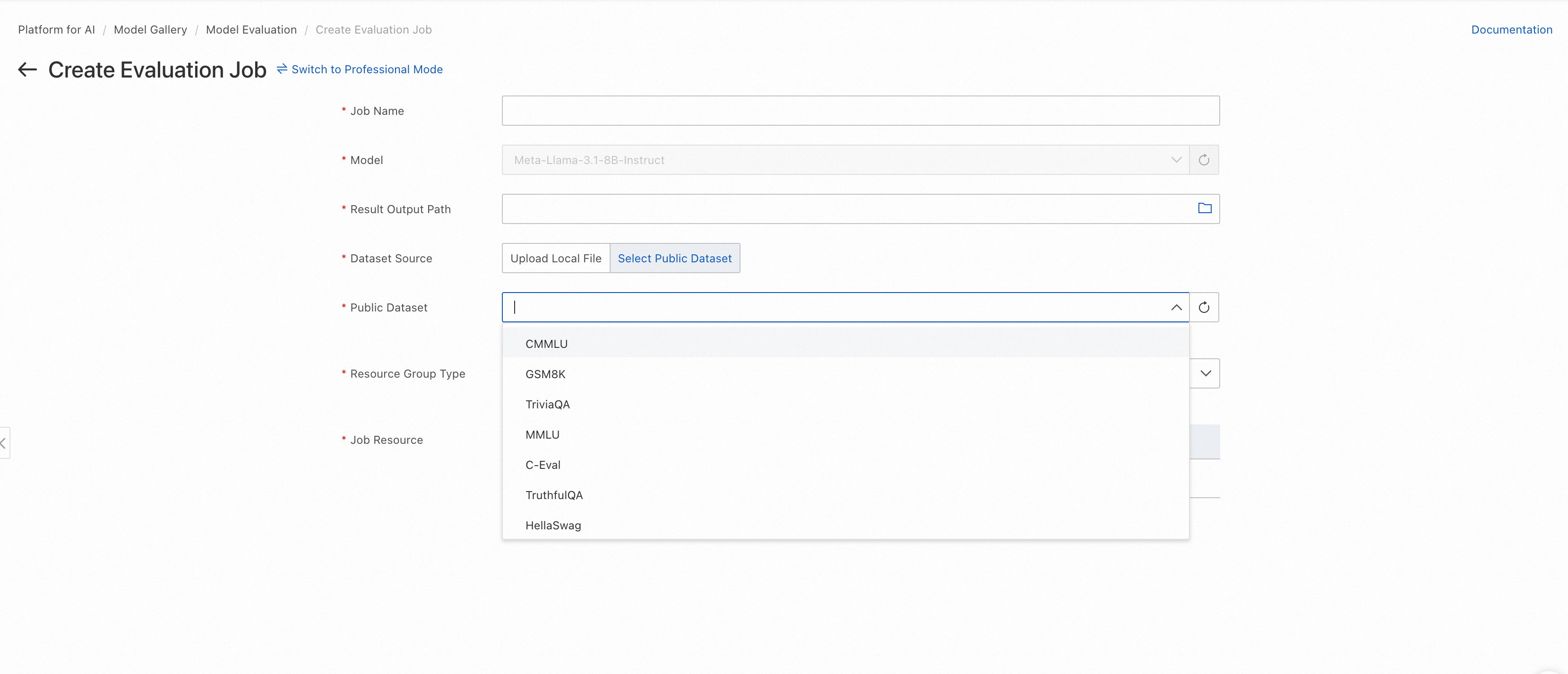
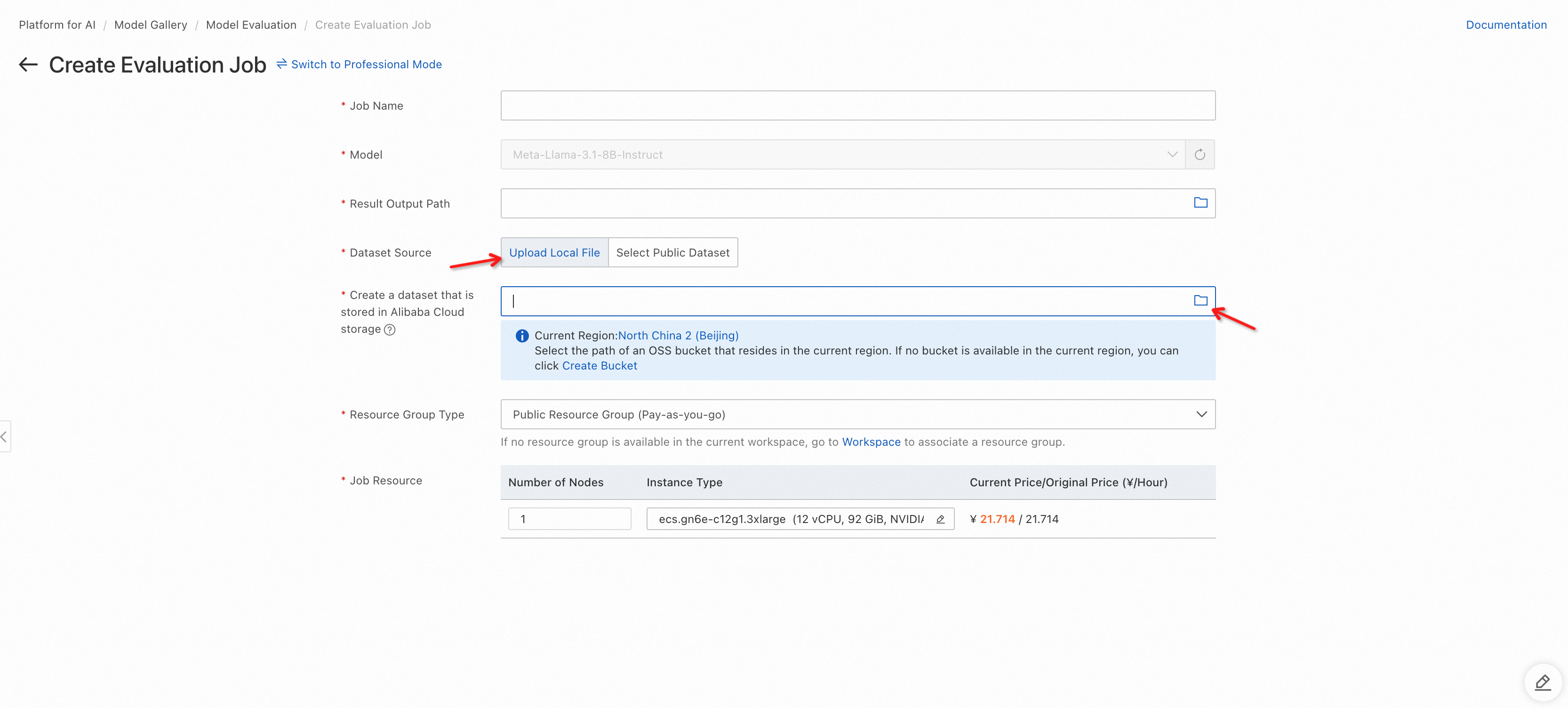
Select a GPU instance type (A10 or V100 recommended) and click Submit. After initialization completes, click the Evaluation Report tab to view results.
Professional mode
Professional mode supports multiple public datasets, custom datasets with judge model evaluation, and hyperparameter configuration.

Click Switch to Professional Mode.
