This sample template is used to pull code from GitHub to create a Docker image, upload it to Container Registry, and then deploy it on multiple Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. This is applicable to scenarios where you need to create an image, upload the image to an image repository, and deploy the image on multiple ECS instances. You can run this template on an existing ECS instance or run this template to create a temporary ECS instance. After the image is created and uploaded, the temporary ECS instance is automatically released. In addition, this template allows you to upload images to and pull images from Container Registry Enterprise Edition or Container Registry Personal Edition based on your business requirements. You are charged for using Container Registry Enterprise Edition. You can use Container Registry Personal Edition free of charge.
Prerequisites
An ECS instance is created and the ECS instance can access the Internet. For more information, see Create an ECS instance and Enable Internet access.
Container Registry Personal Edition or Enterprise Edition is activated. For more information, see What is Container Registry, Differences between Personal Edition instances, Cost-effective Edition instances, and Enterprise Edition instances, and Create a Container Registry Personal Edition instance.
Sample template

You specify the code source, such as Object Storage Service (OSS) or GitHub. CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) generates a temporary URL for the code source to pull code from the code source.
OOS automatically pulls code to install Docker and executes a script to create an image. After the image is created, OOS uploads the image to the specified image repository in Container Registry.
Pull the image created in the previous step and deploy the image as a Docker container on multiple ECS instances at a time.
Example
Prepare the code source
The sample code of a Spring Boot project is used in this example. The code is uploaded to Gitee and GitHub. If you want to use the code, you must fork the code to your own repository. Code address:
Gitee: Sample code (recommended for users in the Chinese mainland)
