NVIDIA Triton Inference Server is a high-performance inference serving platform that supports models from TensorRT, TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, and other frameworks. This guide walks you through deploying Triton-based inference services on Alibaba Cloud PAI-EAS (Elastic Algorithm Service).
Prerequisites
An OSS bucket in the same region as your PAI workspace
Trained model files (e.g.,
.pt,.onnx,.plan,.savedmodel)
Quickstart: Deploy a single-model service
Step 1: Prepare the model repository
Triton requires a specific directory structure within your Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket. Create your directories in the following format. For more information, see Manage directories and Upload files.
oss://your-bucket/models/triton/
└── your_model_name/
├── 1/ # Version directory (must be a number)
│ └── model.pt # Model file
└── config.pbtxt # Model configuration file
Key requirements:
The model version directory must be named with a number (
1,2,3, etc.).A higher number indicates a newer version.
Each model requires a
config.pbtxtconfiguration file.
Step 2: Create the model configuration file
Create a config.pbtxt file to define your model's basic information. The following is an example:
name: "your_model_name"
platform: "pytorch_libtorch"
max_batch_size: 128
input [
{
name: "INPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 3, -1, -1 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 1000 ]
}
]
# Use a GPU for inference
# instance_group [
# {
# kind: KIND_GPU
# }
# ]
# Model version policy
# Load only the latest version (default behavior)
# version_policy: { latest: { num_versions: 1 }}
# Load all versions
# version_policy: { all { }}
# Load the two latest versions
# version_policy: { latest: { num_versions: 2 }}
# Load specific versions
# version_policy: { specific: { versions: [1, 3] }}
Parameter descriptions
Parameter | Required | Description |
| No | The name of the model. If specified, it must match the model directory name. |
| Yes | The model framework. Valid values include Choose this if you are deploying a standard model file (e.g., .pt, .onnx, .savedmodel). |
| Yes | An alternative to Choose this if you need to write custom Python code for pre/post-processing or core inference. Note While Triton's architecture supports developing custom backends in other languages like C++, this is not a common practice and is not covered in this guide. |
| Yes | The maximum batch size. Set to |
| Yes | The input tensor configuration: |
| Yes | The output tensor configuration: |
| No | Specifies the inference device: |
| No | Controls which model versions are loaded. See the |
You must specify either platform or backend.
Step 3: Deploy the service
Log on to the PAI console. Select a region on the top of the page. Then, select the desired workspace and click Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS).
On the Inference Service tab, click Deploy Service, and in the Scenario-based Model Deployment section, click Triton Deployment.
Configure the deployment parameters:
Service Name: Enter a custom service name.
Model Settings: For Type, select OSS. enter the path to your model repository (e.g.,
oss://your-bucket/models/triton/).Instance Count and Resource Group Type: Select the values based on your requirements. To estimate the GPU memory required for your model, see Estimate the VRAM required for a large model.
Click Deploy and wait for the service to start.
Step 4: Enable gRPC (optional)
By default, Triton provides an HTTP service on port 8000. To use gRPC:
In the upper-right corner of the service configuration page, click Convert to Custom Deployment.
In the Environment Information section, change the Port Number to
8001.Under Features > Advanced Networking, click Enable gRPC.
Click Deploy.
After the service deploys successfully, you can call the service.
Deploy a multi-model service
To deploy multiple models in a single Triton instance, place all models in the same repository directory:
oss://your-bucket/models/triton/
├── resnet50_pytorch/
│ ├── 1/
│ │ └── model.pt
│ └── config.pbtxt
├── densenet_onnx/
│ ├── 1/
│ │ └── model.onnx
│ └── config.pbtxt
└── classifier_tensorflow/
├── 1/
│ └── model.savedmodel/
│ ├── saved_model.pb
│ └── variables/
└── config.pbtxt
The deployment steps are the same as for a single model. Triton automatically loads all models in the repository.
Use the Python backend to customize inference logic
Use Triton's Python backend to customize pre-processing, post-processing, or the core inference logic.