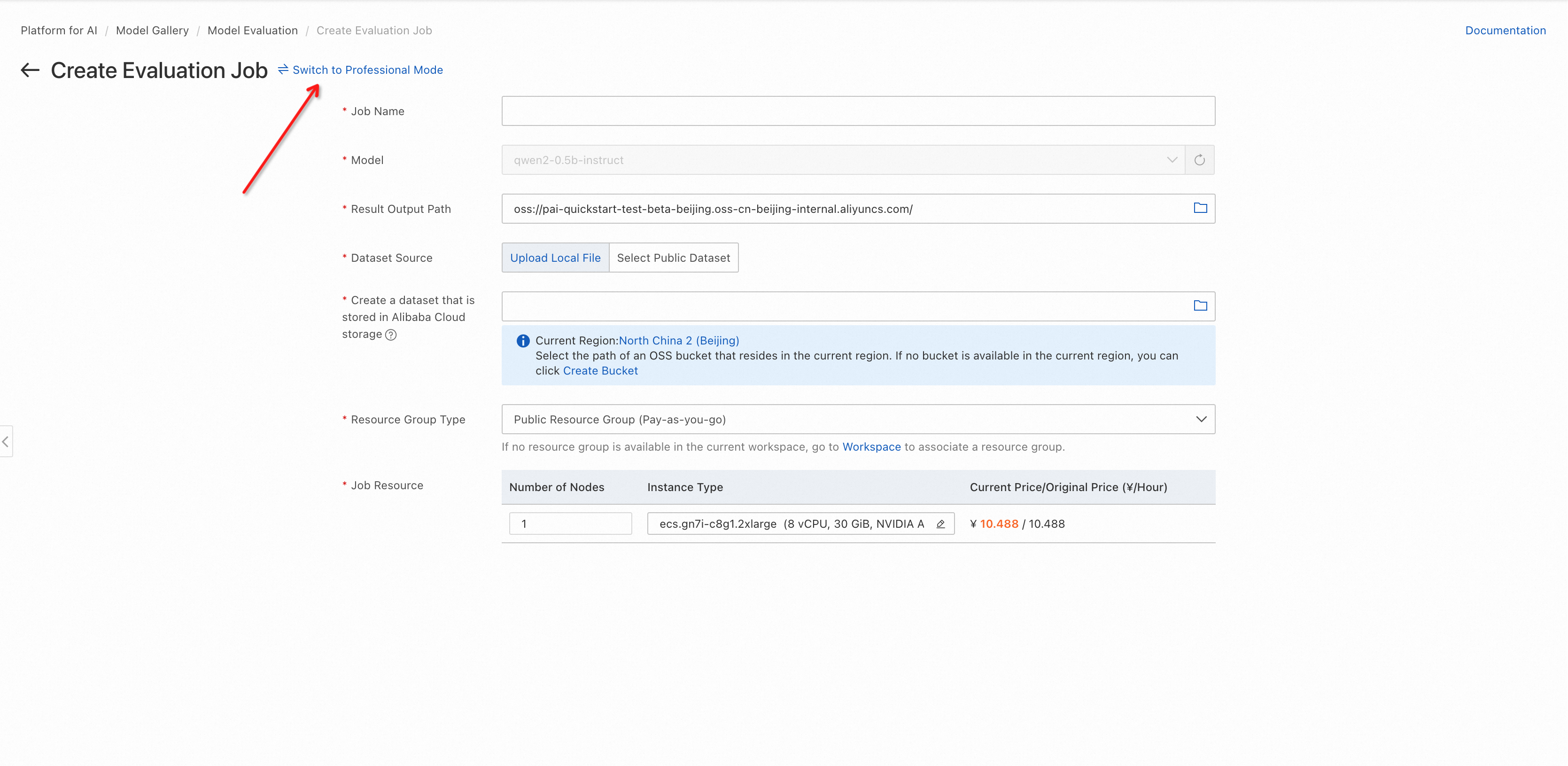
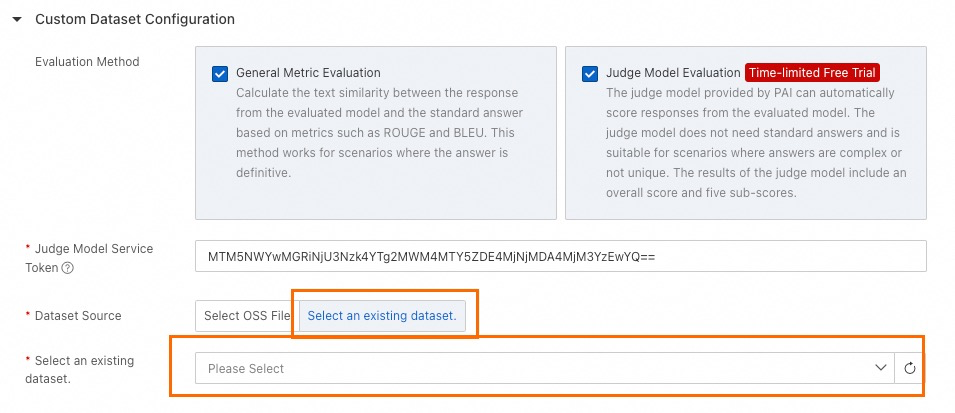
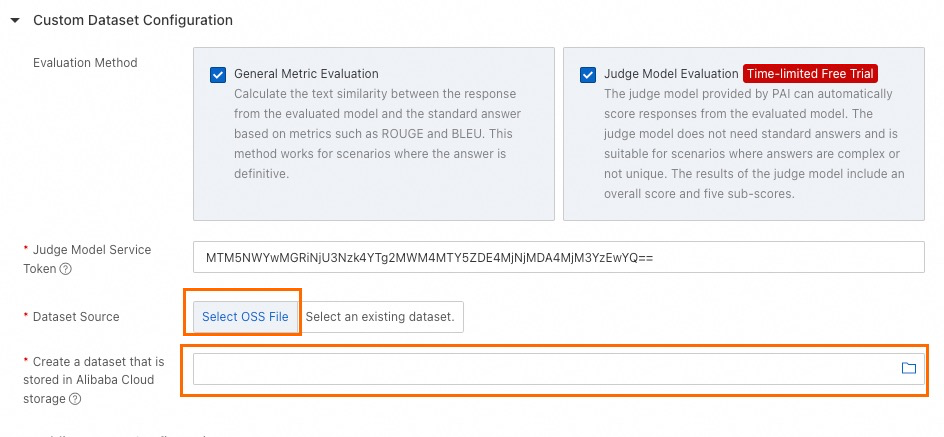
Select datasets. In professional mode, you can select public datasets and a custom dataset.