GitHub:Sample code (recommended for users in the Chinese mainland)
Create a message template
Log on to the CloudOps Orchestration Service console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose and click Create Template.
In the Build and Deploy section, select ACS-ECS-ExampleDockerBuildAndDeployFromGit and click Next Step.
On the Process Configuration tab, set the parameters and click Create Template.
Specify the code source to generate a temporary authorization link.
In this example, Gitee is used as the code source. Set the following parameters: Owner, Organization, Repository, and Branch.
NoteIf Alibaba Cloud is not authorized to access your GitHub or Gitee repository, click Grant the required permissions.
If you have forked the sample code, all repositories that belong to your account are automatically displayed in the Repository drop-down list. In this case, select the repository to which you forked the code.

Create a Docker image and upload it to Container Registry.
Specify the code source and an ECS instance, and specify the configuration script as needed.
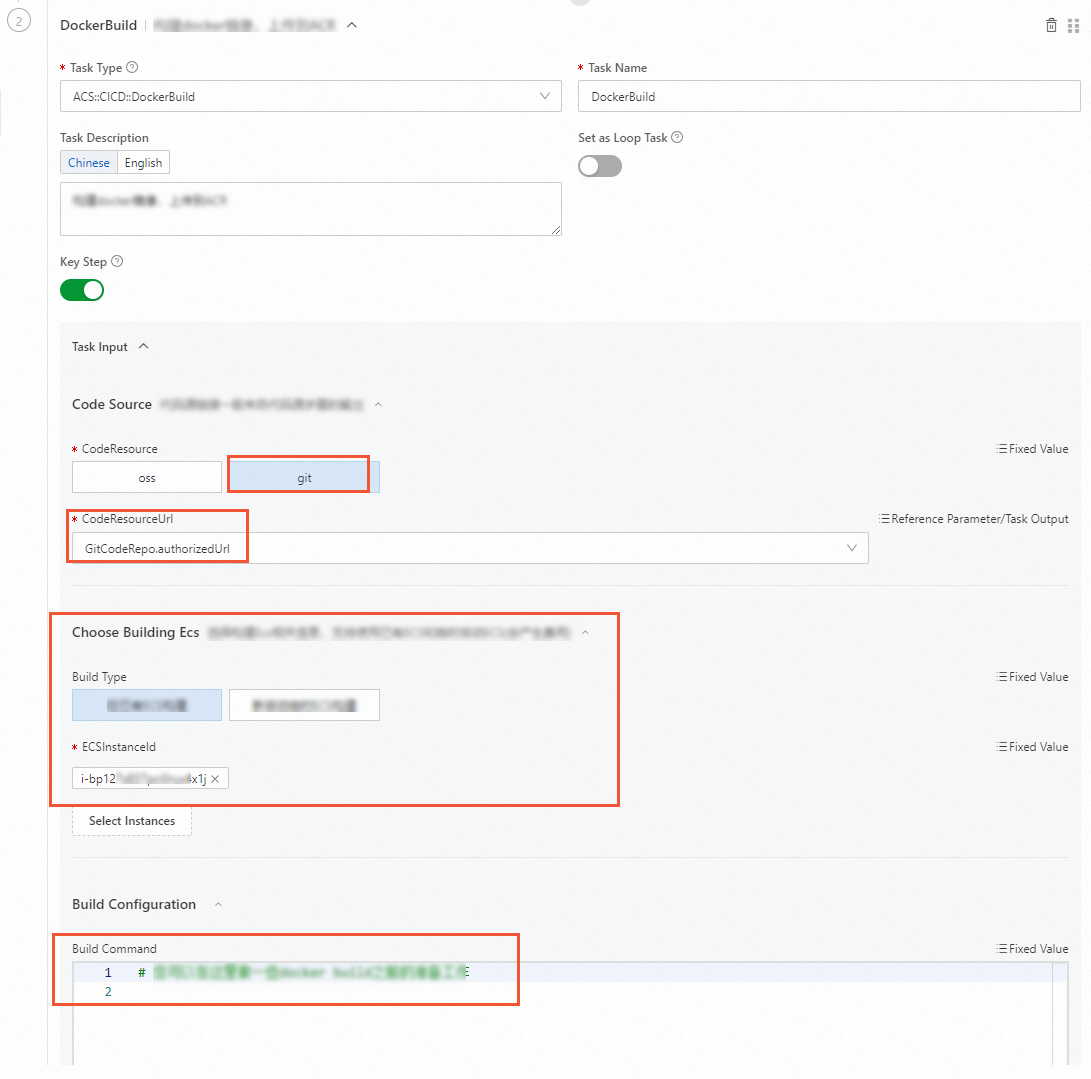
Set CodeResource to
gitand use the default valueauthorizedUrlfor CodeResourceUrl.Choose Building Ecs: Select an ECS instance. You can select Existing ECS or New ECS.
NoteIf you select New ECS, you are charged on a pay-as-you-go basis. OOS automatically checks whether Docker is installed on the ECS instance. If Docker is not installed, OOS automatically installs Docker Community Edition on the ECS instance.
Build Configuration: provides build commands as needed. All builds in the sample code are completed in the Dockerfile. No additional preparation is required.
Create a Docker image and upload it to Container Registry.
OOS automatically runs the
docker buildcommand to create an image. You must specify the path of theDockerfileand the context path in which thedocker buildcommand is run.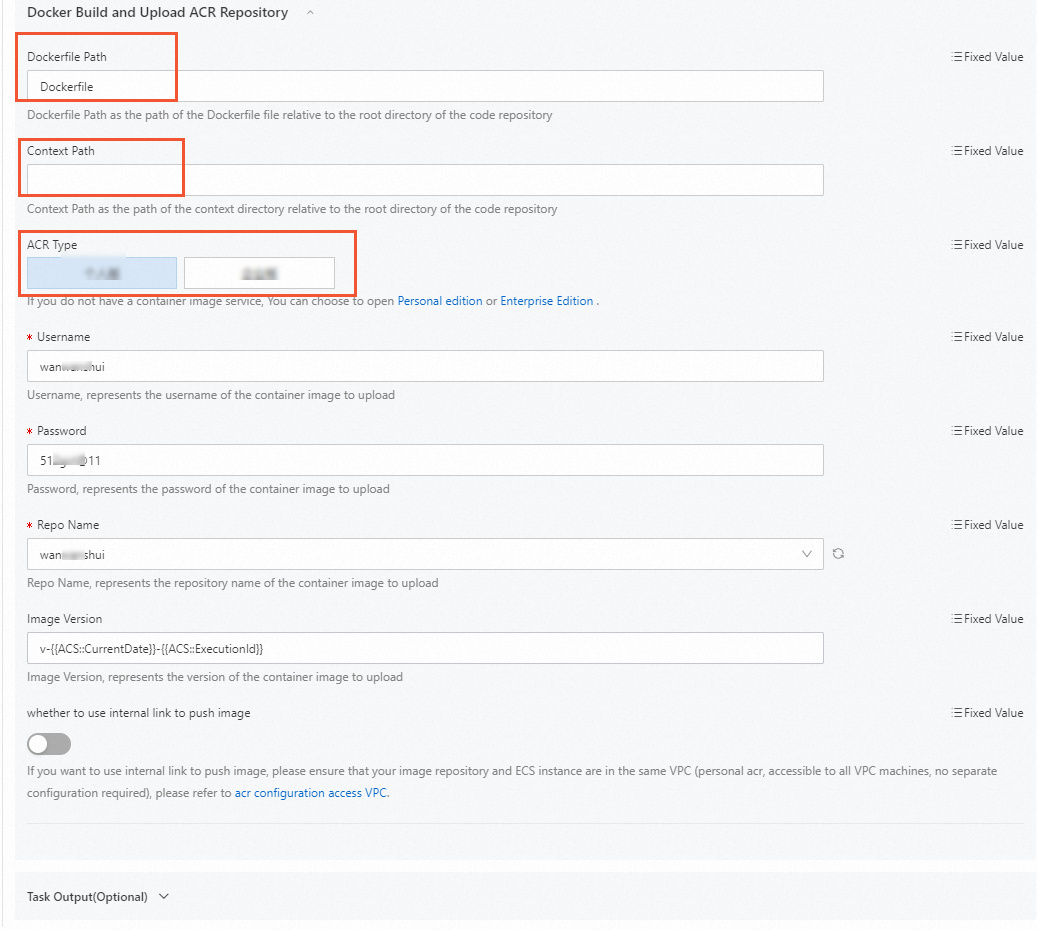
Dockerfile Path: the path of the Dockerfile relative to the repository root directory. As shown in the following figure, Dockerfile is stored in the root directory of the pulled code. Therefore, you can directly specify the name of the Dockerfile.

