Heart disease threatens human lives. When body indicators for heart disease can be analyzed based on medical examination data, heart disease can be prevented. This topic describes how to use data mining algorithms to build a heart disease prediction model in Platform for AI (PAI) based on the medical examination data of heart disease patients.
Prerequisites
A workspace is created. For more information, see Create and manage a workspace.
MaxCompute resources are associated with the workspace. For more information, see Manage workspaces.
Data mining procedure

Predict heart disease
Go to the Machine Learning Designer page.
Log on to the PAI console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Workspaces. On the Workspaces page, click the name of the workspace that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Build a pipeline
On the Visualized Modeling (Designer) page, click the Preset Templates tab.
In the Heart Disease Prediction section of the Pipeline Template tab, click Create.
In the Create Pipeline dialog box, configure the required parameters. You can use the default values.
The value specified for the Data Storage parameter is the Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket path of the temporary data and models generated during the runtime of the pipeline.
Click OK.
It takes about 10 seconds to create the pipeline.
On the Pipeline list tab, find the pipeline named Heart Disease Prediction and click Open.
View the components of the pipeline on the canvas as shown in the following figure. The system automatically creates the pipeline based on the preset template.

Area
Description
①
The components displayed in this section preprocess data. For example, the components denoise the data, fill missing values, and convert values to numbers. In each sample, the patient is either healthy or sick. Therefore, heart disease prediction in this pipeline is a classification problem. The dataset used in this pipeline contains 14 feature fields and one goal field. During data preprocessing, the values of each field must be converted to numbers based on the meaning of the field. Parameters:
Two-valued field: The component converts one value to 0 and the other value to 1. For example, the value of the sex field is female or male. After the conversion, 0 specifies female and 1 specifies male.
Multi-valued field: The component converts the values to 0, 1, 2, or 3. For example, the cp field has four values that specify the type of chest pain from light to heavy. After the conversion, values 0 to 3 are used to specify the level of chest pain from light to heavy.
Sample SQL script:
select age, (case sex when 'male' then 1 else 0 end) as sex, (case cp when 'angina' then 0 when 'notang' then 1 else 2 end) as cp, trestbps, chol, (case fbs when 'true' then 1 else 0 end) as fbs, (case restecg when 'norm' then 0 when 'abn' then 1 else 2 end) as restecg, thalach, (case exang when 'true' then 1 else 0 end) as exang, oldpeak, (case slop when 'up' then 0 when 'flat' then 1 else 2 end) as slop, ca, (case thal when 'norm' then 0 when 'fix' then 1 else 2 end) as thal, (case status when 'sick' then 1 else 0 end) as ifHealth from ${t1};②
The components displayed in this section perform feature engineering, including feature derivation and scale change. The Type Transform component converts input feature data to the DOUBLE type because a logistic regression model accepts only input data of the DOUBLE type. Then, the Feature Select Runner component measures the impact of each feature on the prediction results by using the entropy and Gini index. The Normalize component converts the values of each feature to values that range from 0 to 1. This removes the impact of dimensions on the prediction results. The normalization formula is
result=(val-min)/(max-min).③
The components displayed in this section train the model and perform prediction.
The Split component divides the dataset into a training dataset and a prediction dataset at a 7:3 ratio.
The Logistic Regression component trains the model.
NoteIf you want to export PMML model files, select the Whether To Generate PMML check box on the Field Setting tab. Click a blank area on the canvas and specify Data Storage on the Pipeline Attributes tab.
The training and prediction datasets are imported to the Prediction component. The Prediction component generates the prediction results.
④
The Confusion Matrix and Evaluate components evaluate the model.
Run the pipeline and view the results.
In the upper-left corner of the canvas, click the
 icon.
icon. After the pipeline is run, right-click the Logistic Regression component on the canvas and choose to export the trained heart disease prediction model.
Right-click Prediction on the canvas and choose to view the prediction results. View the evaluation report of the model.
View the results.
Right-click Evaluate on the canvas and click Visual Analysis.
In the Evaluate dialog box, click the Index data tab to view the indexes that are used to evaluate the model.
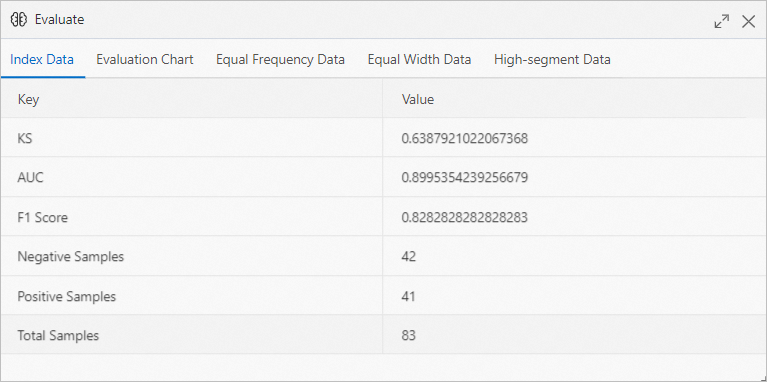 In the evaluation report, the value of AUC indicates that the prediction accuracy of the model is higher than 90%.
In the evaluation report, the value of AUC indicates that the prediction accuracy of the model is higher than 90%. Right-click Confusion Matrix on the canvas and click Visual Analysis.
In the Confusion Matrix dialog box, click the Statistics tab to view the model statistics, such as model accuracy.
Appendix: Heart disease datasets
The pipeline described in this topic uses an open source dataset from UCI Machine Learning Repository. For more information, see Heart Disease Data Set. The dataset contains the medical examination data of 303 heart disease patients in an area of the United States. The following table describes the fields in the dataset.
Field | Type | Description |
age | STRING | The age of the patient. |
sex | STRING | The gender of the patient. Valid values: female and male. |
cp | STRING | The type of chest pain that the patient has. Valid values: typical, atypical, non-anginal, and asymptomatic. |
trestbps | STRING | The resting blood pressure level of the patient. |
chol | STRING | The serum cholesterol level of the patient. |
fbs | STRING | The fasting blood sugar level of the patient. If the fasting blood sugar level is greater than 120 mg/dl, the value is set to true. Otherwise, the value is set to false. |
restecg | STRING | The resting electrocardiogram (ECG) result of the patient. Valid values: norm and hyp. |
thalach | STRING | The maximum heart rate of the patient. |
exang | STRING | Indicates whether the patient has exercise-induced angina. Valid values: true and false. |
oldpeak | STRING | The ST depression that is induced by exercise relative to rest. |
slop | STRING | The slope of the peak exercise ST segment. Valid values: down, flat, and up. |
ca | STRING | The number of major vessels that are colored by fluoroscopy. |
thal | STRING | The type of defect that the patient has. Valid values: norm, fix, and rev. |
status | STRING | The presence of heart disease in the patient. Valid values: buff and sick. |
This dataset is already included in workflows created from the template. For more information or to download the dataset, see Heart Disease Data Set.
What to do next
If the pipeline is running as expected, you can deploy the model for service calling. For more information about deployment, see Deploy a model as an online service and PMML processor.