You can select multiple public datasets.
The custom dataset supports judge model evaluation and general metric evaluation.
You can specify question and answer columns for a custom dataset. If you use the judge model, the answer column is optional.
You can use a data file that meets the format requirements in OSS.
Configure the hyperparameters of the evaluated model.

Click Submit. After initialization completes, click the Evaluation Report tab to view results.
View evaluation results
Evaluation job list
On the Model Gallery page, click Job Management next to the search box.
On the Job Management page, click the Model Evaluation tab.
Evaluation results of a single evaluation job
In the job list on the Model Evaluation tab, find your evaluation job and click View Report. The Evaluation Report tab displays custom and public dataset scores.
Evaluation results based on a custom dataset

If you select general metric evaluation for an evaluation job, the radar chart displays the scores of the model based on ROUGE and BLEU metrics.
The default metrics for the custom dataset include rouge-1-f, rouge-1-p, rouge-1-r, rouge-2-f, rouge-2-p, rouge-2-r, rouge-l-f, rouge-l-p, rouge-l-r, bleu-1, bleu-2, bleu-3, and bleu-4.
ROUGE metrics:
rouge-n metrics are used to calculate the N-gram overlap. N indicates the number of consecutive words. rouge-1 and rouge-2 are the most commonly used. rouge-1 corresponds to unigram, and rouge-2 corresponds to bigram.
rouge-1-p (Precision): the proportion of the unigrams in the system summary to the unigrams in the reference summary.
rouge-1-r (Recall): the proportion of the unigrams in the reference summary that appear in the system summary.
rouge-1-f (F-score): the harmonic average of precision and recall.
rouge-2-p (Precision): the proportion of the bigrams in the system summary to the bigrams in the reference summary.
rouge-2-r (Recall): the proportion of the bigrams in the reference summary that appear in the system summary.
rouge-2-f (F-score): the harmonic average of precision and recall.
rouge-l metrics are based on the longest common subsequence (LCS).
rouge-l-p (Precision): the precision of the matching between the LCS-based system summary and the LCS-based reference summary.
rouge-l-r (Recall): the recall of the matching between the LCS-based system summary and the LCS-based reference summary.
rouge-l-f (F-score): the F-score of the matching between the LCS-based system summary and the LCS-based reference summary.
BLEU metrics:
BLEU is a popular measurement used to evaluate the machine translation quality. BLEU is scored by calculating the N-gram overlap between the machine translations and reference translations.
bleu-1: unigram matching.
bleu-2: bigram matching.
bleu-3: trigram matching (three consecutive words).
bleu-4: 4-gram matching.
If you use the judge model for the evaluation task, the metrics of the judge model scores are displayed through a list.
The judge model is fine-tuned base on Qwen2, performing on par with GPT-4 on open-source datasets such as Alighbench, and achieving superior evaluation results in some scenarios.
The page displays four statistical indicators for the scores given by the judge model for the evaluated model:
Mean: The average score given by the judge model to the generated results (excluding invalid scores), with a minimum value of 1 and a maximum value of 5. A higher mean indicates better model responses.
Median: The median score given by the judge model to the generated results (excluding invalid scores), with a minimum value of 1 and a maximum value of 5. A higher median indicates better model responses.
Standard Deviation: The standard deviation of the scores given by the judge model to the generated results (excluding invalid scores). When the mean and median are the same, a smaller standard deviation signifies a better model performance.
