The K-NN component selects the K-nearest records from a row in the prediction table for classification. The most common class of the K-nearest records is used as the class of the row.
Configure the component
You can use one of the following methods to configure the K-NN component.
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
You can configure the parameters of the K-NN component on the pipeline page of Machine Learning Designer of Machine Learning Platform for AI (PAI). Machine Learning Designer is formerly known as Machine Learning Studio. The following table describes the parameters.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Feature Columns in the Training Table | The feature columns that are used for training. |
Specifies the label column in the training table | The label column that is selected for training. | |
Feature Columns in the Prediction Table | If this parameter is not specified, the feature columns selected from the prediction table are the same as the feature columns in the training table. | |
Append ID Column to Output Table | The ID columns that are used to obtain the predicted values of a column. By default, the feature columns selected from the prediction table are used as the ID columns. | |
Input in Sparse Format | Specifies whether the input data is in the sparse format. If you select the check box, the input data is in the key-value format. | |
KV Pair Delimiter | The delimiter that is used to separate key-value pairs. Commas (,) are used by default. | |
Key and Value Delimiter | The delimiter that is used to separate keys and values. Colons (:) are used by default. | |
Parameters Setting | Number of Neighbors | Default value: 100. |
Tuning | Number of Cores | The number of cores. By default, the system determines the value. |
Memory Size | The memory size of each core. By default, the system determines the value. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
Configure the component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see SQL Script.
PAI -name knn
-DtrainTableName=pai_knn_test_input
-DtrainFeatureColNames=f0,f1
-DtrainLabelColName=class
-DpredictTableName=pai_knn_test_input
-DpredictFeatureColNames=f0,f1
-DoutputTableName=pai_knn_test_output
-Dk=2;Parameter | Required | Description | Default value |
trainTableName | Yes | The name of the training table. | N/A |
trainFeatureColNames | Yes | The names of the feature columns in the training table. | N/A |
trainLabelColName | Yes | The name of the label column in the training table. | N/A |
trainTablePartitions | No | The partitions that are selected from the training table for training. | All partitions |
predictTableName | Yes | The name of the prediction table. | N/A |
outputTableName | Yes | The name of the output table. | N/A |
predictFeatureColNames | No | The names of the feature columns in the prediction table. | Same as the value of the trainFeatureColNames parameter |
predictTablePartitions | No | The partitions that are selected from the prediction table for prediction. | All partitions |
appendColNames | No | The names of the columns appended to the output table. | Same as the value of the predictFeatureColNames parameter |
outputTablePartition | No | The partitions in the output table. | Full table |
k | No | The number of K-nearest neighbors. Valid values: 1 to 1000. | 100 |
enableSparse | No | Specifies whether data in the input table is in the sparse format. Valid values: true and false. | false |
itemDelimiter | No | The delimiter that is used to separate key-value pairs. | , |
kvDelimiter | No | The delimiter that is used to separate the key and value in a key-value pair. | : |
coreNum | No | The number of cores. This parameter must be used with the memSizePerCore parameter. Valid values: 1 to 20000. | Determined by the system |
memSizePerCore | No | The memory size of each core. Valid values: 1024 to 64 x 1024. Unit: MB. | Determined by the system |
lifecycle | No | The lifecycle of the output table. | N/A |
Example
Generate the training data.
create table pai_knn_test_input as select * from ( select 1 as f0,2 as f1, 'good' as class union all select 1 as f0,3 as f1, 'good' as class union all select 1 as f0,4 as f1, 'bad' as class union all select 0 as f0,3 as f1, 'good' as class union all select 0 as f0,4 as f1, 'bad' as class )tmp;Run the following PAI command to submit the parameters of the K-NN component:
pai -name knn -DtrainTableName=pai_knn_test_input -DtrainFeatureColNames=f0,f1 -DtrainLabelColName=class -DpredictTableName=pai_knn_test_input -DpredictFeatureColNames=f0,f1 -DoutputTableName=pai_knn_test_output -Dk=2;View the training result.
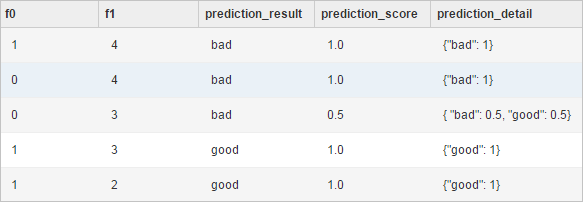 The result contains the following columns:
The result contains the following columns:f0 and f1: the appended columns.
prediction_result: lists the classification results.
prediction_score: lists the probabilities for the classification results.
prediction_detail: lists the classes of the K-nearest neighbors and their probabilities.