Machine Learning Designer uses pipelines to build and debug models. You can create a pipeline and add different components to the pipeline based on your business requirements. A blank pipeline is used as an example to build a binary classification model for heart disease prediction.
Prerequisites
Step 1: Create a pipeline
Go to Visualized Modeling (Designer), select a workspace, and access the Designer page. Create and open a pipeline.
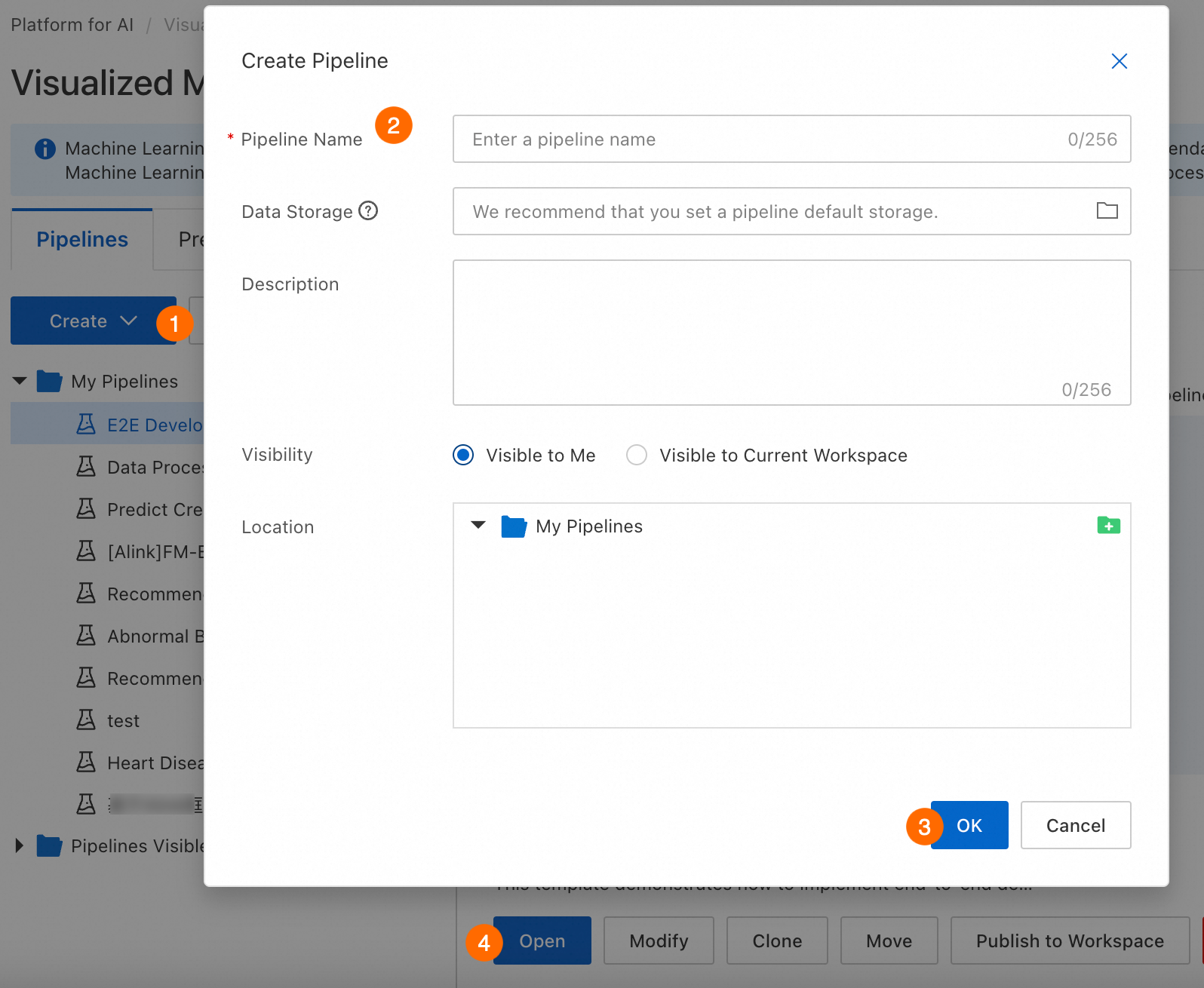
Parameter | Description |
Pipeline Name | Enter a custom name. |
Data Storage | Specify an OSS bucket path to store temporary data and models during runs. If not specified, the default workspace storage is used. The system automatically creates a temporary folder named |
Visibility |
|
Step 2: Prepare and preprocess data
Prepare the data source and preprocess data before building a model to facilitate subsequent model training based on your business requirements.
