Feature description
Analysis is a basic but important feature of search engines. Analysis results directly affect search performance. The meaning of a phrase varies with different business scenarios and contexts. Therefore, the expected analysis results change based on diversified business scenarios. In addition to basic analyzers that apply to all industries, OpenSearch provides industry-specific analyzers, such as the analyzer for text from the E-commerce industry.
To meet diversified business requirements, OpenSearch allows you to create a custom analyzer by using a built-in analyzer and intervention entries. You can select analyzers when you configure index fields for an application. This way, OpenSearch can adjust the process of analysis during indexing and searches to ensure that search results meet your expectations.
Intervention entries
You can manage intervention entries by using the secondary analysis feature.
If you enable secondary analysis, the text in the results of the original custom analyzer is segmented again. If you disable secondary analysis, the results of the original custom analyzer are retained.
For example, if the entry is "开放搜索" (OpenSearch) and the general analyzer for Chinese is specified, the results with secondary analysis enabled are as follows:
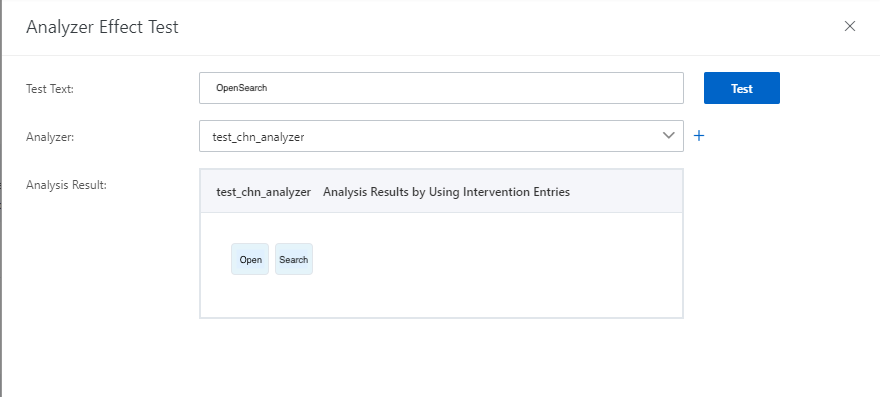
The results with secondary analysis disabled are as follows:
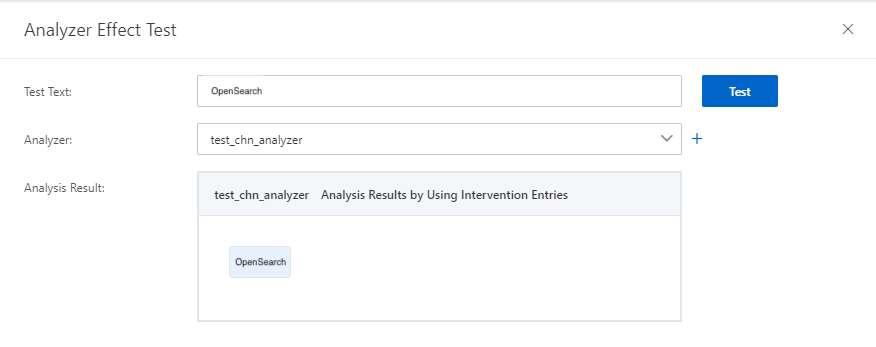
Usage notes
The entries in the custom analyzer are composed of all entries for the specified analyzer type and manually added entries in the analyzer. The manually added entries have a higher priority than the entries for the specified analyzer type.
You can create up to 20 custom analyzers by using the new OpenSearch console.
A custom analyzer can contain up to 1,000 intervention entries.
The key of each entry cannot exceed 10 characters in length and the value of each entry cannot exceed 32 characters in length. Each character can be a Chinese character or a letter.
The key and value of an entry cannot contain uppercase letters, full-width characters (\uff01 - \uff5e), and Chinese punctuations.
The key and value of an intervention entry for semantic-based analysis must be the same after spaces in the value are deleted. Sample entries:
The key is "不正确的词条", and the value is "错误 的 词条". The key is "正确的词条", and the value is "正确 的 词条".The first entry is invalid because the key is not the same as the value after spaces are deleted.
