Background information
CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) allows you to perform an operation on multiple Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances at a time. To do so, go to the Batch Instance Operations page in the OOS console. OOS supports the following batch operations on multiple instances: sending remote commands, performing basic O&M operations, and modifying instance attributes. The supported remote commands include shell commands in Linux and Bat and PowerShell commands in Windows. The supported basic O&M operations include starting, stopping, and restarting ECS instances, and initializing and replacing the system disks of ECS instances. The attributes that can be modified for multiple instances include the instance name, hostname, and instance description.
If you perform an operation such as starting, stopping, or restarting ECS instances, the specified ECS instances are started, stopped, or restarted. This may cause service interruption.
If you perform an operation such as initializing or replacing the system disks of the specified ECS instances, the data on the system disks may be lost.
Procedure
Log on to the OOS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Common O&M Tasks. On the Batch Instance Operations page, click Create.
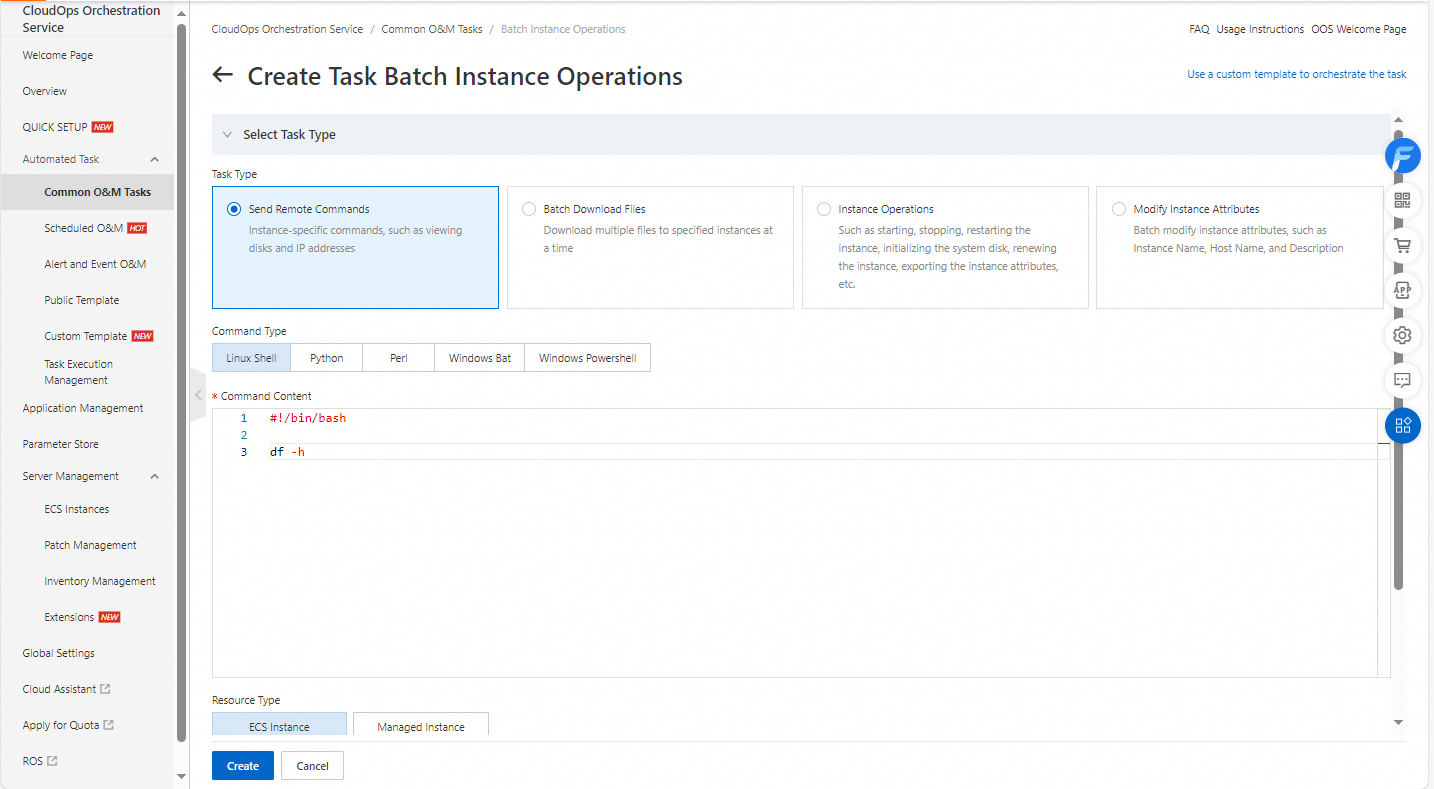
Select a task type. You can select Send Remote Commands, Batch Download Files, Instance Operations, or Modify Instance Attributes as the task type. In this example, Send Remote Commands is selected as the task type. The Command Type parameter is set to Linux Shell, and the df -h command is entered.