Context Path: Set Context Path to the execution context of the
docker buildcommand. Enter a path relative to the code root directory. If you do not specify this parameter, the path is the same as the Dockerfile directory.ACR Type: Select Enterprise Edition (charged) or Personal Edition (free of charge).
ACR Type
Description
References
Personal Edition
You need to specify the username, password, and the name of the repository to which the image is uploaded.
Enterprise Edition
You need to specify the Container Registry instance ID, namespace, and the name of the repository to which the image is uploaded
Specify the image version. The default value consists of the current date and the execution ID. You can specify the image version of your project. Check whether the image is uploaded over a virtual private cloud (VPC). For more information, see Configure a VPC ACL.
Pull the image from Container Registry and deploy it.
Select the ECS instances on which you want to deploy the image.
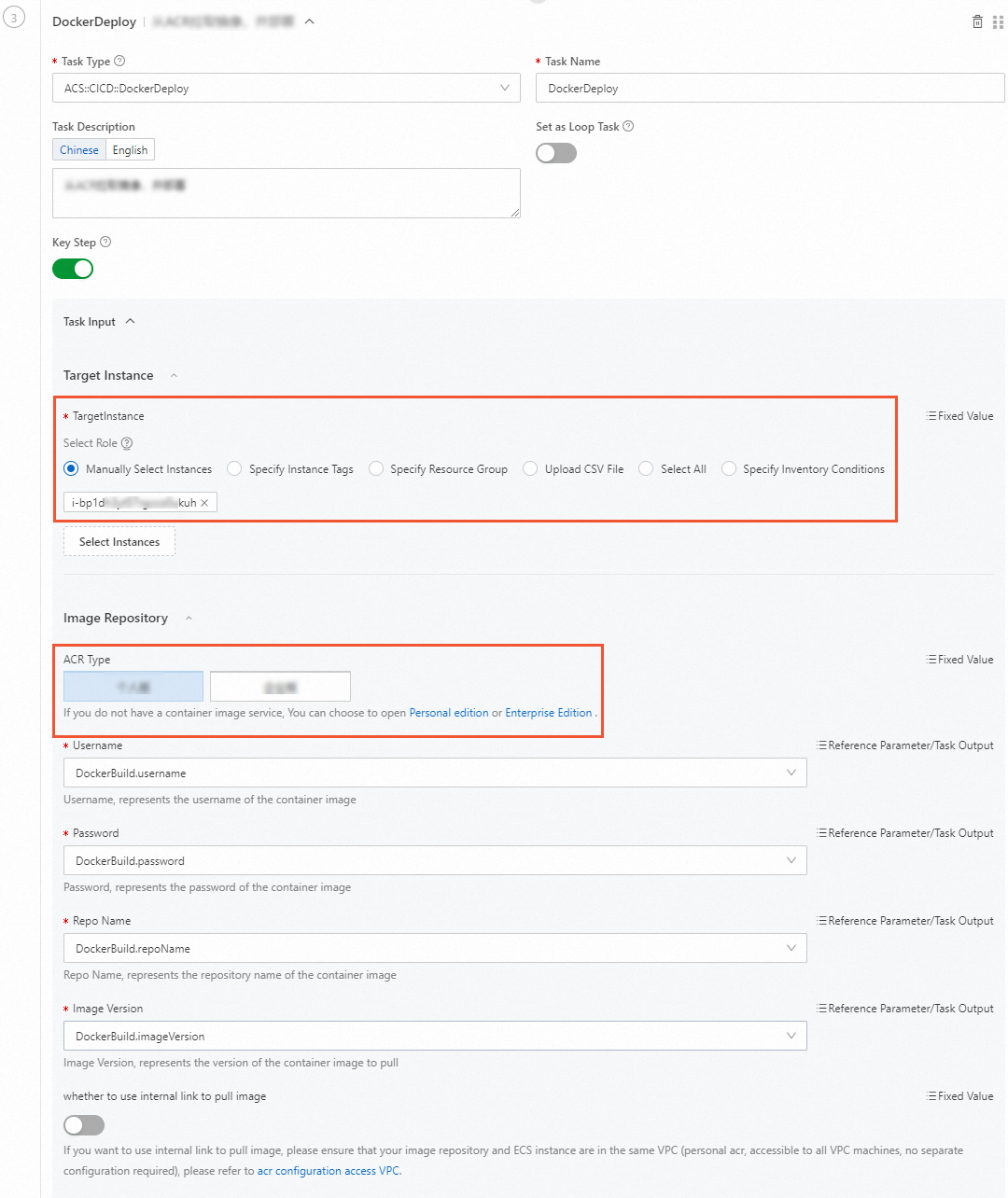
Target Instance: You can select one or more ECS instances at a time.
Image Repository: To pull the image uploaded to Container Registry in the previous step, select the edition of Container Registry. The following parameters are automatically referenced from the previous outputs:
imageVersion,username,password,acrId,namespace, andrepoName.NoteFor more information about how to pull an image by using a VPC, see Configure a VPC ACL.
Specify the running options of Docker.
For example, if you enter
-p 8080:8080, these options will be added to thedocker runcommand and will be executed.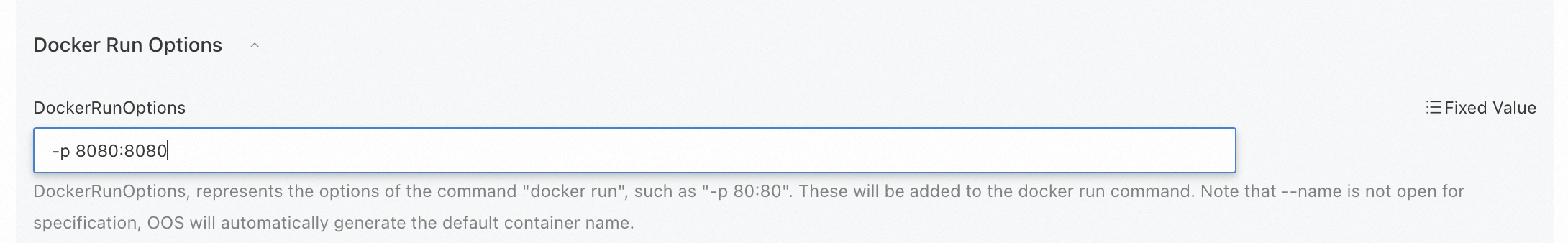
docker run -p 8080:8080 <image_name>NoteThe
