When your Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket is under attack or is used to distribute illegal content, OSS automatically moves the bucket to the sandbox. The buckets that are in the sandbox can still respond to requests, but service degradation may occur. In this case, network availability may be affected, and a request timeout error is returned. After OSS automatically moves the bucket to the sandbox, your application may be aware of the operation.
Notes
If your bucket is under attack, OSS automatically moves the bucket to the sandbox. In this case, you must pay the costs that result from the attack.
If your bucket is used to distribute illegal content that involves pornography, political biases and terrorism, OSS moves the bucket to the sandbox. Users are held liable for violations of the law.
Preventive measures against attacks
To prevent your bucket from being moved to the sandbox due to attacks such as DDoS attacks and Challenge Collapsar (CC) attacks, you can configure OSS DDoS protection for the bucket. You can also configure a reverse proxy by using an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to access the bucket and configure an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance for the ECS instance. The following table describes the advantages and disadvantages of the two solutions.
Solution | Description | Advantage | Disadvantage |
Solution 1: Configure OSS DDoS protection | OSS DDoS protection is a proxy-based attack mitigation service that integrates OSS with Anti-DDoS Proxy. When a bucket for which OSS DDoS protection is enabled suffers a DDoS attack, OSS DDoS protection diverts incoming traffic to an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance for scrubbing and then redirects normal traffic to the bucket. This ensures business continuity in the event of DDoS attacks. |
| Limited number of protected buckets: Within each region, you can create only one Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, to which you can attach up to 10 buckets. |
Solution 2: Configure a reverse proxy by using an ECS instance to access the bucket and configure an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance for the ECS instance | To ensure data security, the default domain name of a bucket is resolved to a random IP address each time the bucket is accessed. If you want to use a static IP address to access the bucket, you can configure a reverse proxy by using an ECS instance to access the bucket. You can associate the elastic IP address (EIP) of the ECS instance with an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance to protect the bucket from DDoS attacks and CC attacks. | You can use this solution to protect your bucket when you use a static IP address to access OSS. |
|
Procedure
Solution 1: Configure OSS DDoS protection
Perform the following steps:
Creates an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance.
Attach the bucket that you want to protect to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance.
After that, the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance starts to protect access to the bucket by using the public endpoint of the bucket.
OSS DDoS protection can protect access by using only the public endpoints of the buckets, such as
oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. OSS DDoS protection cannot protect access by using the following endpoints:OSS-accelerated domain names, including the global OSS-accelerated domain name (
oss-accelerate.aliyuncs.com) and the OSS-accelerated domain name of regions outside the Chinese mainland (oss-accelerate-overseas.aliyuncs.com).Access point endpoints, such as
ap-01-3b00521f653d2b3223680ec39dbbe2****-ossalias.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.Object FC Access Point endpoints, such as
fc-ap-01-3b00521f653d2b3223680ec39dbbe2****-opapalias.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com).Endpoints accessed over IPv6, such as
cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyuncs.com.Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) endpoints, such as
s3.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com.
For more information, see OSS DDoS protection.
Solution 2: Configure a reverse proxy by using an ECS instance to access the bucket and configure an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance for the ECS instance
Perform the following steps:
Configure a reverse proxy by using an ECS instance to access your bucket.
Create an ECS instance that runs CentOS or Ubuntu. For more information, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
ImportantIf the bucket encounters bursts of network traffic or spikes in access requests, you need to upgrade the hardware configurations of ECS or create ECS clusters.
Configure a reverse proxy by using an ECS instance to access the bucket. For more information, see Use ECS instances to configure a reverse proxy to access OSS.
Configure an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance.
Purchase an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance based on your business requirements.