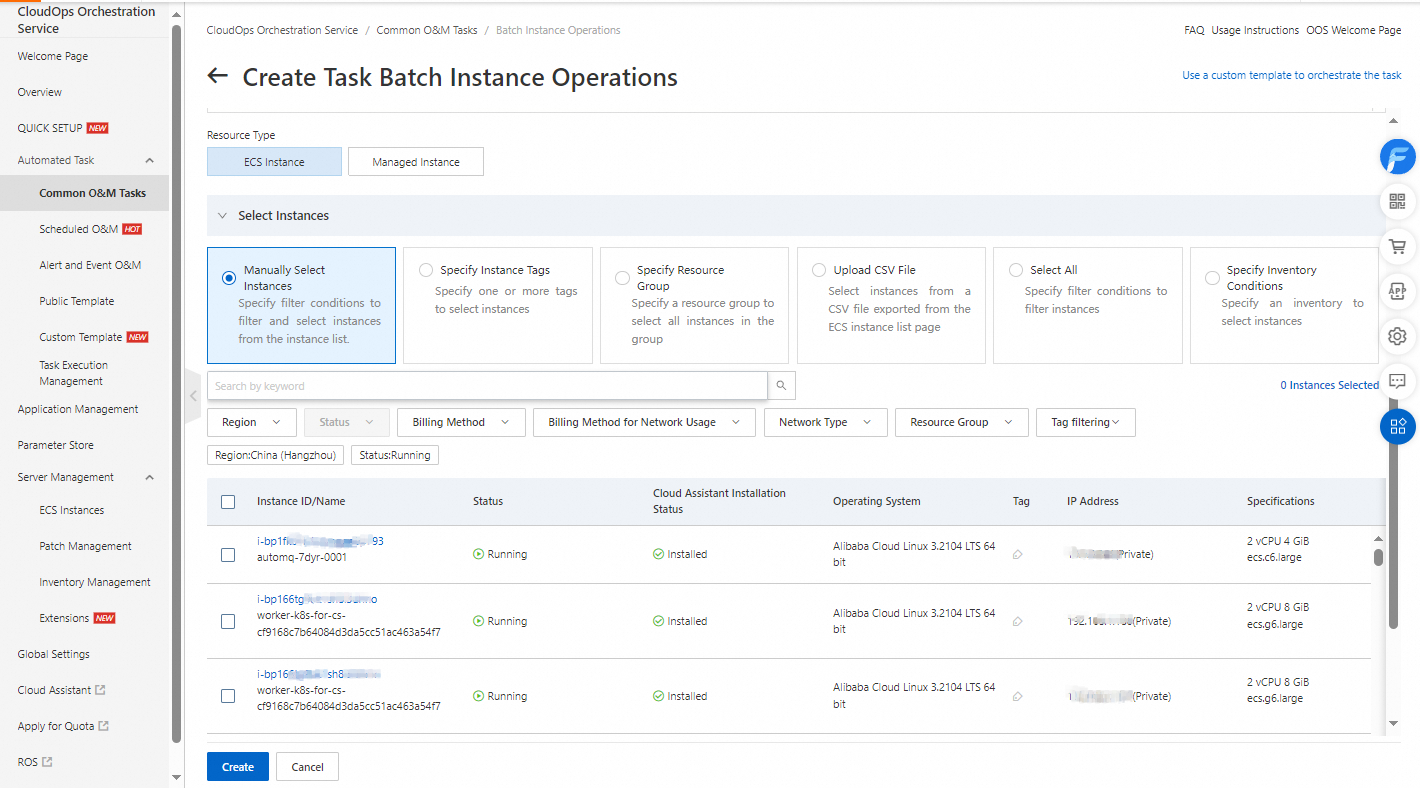
Select instances. You can select Manually Select Instances, Specify Instance Tags, Specify Resource Group, Upload CSV File, Select All, or Specify Inventory Conditions as the instance selection method. In this example, Manually Select Instances is selected.
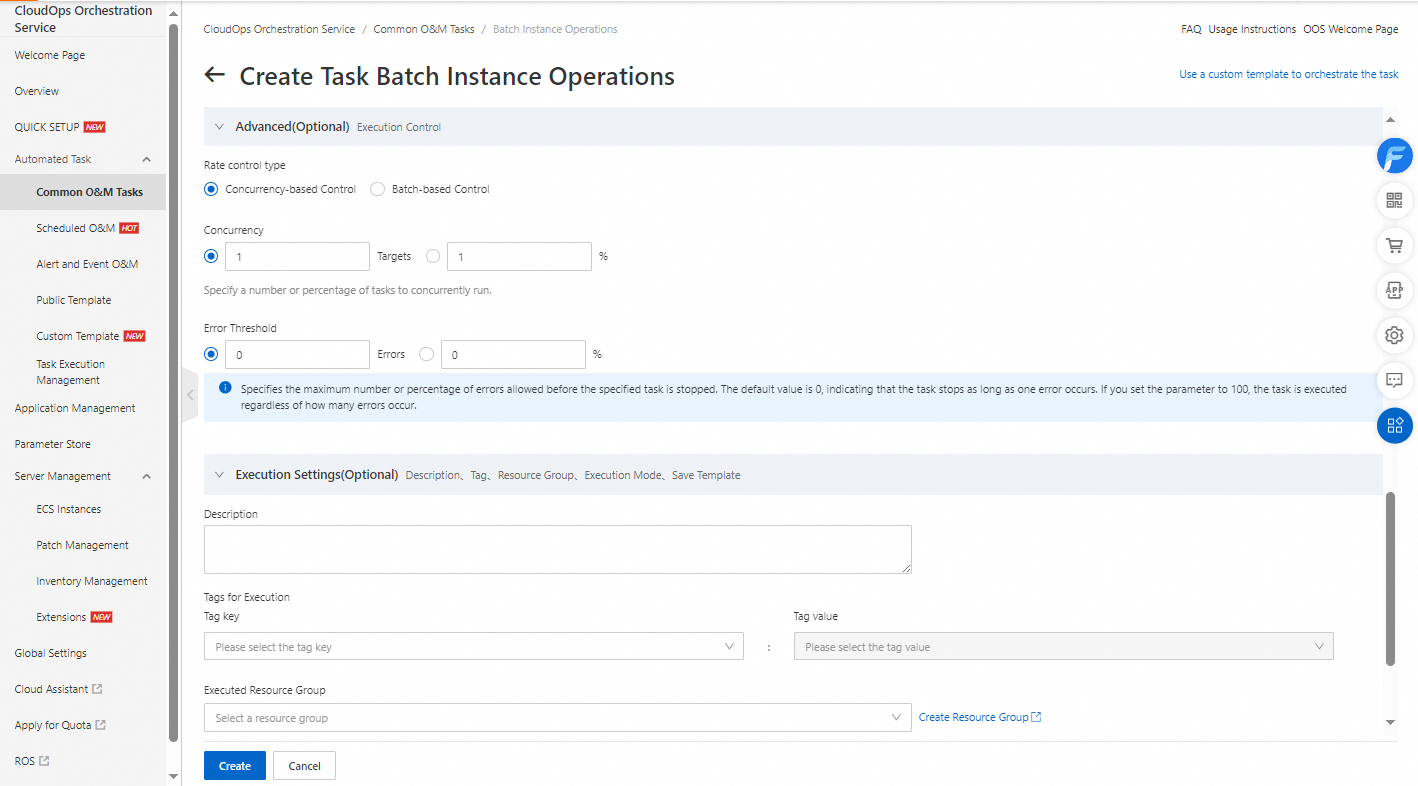
Configure the advanced options. You can set the Execution Mode parameter to Automatic or Suspend upon Failure, set the Rate control type parameter to Concurrency-based Control or Batch-based Control, and configure the Concurrency and Error Threshold parameters. In this example, the default values are used. Click Create.
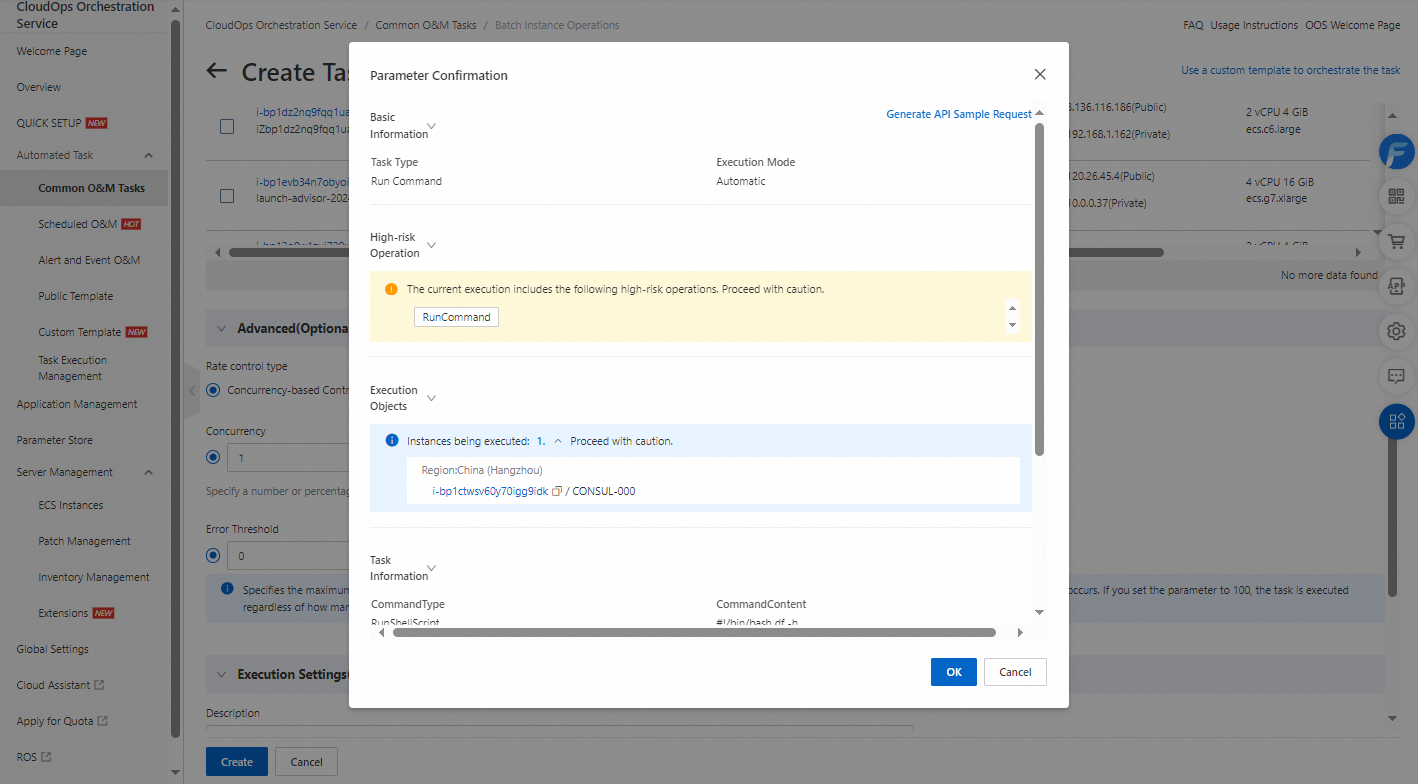
Confirm the parameter settings. If the settings are correct, click OK.
On the Batch Instance Operations page, find the execution that you create and check whether the execution is in the Running state. When the state of the execution changes to Success, the command is successfully run. To view more information about the execution, click Details in the Actions column. On the page that appears, click the Log tab in the Output section to view the execution logs.