Prepare data
In the pipeline that you created, add components in the Data Source/Target category to read data from a data source, such as MaxCompute or Object Storage Service (OSS). For more information, see the specific component documentation under Component reference: data source or destination. The following example uses the Read Table component to read the public data related to heart disease cases provided by PAI. For more information about datasets, see Heart disease datasets.
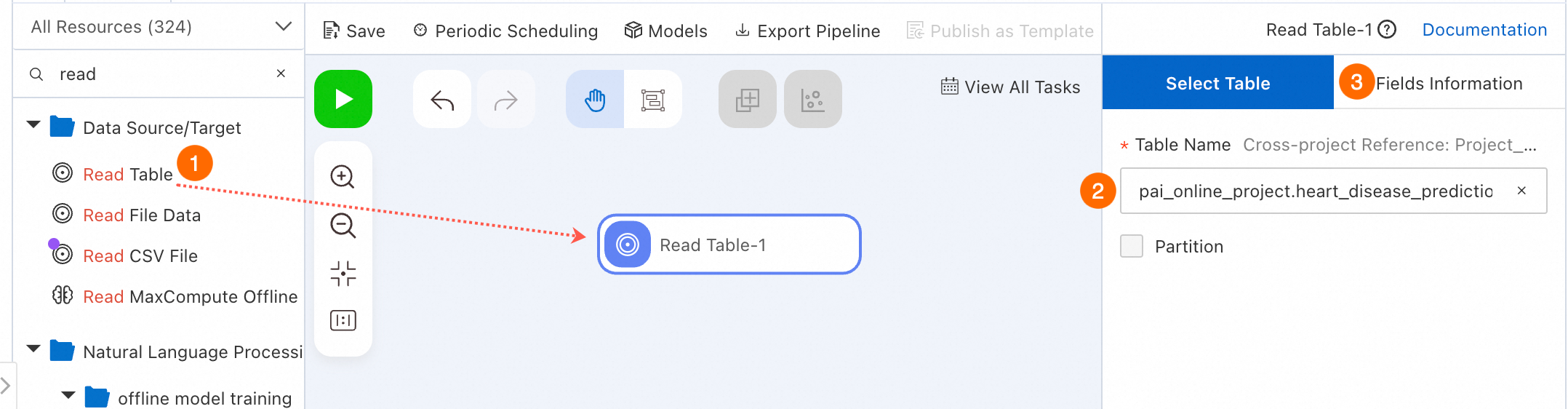
Select an appropriate table for the Read Table component in the Data Source/Target category to read data.
In the left-side component list, click Data Source/Target, drag the Read Table component to the canvas on the right to read MaxCompute table data. A pipeline node named Read Table-1 is automatically generated on the canvas.
Configure the source data table on the node configuration page.
Click the Read Table-1 node on the canvas, and enter the MaxCompute table name in the Table Name field in the node configuration section on the right. The
pai_online_project.heart_disease_predictiontable is used in this example to read the public heart disease case data provided by PAI.Switch to the Fields Information tab in the node configuration section to view the field details of the public data.
Preprocess data
Heart disease prediction is a binary classification problem. The logistic regression model component requires input data of the DOUBLE or BIGINT type. The following describes how to preprocess heart disease case data, including data type conversion, for model training.