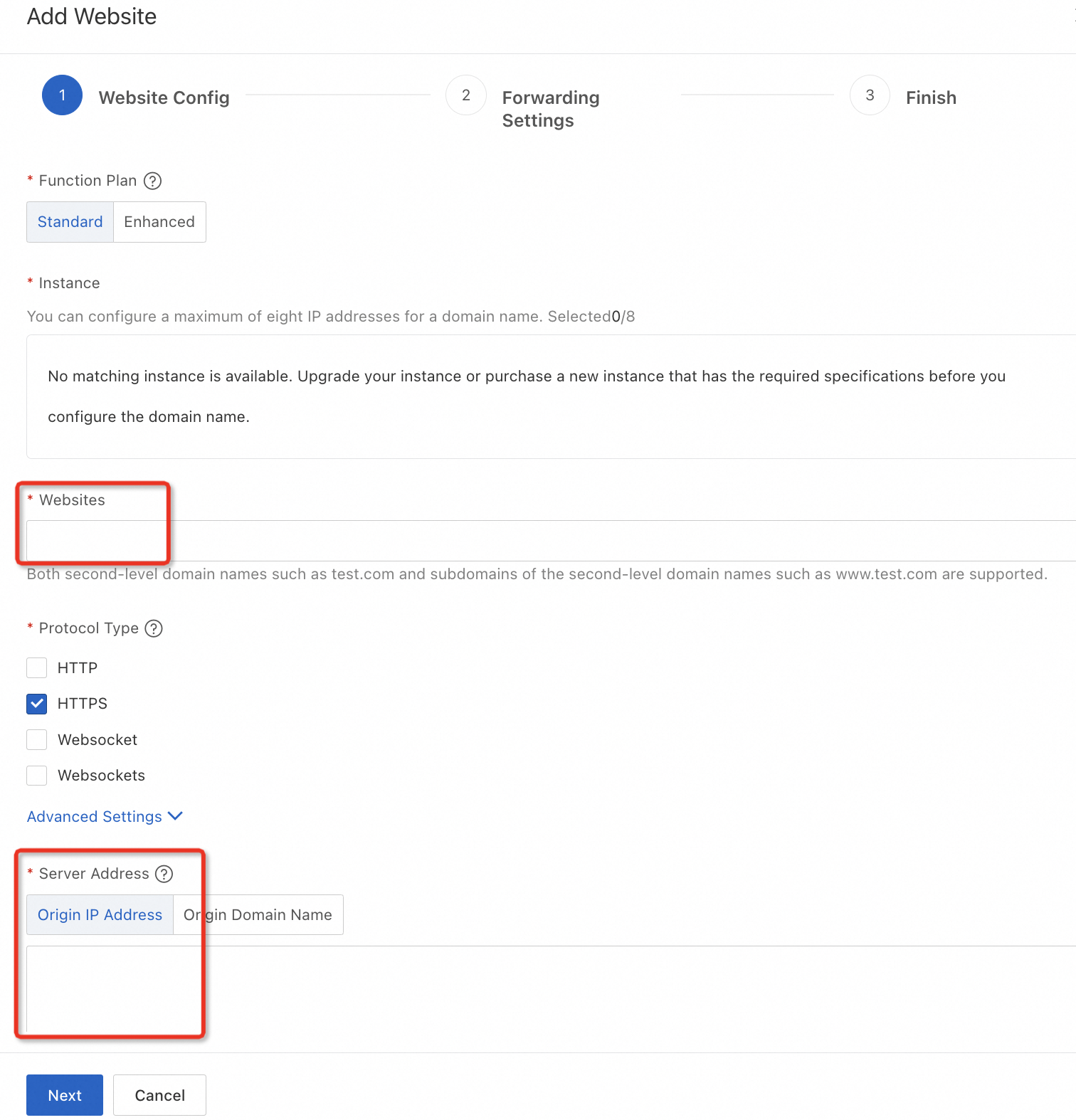
Add website(s): Enter the endpoint of the bucket that you want to protect by using the ECS reverse proxy in Websites. Select Origin IP Address for Server Address and enter the public IP address of the ECS instance in the field.
Remove buckets from the sandbox that were added as a result of attacks
Alibaba Cloud does not allow you directly remove buckets from the sandbox that were added due to attacks.
To remove buckets sandboxed due to the following attack-related reasons, you need to configure OSS DDoS protection.
Buckets get sandboxed because they suffered multiple attacks.
Existing and new buckets get sandboxed because some other buckets in the account suffered multiple attacks.
For detailed information about how to configure OSS DDoS protection, see Configure OSS DDoS protection. After you configure OSS DDoS protection, the buckets will automatically be removed from the sandbox and remain accessible by using their original IP addresses or DDoS-protected IP addresses.