Directory structure
your_model_name/
├── 1/
│ ├── model.pt # Model file
│ └── model.py # Custom inference logic
└── config.pbtxt
Implement the Python Backend
Create a model.py file and define the TritonPythonModel class:
import json
import os
import torch
from torch.utils.dlpack import from_dlpack, to_dlpack
import triton_python_backend_utils as pb_utils
class TritonPythonModel:
"""The class name must be 'TritonPythonModel'."""
def initialize(self, args):
"""
Optional. Called once when the model is loaded. Use this function to initialize
model properties and configurations.
Parameters
----------
args : A dictionary where both keys and values are strings. It includes:
* model_config: The model configuration in JSON format.
* model_instance_kind: The device type.
* model_instance_device_id: The device ID.
* model_repository: The path to the model repository.
* model_version: The model version.
* model_name: The model name.
"""
# Parse the model configuration from its JSON representation.
self.model_config = model_config = json.loads(args["model_config"])
# Get properties from the model configuration file.
output_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(model_config, "OUTPUT__0")
# Convert Triton types to NumPy types.
self.output_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(output_config["data_type"])
# Get the path to the model repository.
self.model_directory = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
# Get the device for model inference. This example uses a GPU.
self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("device: ", self.device)
model_path = os.path.join(self.model_directory, "model.pt")
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
raise pb_utils.TritonModelException("Cannot find the pytorch model")
# Load the PyTorch model to the GPU by using .to(self.device).
self.model = torch.jit.load(model_path).to(self.device)
print("Initialized...")
def execute(self, requests):
"""
Required. This method is called for every inference request. If batching is enabled,
you must implement the batch processing logic yourself.
Parameters
----------
requests : A list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest objects.
Returns
-------
A list of pb_utils.InferenceResponse objects. The list must contain one
response for each request.
"""
output_dtype = self.output_dtype
responses = []
# Iterate through the request list and create a corresponding response for each request.
for request in requests:
# Get the input tensor.
input_tensor = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT__0")
# Convert the Triton tensor to a Torch tensor.
pytorch_tensor = from_dlpack(input_tensor.to_dlpack())
if pytorch_tensor.shape[2] > 1000 or pytorch_tensor.shape[3] > 1000:
responses.append(
pb_utils.InferenceResponse(
output_tensors=[],
error=pb_utils.TritonError(
"Image shape should not be larger than 1000"
),
)
)
continue
# Run inference on the target device.
prediction = self.model(pytorch_tensor.to(self.device))
# Convert the Torch output tensor to a Triton tensor.
out_tensor = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("OUTPUT__0", to_dlpack(prediction))
inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(output_tensors=[out_tensor])
responses.append(inference_response)
return responses
def finalize(self):
"""
Optional. Called when the model is unloaded. Use this for cleanup tasks, such as
releasing resources.
"""
print("Cleaning up...")Note that when you use the Python Backend, some of Triton's behaviors change:
max_batch_sizehas no effect: Themax_batch_sizeparameter inconfig.pbtxtdoes not enable dynamic batching in the Python Backend. You must iterate through therequestslist in theexecutemethod and manually build the batch for inference.instance_grouphas no effect: Theinstance_groupinconfig.pbtxtdoes not control whether the Python Backend uses a CPU or a GPU. You must explicitly move the model and data to the target device in theinitializeandexecutemethods using code, such aspytorch_tensor.to(torch.device("cuda")).
Update the configuration file
name: "resnet50_pt"
backend: "python"
max_batch_size: 128
input [
{
name: "INPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 3, -1, -1 ]
}
]
output [
{
name: "OUTPUT__0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [ 1000 ]
}
]
parameters: {
key: "FORCE_CPU_ONLY_INPUT_TENSORS"
value: {string_value: "no"}
}Key parameter descriptions are as follows:
backend: Must be set to
python.parameters: When using a GPU for inference, you can optionally set the
FORCE_CPU_ONLY_INPUT_TENSORSparameter tonoto avoid the overhead of copying input tensors between the CPU and GPU.