The key of an entry cannot contain spaces. Sample entries:
The key is "不正确 词条", and the value is "不 正确 词条". The key is "正确词条", and the value is "正确 词条".The first entry is invalid because the key contains spaces.
The key of an entry cannot be part of the value of another entry in the same intervention dictionary. Sample entries:
The key is "自定义分词器", and the value is "自定义 分词器". The key is 分词器. The key is 分词.The second entry is invalid because its key "分词器" is part of the value of the first entry. The third entry is valid..
Procedure
Overview
1. Create a custom analyzer. 2. Modify the offline version of an application. 3. Perform reindexing. 4. Use the custom analyzer.
Procedure
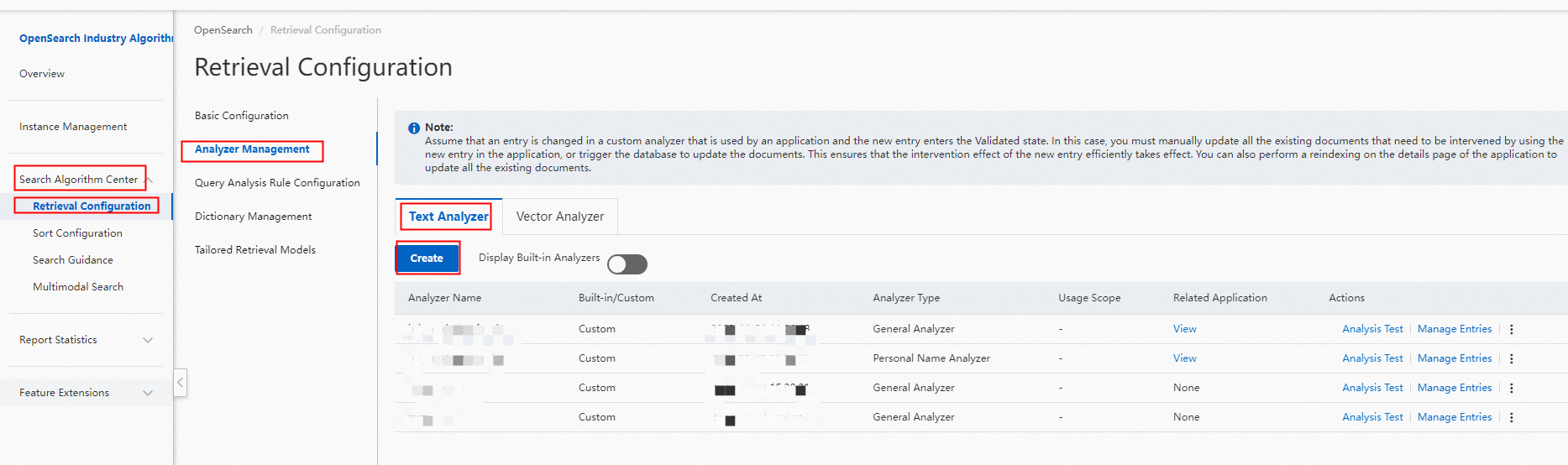
1. Log on to OpenSearch console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Search Configuration Center > Retrieval Configuration. On the Basic Configuration page, click Analyzer Management in the left-side pane. On the Analyzer Management page, click Create.
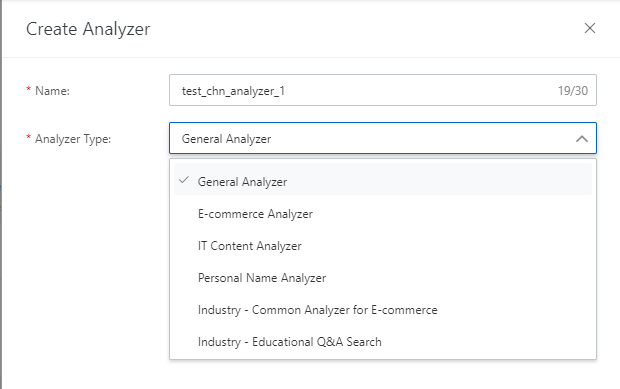
2. In the Create Analyzer panel, enter an analyzer name, select a analyzer type, and then click Save.
3. On the Manage Entries page of the created custom analyzer, click Add. In the Add Intervention Entry panel, set the Search Query and Analysis Results parameters, and turn on Secondary Analysis. In this example, the phrase "糯米" (sticky rice) is used.