Data preprocessing: Convert non-numeric fields into numeric fields.
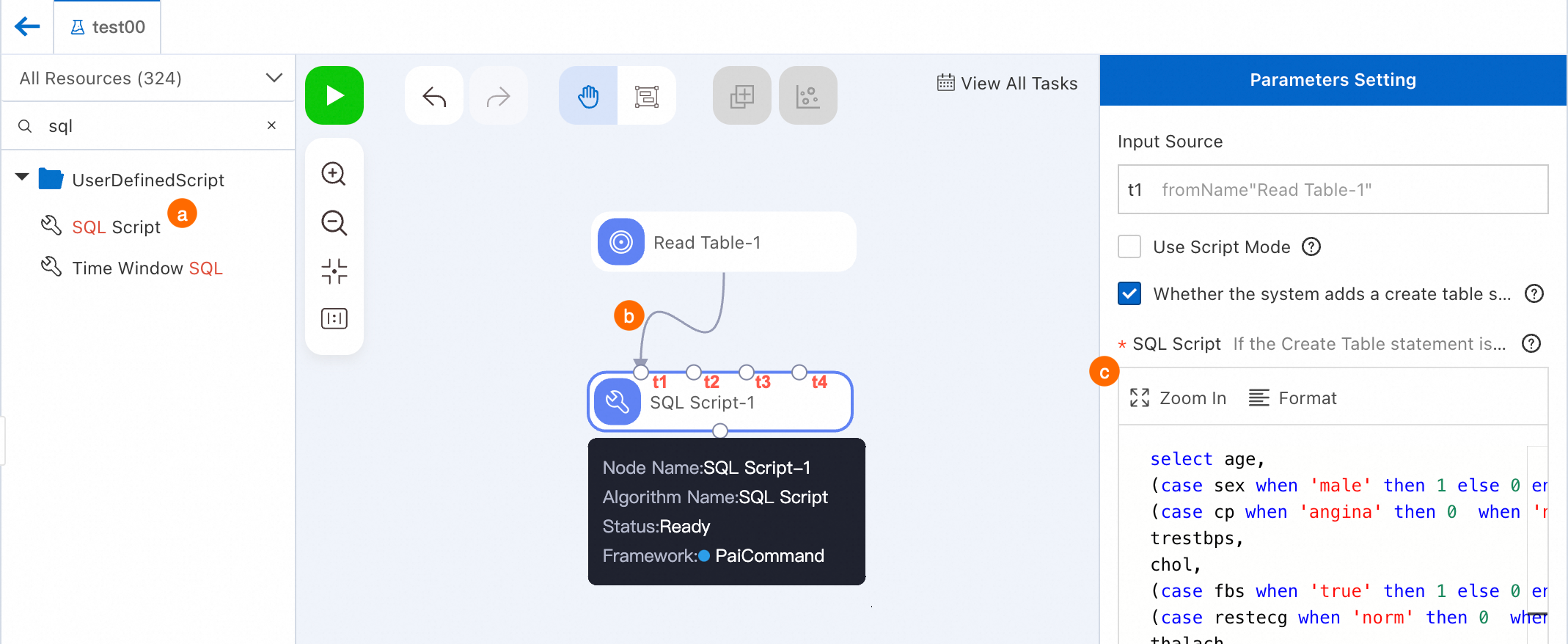
Search for the SQL Script component and drag it to the canvas. A pipeline node named SQL Script-1 is generated.
Draw a line from the Read Table-1 node to the t1 input port of the SQL Script-1 node. This way, the Read Table-1 node becomes the data source of the SQL Script-1 node.
Configure the SQL Script-1 node.
