Perform the following steps to diagnose the iOS client problems:
- Initialize diagnosis service
- Set user ID
- Write diagnosis logs
- View local diagnosis logs
- Obtain online user diagnosis logs
Initialize diagnosis service
Before using the diagnosis function, initialize it first.
#import <MPDiagnosis/MPDiagnoseAdapter.h>[MPDiagnoseAdapter initDiagnose];
The diagnosis service supports pulling logs through Sync or Push method. Codes for initializing the diagnosis service vary with the log pulling method.
Use Mobile Sync Service (Sync)
If you use the Sync method to pull diagnostic logs, you need to initialize the service before using the diagnostic function.
#import <MPDiagnosis/MPDiagnoseAdapter.h>[MPDiagnoseAdapter initDiagnose];
Use Message Push Service (Push)
You need to integrate the Message Push Service, and complete Message Push Service initialization first. After receiving the message pushed, call the following method:
#import <APLog/APLogMgr.h>[[APLogMgr sharedInstance] handlePushDiagnosisCmd:[notification.userInfo objectForKey:@"content"]];
Upgrade precautions
The Category file of the APLogUser class does not need to be added since version 10.1.32. The middle tier implements packaging. After upgrade, check for configurations of the earlier version in the project and delete them if any. The following shows the configurations that must be removed from the new version.
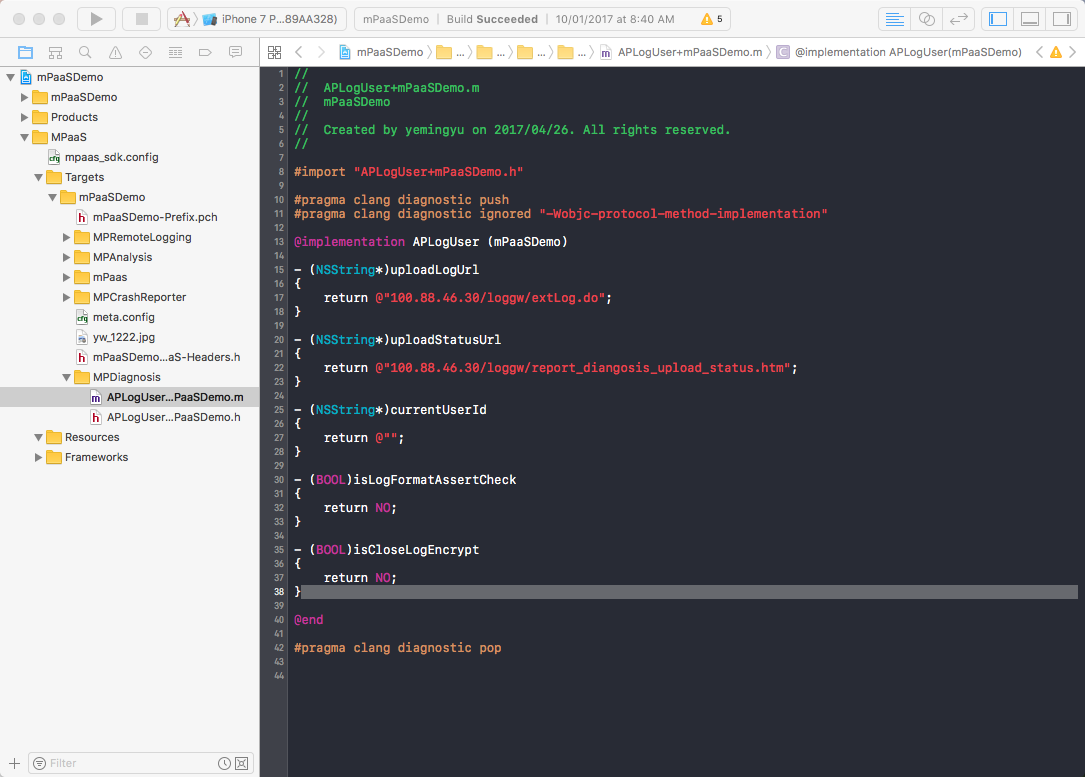
Set user ID
The diagnosis service extracts logs based on user ID.
