The data pivoting algorithm is used to visualize datasets and explore analytical methods for the datasets in machine learning. It uses charts, tables, or other visual tools to show the structure, distribution, and relationships of the data. This helps users understand data characteristics, recognize patterns, and identify exceptions. The data pivoting algorithm is essential to data preprocessing and feature engineering, offering a clear and intuitive reference for modeling and analysis.
Configure the component
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
On the pipeline details page in Machine Learning Designer, add the Data Pivoting component to the pipeline and configure the parameters described in the following table.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Feature Columns | The feature columns to be visualized or analyzed. The distribution and relationships of the features are showed in charts or tables. |
Target Column | The column that you want to use for prediction or analysis. The column usually refers to tags or response variables. | |
Enumeration Features | The features that you want to use as enumeration features. | |
Sparse Format (K:V,K:V) | Specifies whether data in the sparse format is used. | |
Parameters Setting | Continuous Feature Discretization Intervals | The maximum number of discrete intervals into which continuous features are divided. |
Tuning | Cores | The number of cores used in computing. The value must be a positive integer. |
Memory Size per Core | The memory size of each core. Valid values: 1 to 65536. Unit: MB. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
Configure the component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see Scenario 4: Execute PAI commands within the SQL script component.
PAI
-name fe_meta_runner
-project algo_public
-DinputTable="pai_dense_10_10"
-DoutputTable="pai_temp_2263_20384_1"
-DmapTable="pai_temp_2263_20384_2"
-DselectedCols="pdays,previous,emp_var_rate,cons_price_idx,cons_conf_idx,euribor3m,nr_employed,age,campaign,poutcome"
-DlabelCol="y"
-DcategoryCols="previous"
-Dlifecycle="28"-DmaxBins="5" ;Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
inputTable | Yes | None | The name of the input table. |
inputTablePartitions | No | None | The partitions that are selected from the input table for training. Valid values:
Note If you specify multiple partitions, separate them with commas (,). For example, name1=value1,value2. |
outputTable | Yes | None | The name of the output table. |
mapTable | Yes | None | The output mapping table. The Data Pivoting component maps STRING-type data to INT-type data for PAI to use for training. |
selectedCols | Yes | None | The columns that are selected from the input table. |
labelCol | No | None | The column that you want to use for training. |
categoryCols | No | None | The INT- or DOUBLE-type columns that you want to use as enumeration features. |
maxBins | No | 100 | The maximum number of intervals for the equal-distance division of continuous features. |
isSparse | No | false | Specifies whether the input data is sparse. Valid values: true and false. |
itemSpliter | No | , | The delimiter that is used to separate key-value pairs if data in the input table is in the sparse format. |
kvSpliter | No | : | The delimiter that is used to separate keys and values if data in the input table is in the sparse format. |
lifecycle | No | 28 | The lifecycle of the output table. |
coreNum | No | Determined by the system | The number of cores used in computing. The value must be a positive integer. Valid values: 1 to 9999. |
memSizePerCore | No | Determined by the system | The memory size of each core. Valid values: 1 to 65536. Unit: MB. |
Examples
Generate the following test data.
age
workclass
fwlght
edu
edu_num
married
c
family
race
sex
gail
loss
work_year
country
income
39
State-gov
77516
Bachelors
13
Never-married
Adm-clerical
Not-in-family
White
Male
2174.0
0.0
40.0
United-States
<=50K
50
Self-emp-not-inc
83311
Bachelors
13
Married-civ-spouse
Exec-managerial
Husband
White
Male
0.0
0.0
13.0
United-States
<=50K
38
Private
215646
HS-grad
9
Divorced
Handlers-cleaners
Not-in-family
White
Male
0.0
0.0
40.0
United-States
<=50K
53
Private
234721
11th
7
Married-civ-spouse
Handlers-cleaners
Husband
Black
Male
0.0
0.0
40.0
United-States
<=50K
28
Private
338409
Bachelors
13
Married-civ-spouse
Prof-specialty
Wife
Black
Female
0.0
0.0
40.0
Other
<=50K
37
Private
284582
Masters
14
Married-civ-spouse
Exec-managerial
Wife
White
Female
0.0
0.0
40.0
United-States
<=50K
49
Private
160187
9th
5
Married-spouse-absent
Other-service
Not-in-family
Black
Female
0.0
0.0
16.0
Jamaica
<=50K
52
Self-emp-not-inc
209642
HS-grad
9
Married-civ-spouse
Exec-managerial
Husband
White
Male
0.0
0.0
45.0
United-States
>50K
31
Private
45781
Masters
14
Never-married
Prof-specialty
Not-in-family
White
Female
14084.0
0.0
50.0
United-States
>50K
42
Private
159449
Bachelors
13
Married-civ-spouse
Exec-managerial
Husband
White
Male
5178.0
0.0
40.0
United-States
>50K
Add the Read Table and Data Pivoting components and connect the components.
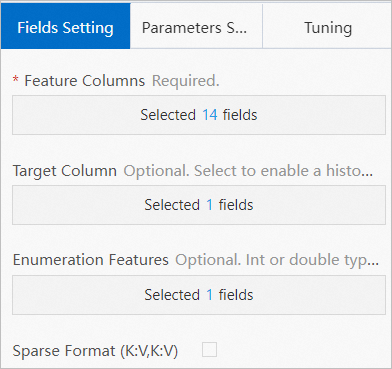
Click the Data Pivoting component and then click the Fields Setting tab. Set the Target Column parameter to income and specify the other 14 columns for the Feature Columns parameter. The BIGINT-type values in the edu_num column are used as enumeration values.