 Note: Separate terms with spaces. Example: The key is "糯米", and the value is "糯 米".
Note: Separate terms with spaces. Example: The key is "糯米", and the value is "糯 米".
4. Run an analysis test to check analysis results after the added intervention entry takes effect.
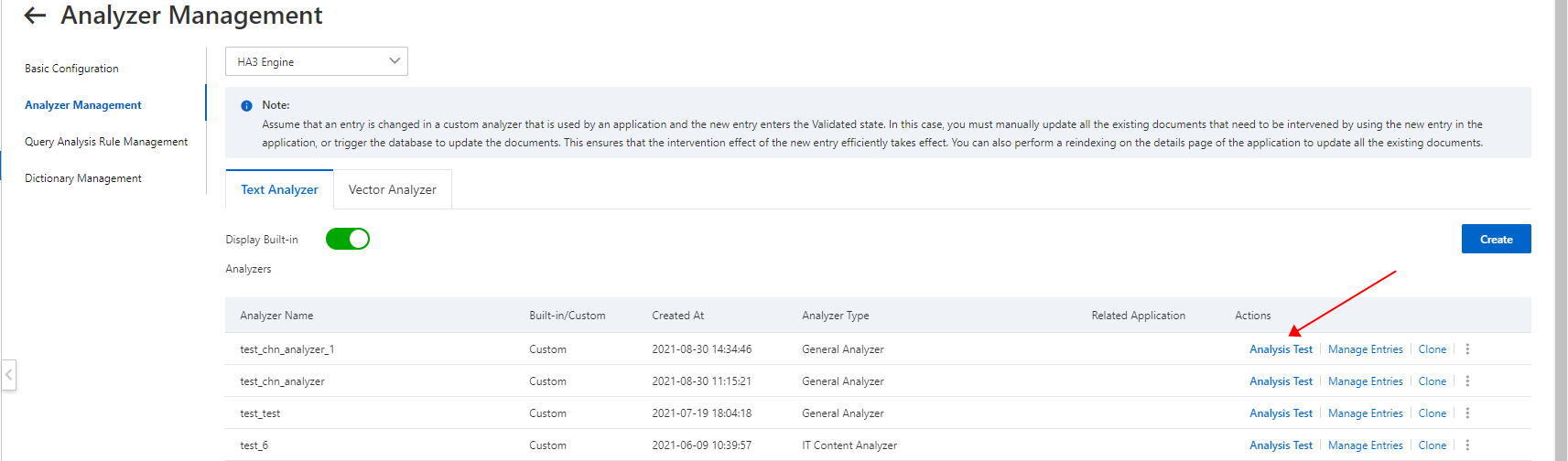
4.1. Enter Sticky rice in the Test Text field.
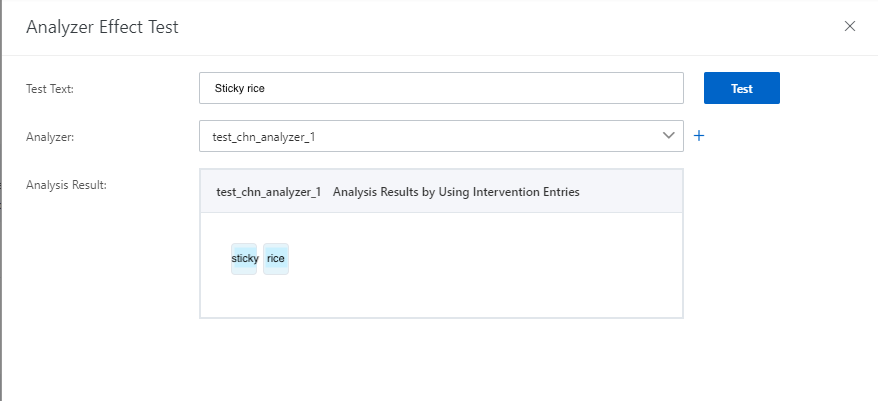
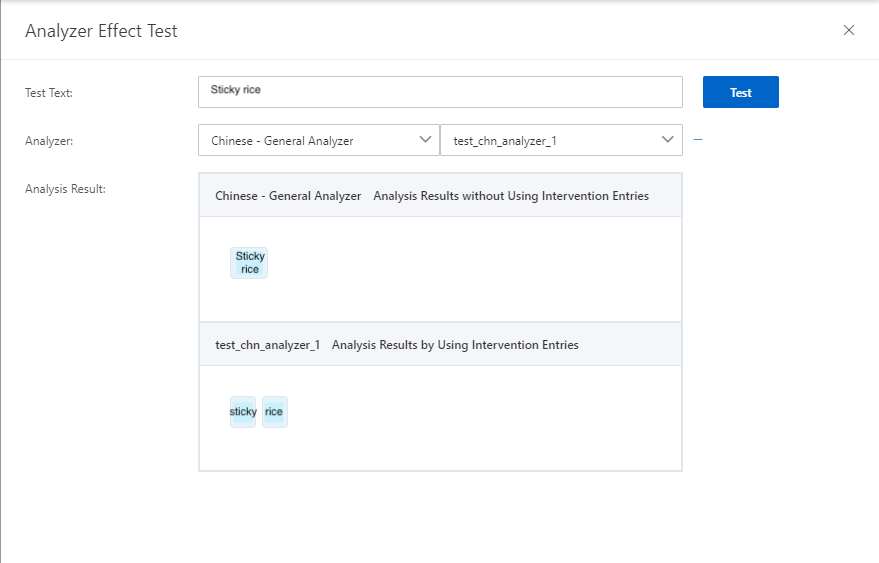
4.2. The following figure shows the analysis results of multiple custom analyzers.
5. After the analysis test is complete, go to the Basic Configuration page to modify an application configurations offline.
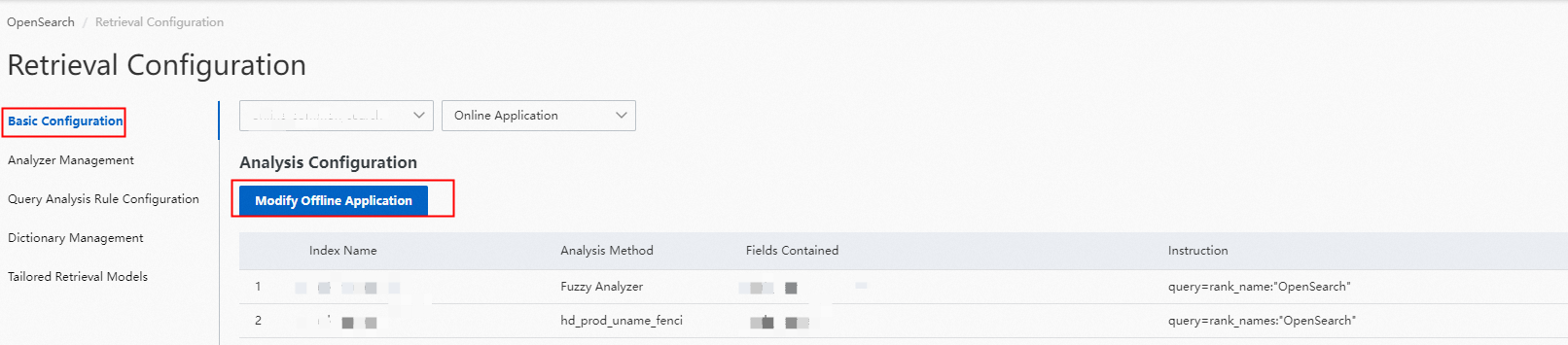
Note: OpenSearch generates an offline application based on your settings. If you modify the offline application, the online application is not affected.
6. In the Index Field List section, find the index for which you want to configure the custom analyzer and select the custom analyzer from the drop-down list in the Analysis Method column.
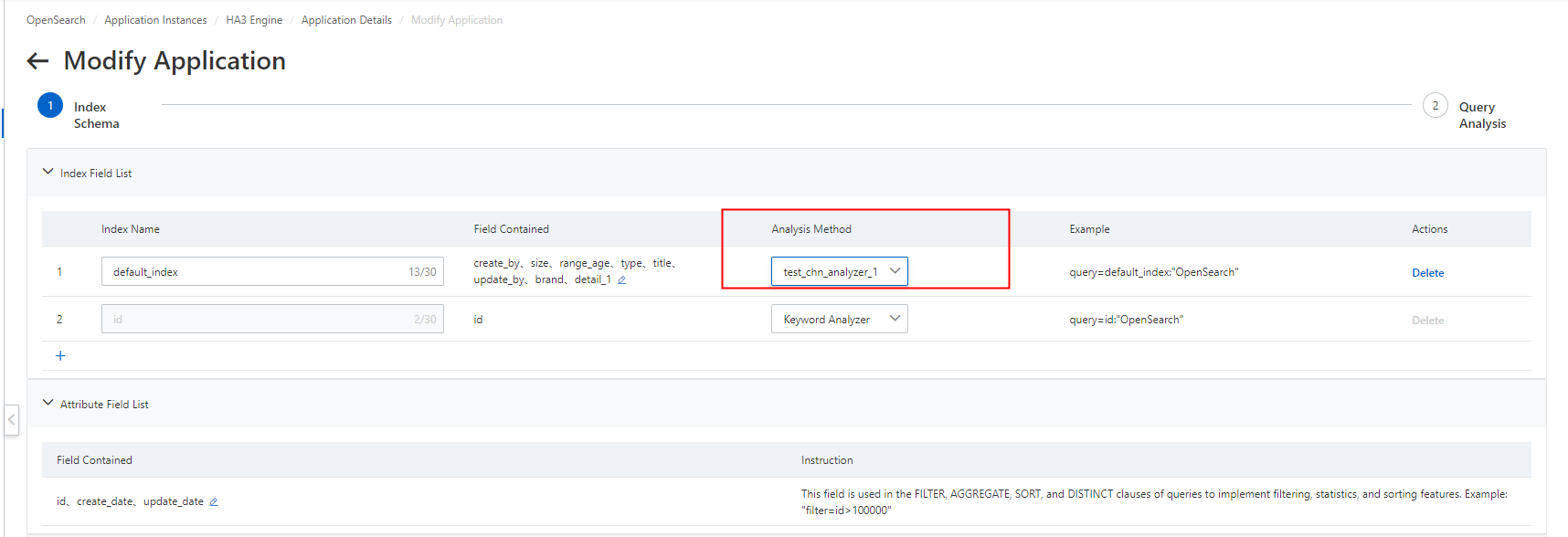
7. Wait until the custom analyzer takes effect after reindexing.
Search results of the custom analyzer
If you use the general analyzer for Chinese, documents that contain "糯米", "小米", or "大米" cannot be retrieved when you search for "米." In this case, you can perform the preceding operations to create a custom analyzer that is named test_zw. After you modify the schema of the application for which the custom analyzer is configured and perform reindexing, the documents can be retrieved as expected, as shown in the following figure.
Usage notes
The new OpenSearch console allows you to add intervention entries to existing custom analyzers. If you add intervention entries to a custom analyzer that is used by an application, the intervention entries take effect only after reindexing is performed. If you want the intervention entries to take effect at the earliest opportunity, you can update documents whose analysis results are not expected to trigger reindexing.
The key of an entry in a custom analyzer cannot exceed 10 characters in length.
The key of an entry in a custom analyzer cannot contain uppercase letters, full-width characters, and Chinese punctuations.
The value of an entry in a custom analyzer cannot contain uppercase letters, full-width characters, and Chinese punctuations.
If you turn off Secondary Analysis, OpenSearch does not segment the terms that are generated at the first time. Otherwise, OpenSearch further segments the terms.
You cannot delete a custom analyzer that is used by an application.