Skewness: The skewness of the score distribution (excluding invalid scores). Positive skewness suggests a longer tail on the right side (higher score range), while negative skewness indicates a longer tail on the left side (lower score range).
Additionally, the bottom of the page displays detailed evaluation results for each data entry in the evaluation dataset.
Evaluation results based on public datasets
If you select public datasets for model evaluation, the radar chart displays the scores of the model on the public datasets.
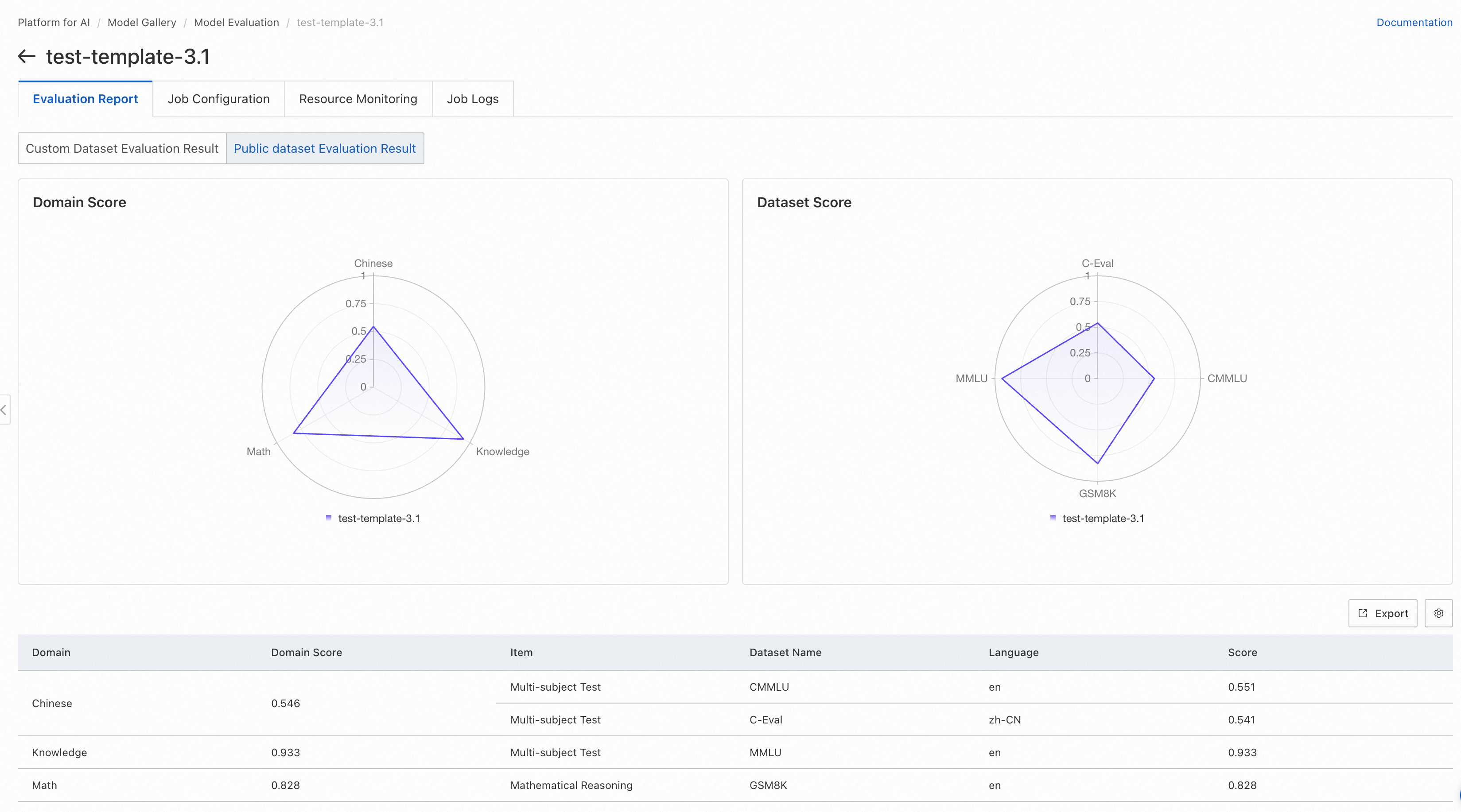
The radar chart on the left displays the scores of the model in different domains. Each domain may have multiple datasets. For datasets that belong to the same domain, the average of the evaluation scores is used as the score of the model in the domain.