On the toolbar of the pipeline, click
 .
.After the pipeline is run, view the training result.
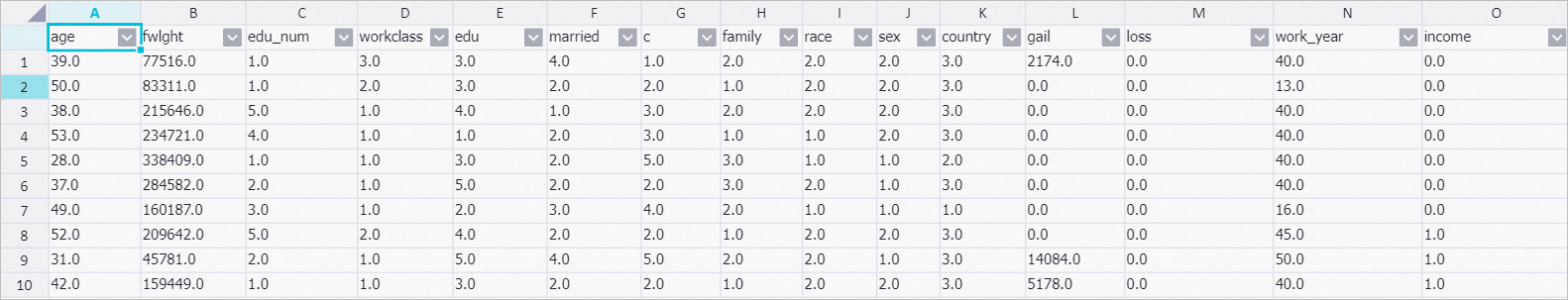
Right-click Data Pivoting and choose . The values in the family, race, sex, and income columns of the STRING data type are converted into numeric values for PAI to use for training. This is similar to data format conversion.
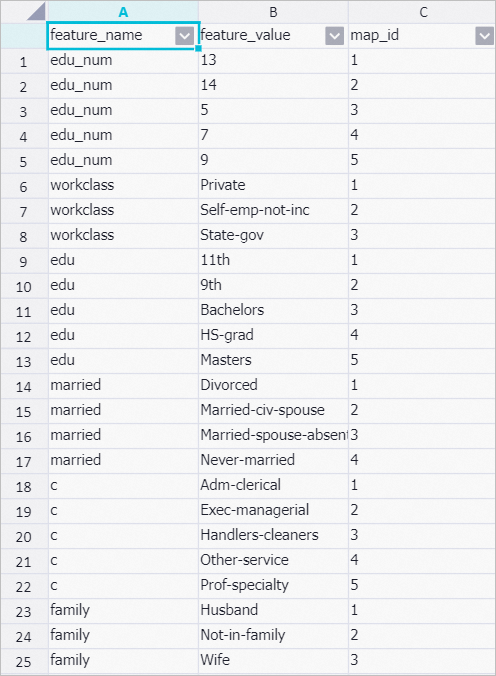
Right-click Data Pivoting and choose .
NoteIf you do not specify STRING-type data for the Feature Columns parameter, the String Column Feature Mapping Table parameter is left empty in the output.
Right-click Data Pivoting and choose .
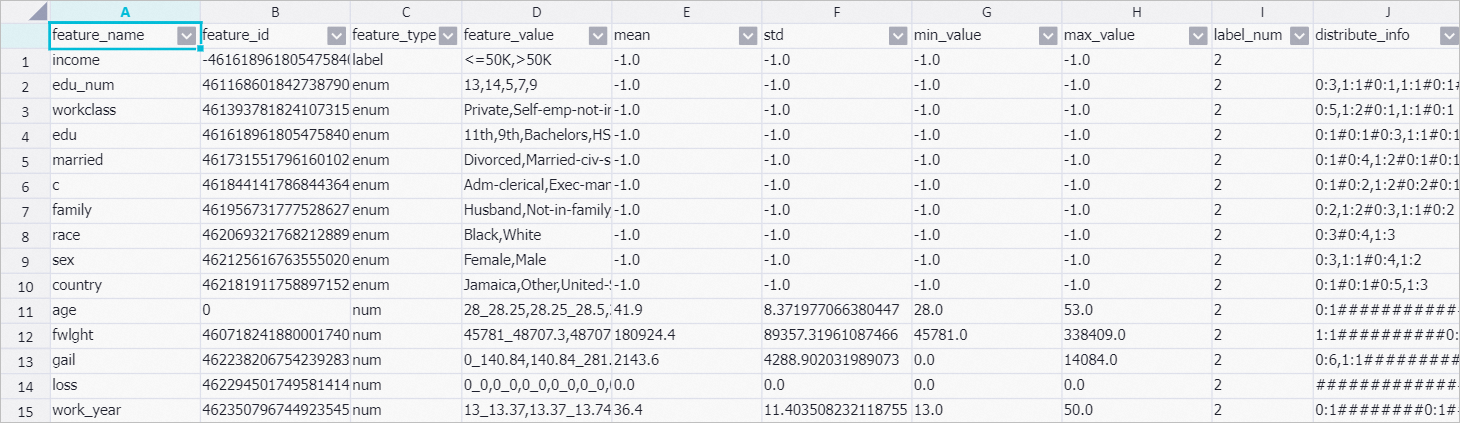 distribute_info indicates the number of records in each interval based on the uniform distribution between the maximum value and the minimum value.
distribute_info indicates the number of records in each interval based on the uniform distribution between the maximum value and the minimum value.