--nameoption is not available because OOS assigns a default name that corresponds to the Container Registry repository to the container. Each time before OOS runs thedocker runcommand to use the image of the current version, OOS first checks whether any image with the same name is running. If so, it stops the container and then runs thedocker runcommand to use the current image version. This way, the next time you upload the latest version of the image to the Container Registry repository, you can directly execute the template again without manually stopping the container corresponding to the previous version of the image.Optional. Set the concurrency control parameters to control the concurrency rate of multiple ECS instances.
Click Create Template.
Execute the template
Log on to the CloudOps Orchestration Service console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Custom Template page, find the template and click Create Execution in the Actions column.
In the Basic Information step, set the parameters and click Next Step: Parameter Settings.
In the Parameter Settings step, click OK if no parameters are available.
Click Create.
On the Task Execution Management page, if the execution status is Success, the execution is complete.

Log on to the ECS console.
Find the ECS instance and connect to the instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Run the following command to check whether the deployment is successful.
curl http://localhost:8080/helloIf the following message is returned, the deployment is successful.

You can also run the
docker pscommand to view the corresponding container.
What to do next
If your code is modified, you only need to upload the new code to the Git repository and re-execute the CI/CD template. The template stops the current container, regenerates an image, and pushes it to Container Registry. Then, the latest version of the image is deployed on the specified ECS instances in batches. You can also modify the template if needed and execute the template again.