Deploy the service
The Python backend requires shared memory. In , enter the following JSON configuration and click Deploy.
{
"metadata": {
"name": "triton_server_test",
"instance": 1
},
"cloud": {
"computing": {
"instance_type": "ml.gu7i.c8m30.1-gu30",
"instances": null
}
},
"containers": [
{
"command": "tritonserver --model-repository=/models",
"image": "eas-registry-vpc.<region>.cr.aliyuncs.com/pai-eas/tritonserver:25.03-py3",
"port": 8000,
"prepare": {
"pythonRequirements": [
"torch==2.0.1"
]
}
}
],
"storage": [
{
"mount_path": "/models",
"oss": {
"path": "oss://oss-test/models/triton_backend/"
}
},
{
"empty_dir": {
"medium": "memory",
// Configure 1 GB of shared memory.
"size_limit": 1
},
"mount_path": "/dev/shm"
}
]
}
Key JSON configuration description:
containers[0].image: The Triton official Image. Replace<region>with the region where your service is located.containers[0].prepare.pythonRequirements: List your Python dependencies here. EAS automatically installs them before the service starts.storage: Contains two mount points.The first mounts your OSS model repository path to the
/modelsdirectory in the container.The second
storageentry configures shared memory, which is required. The Triton server and Python backend use the/dev/shmpath to pass tensor data with zero-copy, maximizing performance. Thesize_limitis in GB. Estimate the required size based on your model and expected concurrency.
Call the service
Get the service endpoint and token
On the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page, click the service name.
On the Service Details tab, click View Endpoint Information. Copy the Internet Endpoint and Token.
Send an HTTP request
When the port number is set to 8000, the service supports HTTP requests.
import numpy as np
# To install the tritonclient package, run: pip install tritonclient
import tritonclient.http as httpclient
# The service endpoint URL. Do not include the `http://` scheme.
url = '1859257******.cn-hangzhou.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com/api/predict/triton_server_test'
triton_client = httpclient.InferenceServerClient(url=url)
image = np.ones((1,3,224,224))
image = image.astype(np.float32)
inputs = []
inputs.append(httpclient.InferInput('INPUT__0', image.shape, "FP32"))
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(image, binary_data=False)
outputs = []
outputs.append(httpclient.InferRequestedOutput('OUTPUT__0', binary_data=False)) # Get a 1000-dimension vector
# Specify the model name, request token, inputs, and outputs.
results = triton_client.infer(
model_name="<your-model-name>",
model_version="<version-num>",
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
headers={"Authorization": "<your-service-token>"},
)
output_data0 = results.as_numpy('OUTPUT__0')
print(output_data0.shape)
print(output_data0)Send a gRPC request
When the port number is set to 8001 and gRPC-related settings are configured, the service supports gRPC requests.
The gRPC endpoint is different from the HTTP endpoint. Obtain the correct gRPC endpoint from the service details page.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import grpc
# To install the tritonclient package, run: pip install tritonclient
from tritonclient.grpc import service_pb2, service_pb2_grpc
import numpy as np
if __name__ == "__main__":
# The access URL (service endpoint) generated after service deployment.
# Do not include the `http://` scheme. Append the port `:80`.
# Although Triton listens on port 8001 internally, PAI-EAS exposes gRPC via port 80 externally. Use :80 in your client.
host = (
"service_name.115770327099****.cn-beijing.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com:80"
)
# Service token. Use your actual token in a real application.
token = "<your-service-token>"
# Model name and version.
model_name = "<your-model-name>"
model_version = "<version-num>"
# Create gRPC metadata for token authentication.
metadata = (("authorization", token),)
# Create a gRPC channel and stub to communicate with the server.
channel = grpc.insecure_channel(host)
grpc_stub = service_pb2_grpc.GRPCInferenceServiceStub(channel)
# Build the inference request.
request = service_pb2.ModelInferRequest()
request.model_name = model_name
request.model_version = model_version
# Build the input tensor. It must match the input in the model configuration.
input_tensor = service_pb2.ModelInferRequest().InferInputTensor()
input_tensor.name = "INPUT__0"
input_tensor.datatype = "FP32"
input_tensor.shape.extend([1, 3, 224, 224])
# Build the output tensor. It must match the output in the model configuration.
output_tensor = service_pb2.ModelInferRequest().InferRequestedOutputTensor()
output_tensor.name = "OUTPUT__0"
# Add the input and output tensors to the request.
request.inputs.extend([input_tensor])
request.outputs.extend([output_tensor])
# Create a random array and serialize it into a byte sequence as input data.
request.raw_input_contents.append(np.random.rand(1, 3, 224, 224).astype(np.float32).tobytes())
# Send the inference request and receive the response.
response, _ = grpc_stub.ModelInfer.with_call(request, metadata=metadata)
# Extract the output tensor from the response.
output_contents = response.raw_output_contents[0] # Assume there is only one output tensor.
output_shape = [1, 1000] # Assume the output tensor shape is [1, 1000].
# Convert the output bytes to a NumPy array.
output_array = np.frombuffer(output_contents, dtype=np.float32)
output_array = output_array.reshape(output_shape)
# Print the model's output.
print("Model output:\n", output_array)Debugging tips
Enable verbose logging
Set verbose=True to print the JSON data for requests and responses:
client = httpclient.InferenceServerClient(url=url, verbose=True)
Example output:
POST /api/predict/triton_test/v2/models/resnet50_pt/versions/1/infer, headers {'Authorization': '************1ZDY3OTEzNA=='}
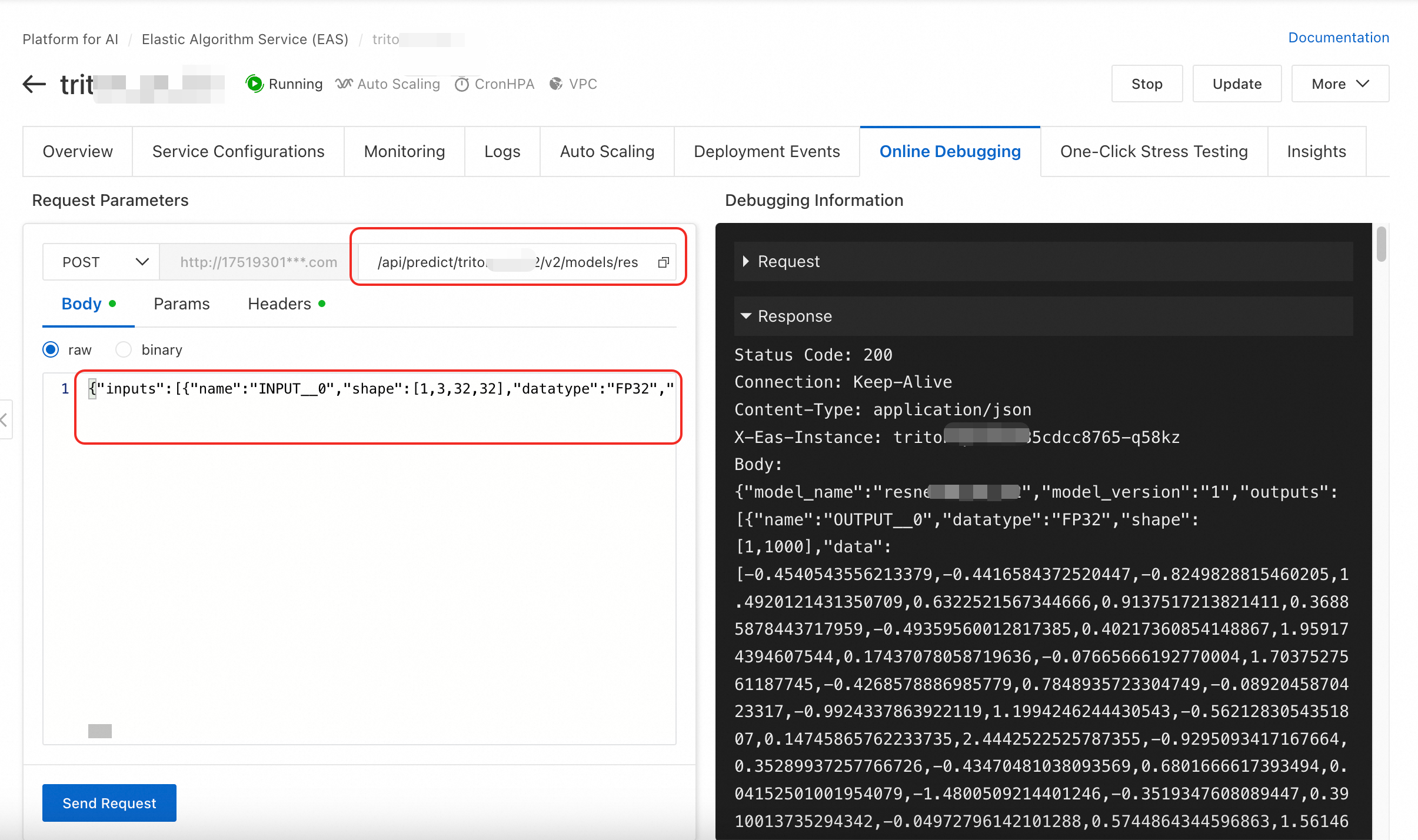
b'{"inputs":[{"name":"INPUT__0","shape":[1,3,32,32],"datatype":"FP32","data":[1.0,1.0,1.0,.....,1.0]}],"outputs":[{"name":"OUTPUT__0","parameters":{"binary_data":false}}]}'Online debugging
You can test directly using online debugging in the console. Complete the request URL to /api/predict/triton_test/v2/models/resnet50_pt/versions/1/infer and use the JSON request data from the verbose logs as the Body.
Stress test the service
The following steps describe how to perform a stress test using a single piece of data as an example. For more information about stress testing, see Stress testing for services in common scenarios.
On the One-Clink Stress Testing tab, click Create Stress Testing Task, select your deployed Triton service, and enter the stress test URL.
Set the Data Source to Single Data Entry. Use the following code to Base64-encode your JSON request body:
import base64 # Existing JSON request body string json_str = '{"inputs":[{"name":"INPUT__0","shape":[1,3,32,32],"datatype":"FP32","data":[1.0,1.0,.....,1.0]}]}' # Direct encoding base64_str = base64.b64encode(json_str.encode('utf-8')).decode('ascii') print(base64_str)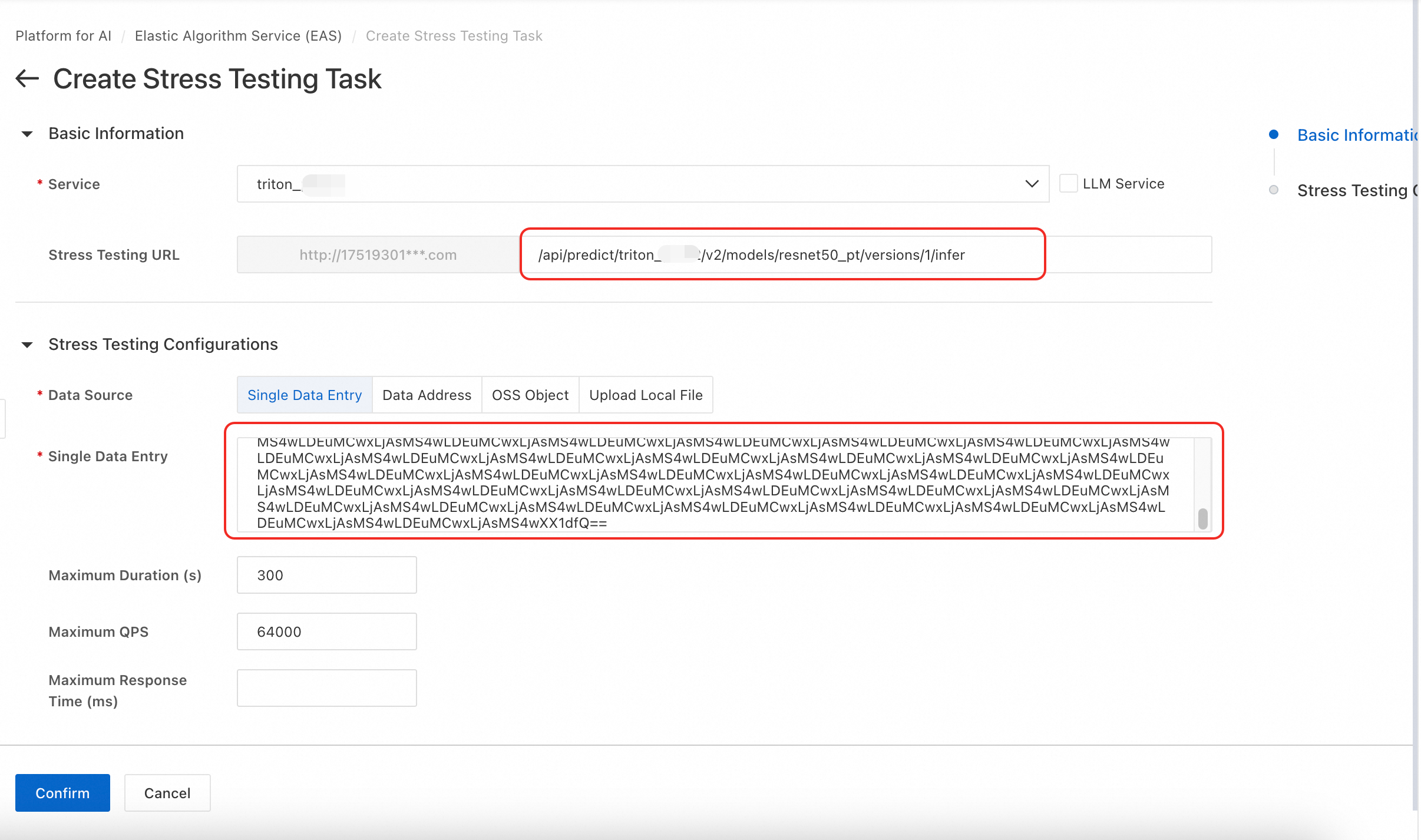
FAQ
Q: Why do I get a "CUDA error: no kernel image is available for execution on the device"?
This error indicates a compatibility mismatch between the CUDA version in the Triton image and the architecture of the selected GPU instance.
To resolve this, switch to a different GPU instance type that is compatible with your image's CUDA version. For example, try using an A10 or T4 instance.
Q: How can I fix the "InferenceServerException: url should not include the scheme" for HTTP requests?
This error occurs because the tritonclient.http.InferenceServerClient requires the URL to be provided without the protocol scheme (e.g., http:// or https://).
To fix this, remove the scheme from your URL string.
Q: How do I resolve a "DNS resolution failed" error when making gRPC calls?
This error occurs because the service host is incorrect. The format of the service endpoint is http://we*****.1751930*****.cn-hangzhou.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com/ (note that this is different from the HTTP endpoint). Remove the http:// prefix and the trailing /. Then, append :80 to the end. The final format is we*****.1751930*****.cn-hangzhou.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com:80.
References
To learn how to deploy an EAS service using the TensorFlow Serving inference engine, see TensorFlow Serving image deployment.
You can also develop a custom image and use it to deploy an EAS service. For more information, see Custom images.
For more information about NVIDIA Triton, see the official Triton documentation.