Click the SQL Script-1 node, and enter the following code in the SQL script editor on the right. On the Parameters Setting tab, t1 is displayed in the Input Source field.
select age, (case sex when 'male' then 1 else 0 end) as sex, (case cp when 'angina' then 0 when 'notang' then 1 else 2 end) as cp, trestbps, chol, (case fbs when 'true' then 1 else 0 end) as fbs, (case restecg when 'norm' then 0 when 'abn' then 1 else 2 end) as restecg, thalach, (case exang when 'true' then 1 else 0 end) as exang, oldpeak, (case slop when 'up' then 0 when 'flat' then 1 else 2 end) as slop, ca, (case thal when 'norm' then 0 when 'fix' then 1 else 2 end) as thal, (case status when 'sick' then 1 else 0 end) as ifHealth from ${t1};Click Save in the upper-left corner of the canvas to save the pipeline settings.
Right-click the SQL Script-1 component, and click Run from Root Node To Here to debug and run the pipeline.
Each node in the pipeline is run in sequence. After a node is run as expected, the node is marked with a
 icon in the node box displayed in the upper right corner of the node.Note
icon in the node box displayed in the upper right corner of the node.NoteYou can also click the
 (Run) icon in the left-corner of the canvas to run the entire pipeline. For complex pipelines, run specific nodes to facilitate debugging. If a node fails, right-click it and select View Log to diagnose the issue.
(Run) icon in the left-corner of the canvas to run the entire pipeline. For complex pipelines, run specific nodes to facilitate debugging. If a node fails, right-click it and select View Log to diagnose the issue.After the pipeline is run, right-click a node, such as SQL Script-1, and select to check whether the output data of the node is correct.
Data preprocessing: Convert the fields into the DOUBLE data type to meet the input data requirements of the logistic regression model.
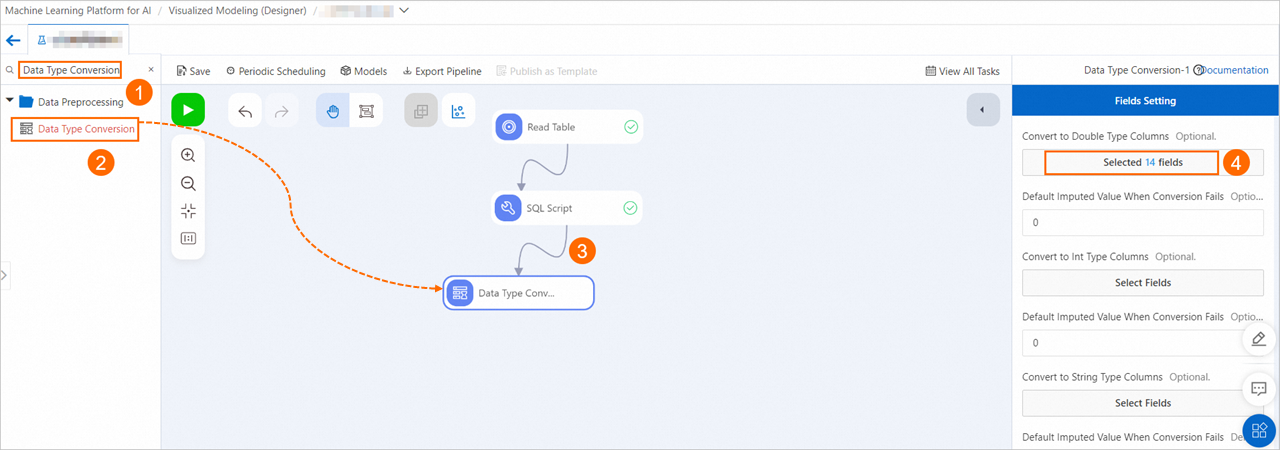
Drag the Data Type Conversion component to the canvas and connect the SQL Script-1 node to the Data Type Conversion-1 node by referring to the previous step. This way, the Data Type Conversion-1 node becomes the downstream node of the SQL Script-1 node. Click the Data Type Conversion-1 node. On the Fields Setting tab, click Select Fields in the Convert To Double Type Columns field, select all fields, and then convert the fields into the DOUBLE data type.
Data preprocessing: Normalize the data to convert the values of each feature to values ranging from 0 to 1. This removes the impact of dimensions on the prediction results.