The radar chart on the right displays the scores of the model in each public dataset. For more information about the evaluation scope of each public dataset, see the official introduction of the dataset.
Comparison of evaluation results for multiple models
To compare multiple models, select the evaluation jobs on the Model Evaluation tab and click Compare.
Comparison results of models based on custom datasets
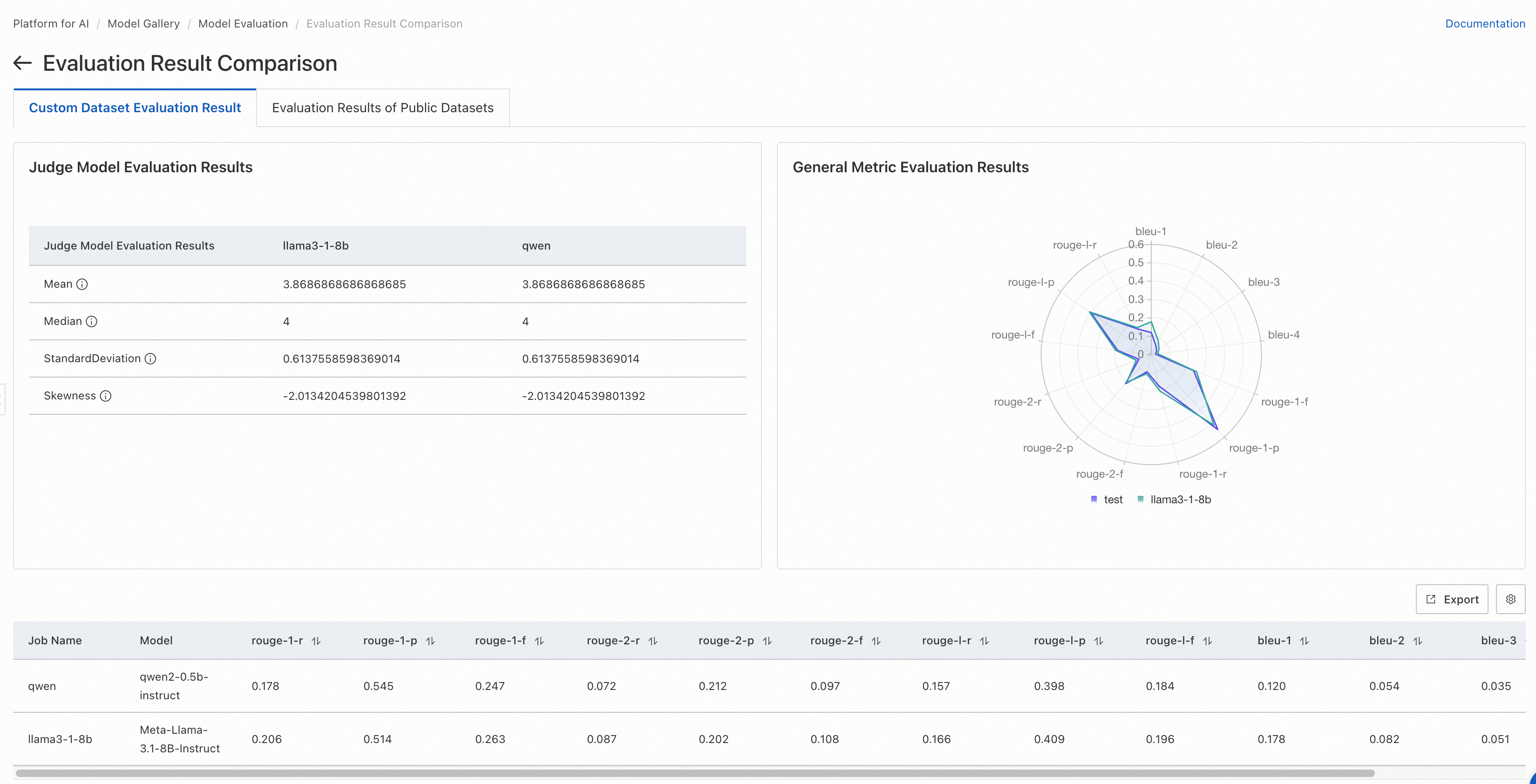
Comparison results of models based on public datasets
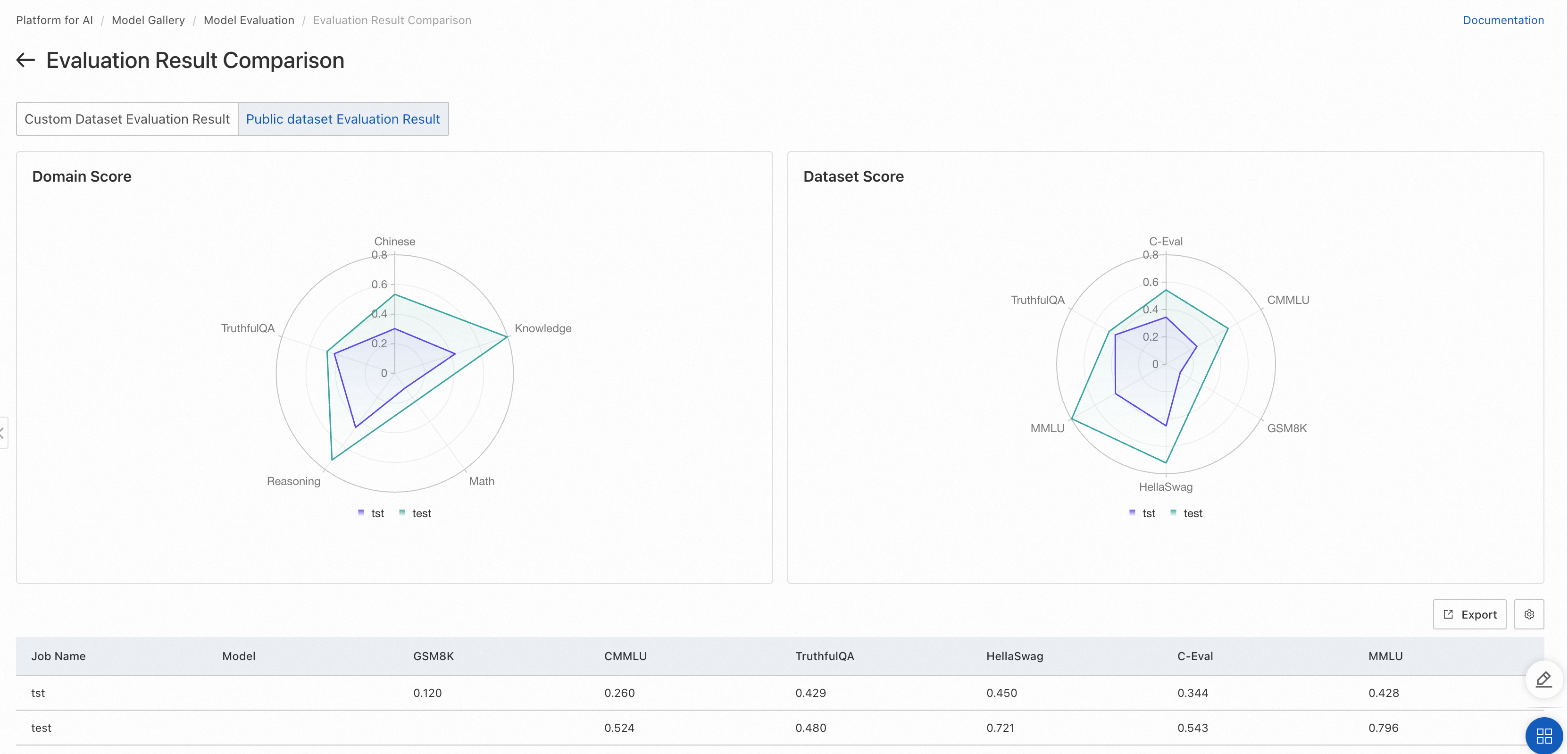
Result analysis
Evaluation results include custom dataset and public dataset scores:
Evaluation results based on custom datasets:
Text matching scores: Higher scores indicate better alignment between model output and ground truth.
Judge model scores: Higher mean/median and lower standard deviation indicate better model performance.
Custom datasets help evaluate whether a model fits your specific business scenario.
Evaluation results based on public datasets: Evaluate comprehensive LLM capabilities (math, code, reasoning) using open-source benchmarks. Higher scores indicate better performance. PAI continues to integrate more public datasets.
References
You can also use the PAI SDK for Python to evaluate models. See these notebooks: