The k-core algorithm is used to find the subgraph with the specified coreness in a graph. The k-core of a graph refers to the remaining subgraph after vertices with the degree k or a lower degree are repeatedly excluded. The K-Core component can generate the vertices that are connected to each vertex in the subgraph.
Configure the component
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
You can add the K-Core component on the pipeline page of Machine Learning Designer in the Platform for AI (PAI) console. The following table describes the parameters.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Source Vertex Column | The start vertex column in the edge table. |
Target Vertex Column | The end vertex column in the edge table. | |
Parameters Setting | k | The coreness of a vertex. Default value: 1. If a vertex belongs to the k-core but is not included in the (k+1)-core, the coreness of the vertex is k. |
Tuning | Workers | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
Memory Size per Worker | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the |
Method 2: Configure the component by using PAI commands
You can configure the K-Core component by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to run PAI commands. For more information, see Scenario 4: Execute PAI commands within the SQL script component in the "SQL Script" topic.
PAI -name KCore
-project algo_public
-DinputEdgeTableName=KCore_func_test_edge
-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id
-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id
-DoutputTableName=KCore_func_test_result
-Dk=2;Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
inputEdgeTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the input edge table. |
inputEdgeTablePartitions | No | Full table | The partitions in the input edge table. |
fromVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The start vertex column in the input edge table. |
toVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The end vertex column in the input edge table. |
outputTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the output table. |
outputTablePartitions | No | No default value | The partitions in the output table. |
lifecycle | No | No default value | The lifecycle of the output table. |
workerNum | No | Not specified | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
workerMem | No | 4096 | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the |
splitSize | No | 64 | The data split size. |
k | Yes | 1 | The coreness of a vertex. |
Example
Add the SQL Script component as a vertex to the canvas and execute the following SQL statements to generate training data.
drop table if exists KCore_func_test_edge; create table KCore_func_test_edge as select * from ( select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id union all select '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id union all select '2' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id union all select '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id union all select '3' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id union all select '3' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id union all select '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id )tmp;Data structure
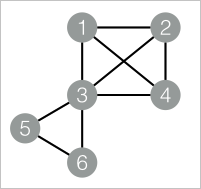
Add the SQL Script component as a vertex to the canvas and run the following PAI commands to train the model.
drop table if exists ${o1}; PAI -name KCore -project algo_public -DinputEdgeTableName=KCore_func_test_edge -DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id -DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id -DoutputTableName=${o1} -Dk=2;Right-click the SQL Script component and choose View Data > SQL Script Output to view the training results.
| node1 | node2 | | ----- | ----- | | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 3 | | 1 | 4 | | 2 | 1 | | 2 | 3 | | 2 | 4 | | 3 | 1 | | 3 | 2 | | 3 | 4 | | 4 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | 4 | 3 |