Drag the Normalization component to the canvas and connect the Data Type Conversion-1 node to the Normalization-1 node by referring to the previous step. This way, the Normalization-1 node becomes the downstream node of the Data Type Conversion-1 node. Click the Normalization-1 node. On the Fields Setting tab, select all fields.
Data preprocessing: Split the data into a training dataset and a prediction dataset for subsequent model training and prediction.
Drag the Split component to the canvas and connect the Normalization-1 node to the Split-1 node. This way, the Split-1 node becomes the downstream node of the Normalization-1 node. After the Split-1 node is run, two data tables are generated.
By default, the Split component splits data into a model training set and a model prediction set at a ratio of 4:1. Click the Split-1 node. On the Parameters Setting tab on the right, specify the Splitting Fraction parameter. For more information about other parameters, see Split.
Right-click the Data Type Conversion-1 node, and click Run from Here to run the nodes in the pipeline from the Data Type Conversion-1 node.
Step 3: Train the model
In each sample, each patient is either sick or healthy. Therefore, heart disease prediction is a binary classification problem. The following steps show you how to use the logistic regression for binary classification component to build a heart disease prediction model.
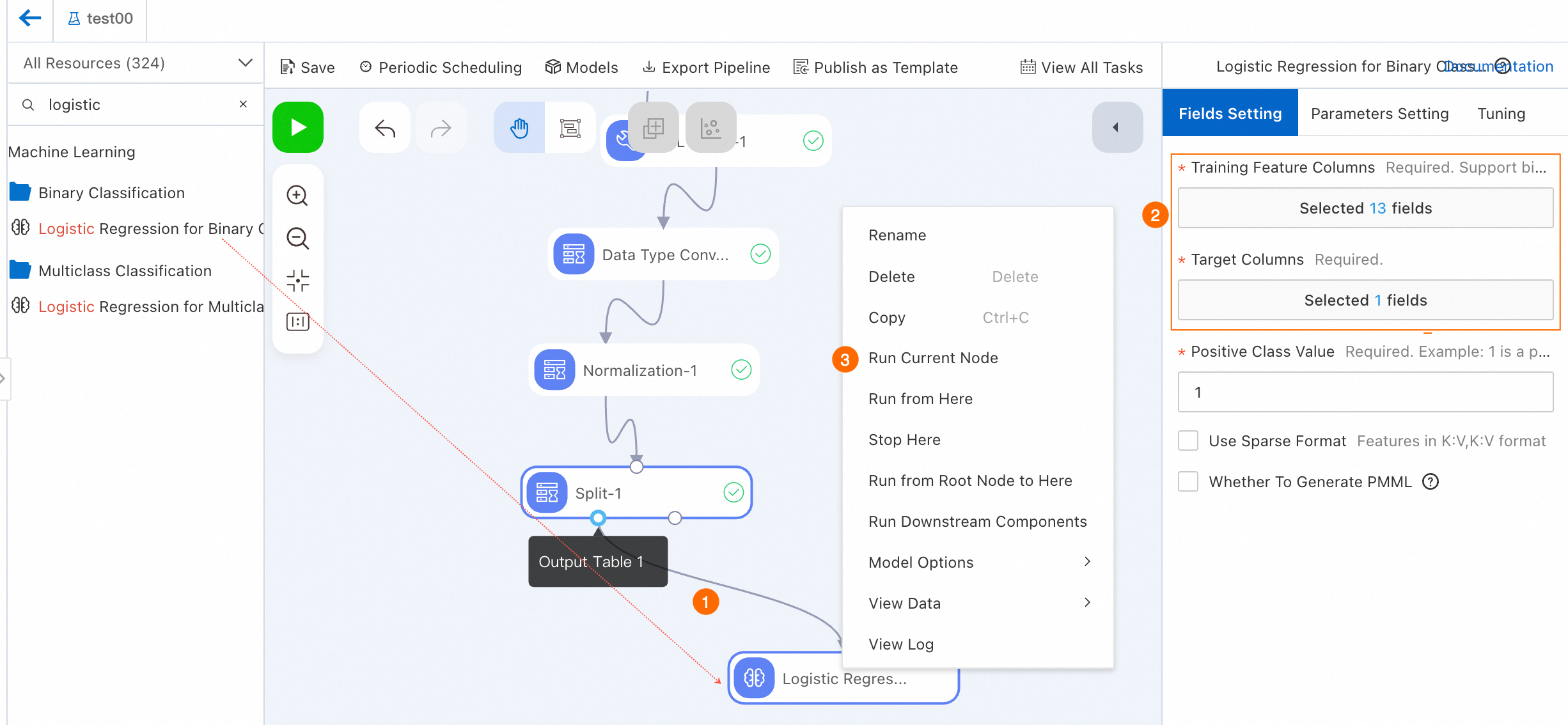
Drag the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification component to the canvas and connect Output Table 1 of the Split-1 node to the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification-1 node. This way, the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification-1 node becomes the downstream node of the Output Table 1 of the Split-1 node.
Configure the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification-1 node.
Click the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification-1 node. On the Fields Setting tab on the right, select the ifhealth field for the Target Columns parameter, and select all fields except the value of the Target Column parameter for the Training Feature Columns parameter. For more information about other parameters, see Logistic regression for binary classification.
NoteIf you need to deploy a model by following instructions in (Optional) Step 6: Deploy the model, click the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification-1 component. On the Fields Setting tab, select Whether To Generate PMML.
Run the Logistic Regression for Binary Classification node.
Step 4: Use the model for prediction
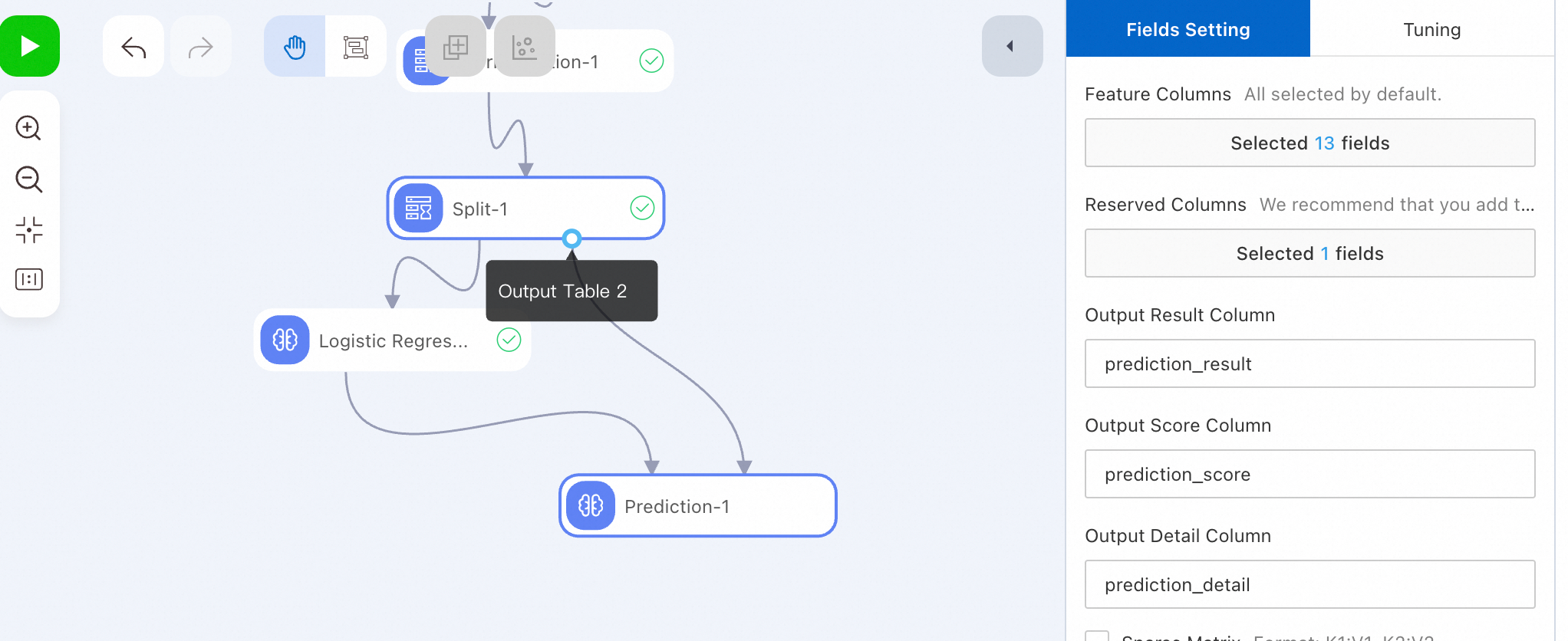
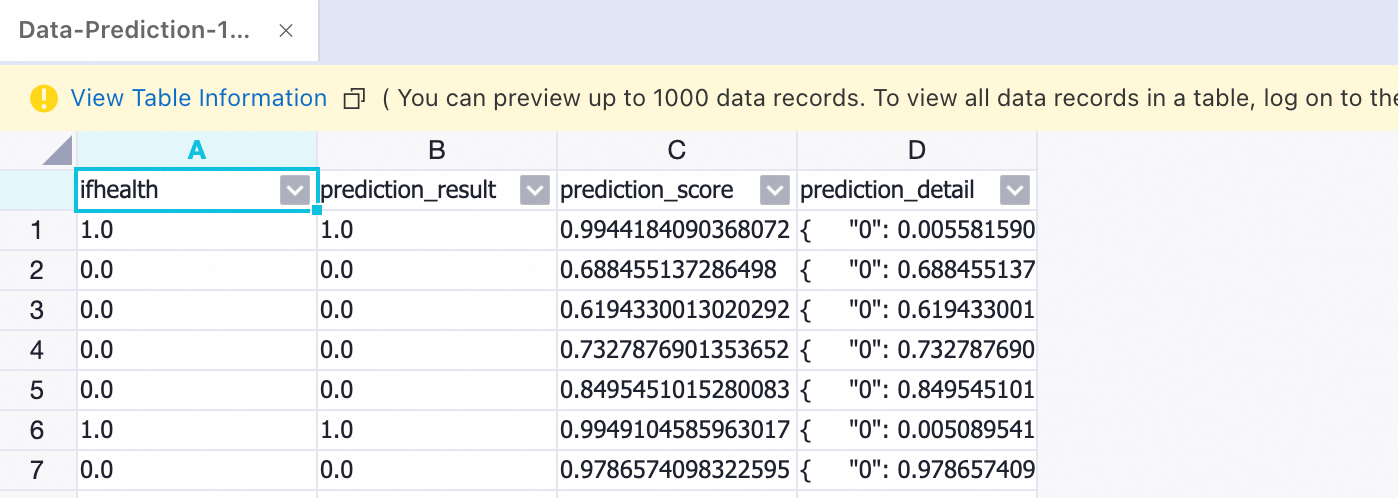
Run the Prediction-1 node and view the prediction results.
After the Prediction-1 node is run, right-click the Prediction-1 node, select , and then view the prediction data.
Step 5: Evaluate the model
Drag the Binary Classification Evaluation component to the canvas and connect the Prediction-1 node to the Binary Classification Evaluation-1 node. This way, the Binary Classification Evaluation-1 node becomes the downstream node of the Prediction-1 node.
Click the Binary Classification Evaluation-1 node. On the Fields Setting tab on the right, select the ifhealth field for the Original Label Column parameter.
(Optional) Step 6: Deploy the model
Machine Learning Designer can seamlessly integrate with Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS). After you train the model offline, complete model prediction, and evaluate the model, you can deploy the model to EAS as an online model service.
After the pipeline is run, click Models in the upper-left corner of the canvas. In the Models dialog box, select the desired model and click Deploy in EAS.
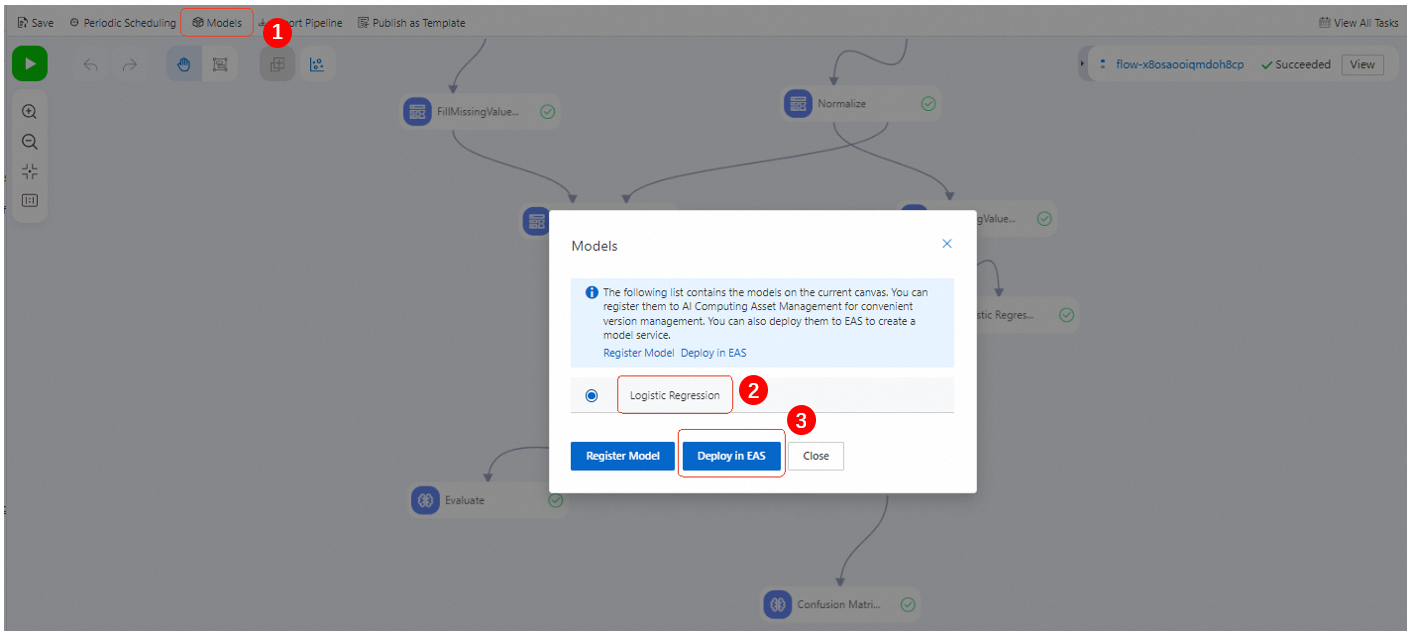
Confirm the parameter configurations. For more information, see Deploy a single model as an online service.
On the Create Service page, the Model File and Processor Type parameters are automatically configured. Configure other parameters as needed.
Click Deploy.
When the value of the Service Status parameter changes from Creating to Running, the model is deployed.
ImportantIf you no longer need a deployed model service, click Stop in the Actions column to avoid unnecessary costs.
References
Machine Learning Designer provides a variety of templates that you can use to build models. For more information, see Demo for creating a pipeline by using a template.
Pipelines can be scheduled in Machine Learning Designer by using DataWorks tasks. For more information, see Use DataWorks tasks to schedule pipelines in Machine Learning Designer.
You can configure global variables in pipelines to manage online pipelines and use DataWorks tasks to schedule pipelines, improving flexibility and efficiency. For more information, see Global variable.