Set user ID by using the
userIdfunction during the implementation ofMPaaSInterface.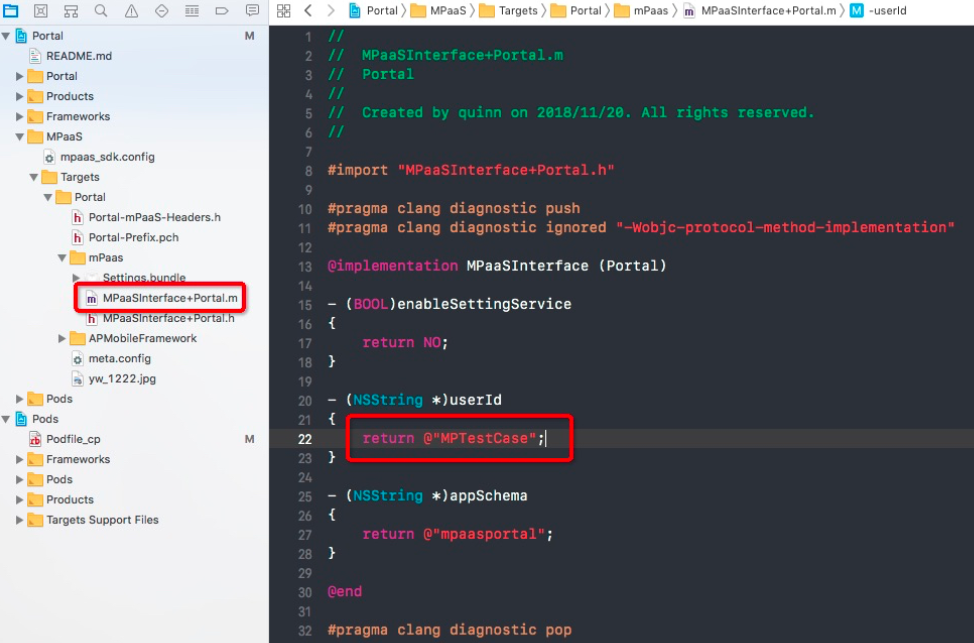
- During user switching, that is, when the value configured in the
userIdfunction ofMPaaSInterfacechanges, call the following function:
For more information, see the[MPDiagnoseAdapter userChange];
MPDiagnoseAdapter.hfile underMPDiagnosis.
Write diagnosis logs
Call the following method to write diagnosis logs on the critical link of the App:
/*** Log a message with kAPLogLevelInfo level.** @param message An NSString object that contains a printf-style string containing a log message and placeholders for the arguments.* @param ... The arguments displayed in the format string.*/#define APLogInfo(tag,fmt, ...) \APLogToFile(tag, kAPLogLevelInfo, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
For more information, see the APLog.h file under APLog.
For example, call the following statement to write diagnosis logs after startup:
APLogInfo(@"mPaaS", @"Start Cost %d", time);
- Logs written by APLogInfo are not printed in the Xcode console. To print related logs in the console during the development phase, add the ConsoleLog file to the project.
- Out of security concerns, if you do not want your App to print any logs (including logs printed by NSLog and APLogInfo) after going online, you can add the RemoveNSLog file to the project when the app’s release package is generated.
View local diagnosis logs
You can find diagnosis logs in the sandbox directory, as shown in the following figure. This type of logs are not reported by default. The console delivers a command to extract the logs when required.
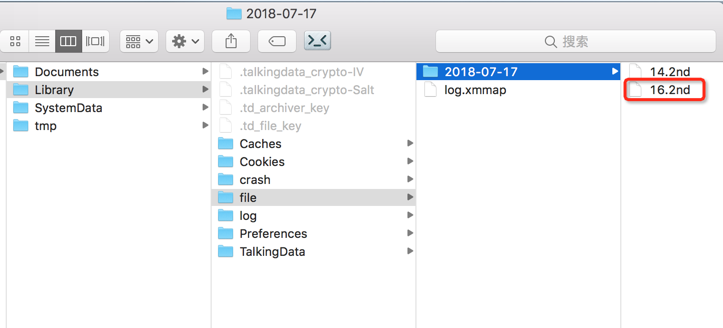
- Retention period: 6 days by default. If the SDK detects that the file of logs of the previous 3 days exceeds 30 MB, the logs of the previous 3 days are all deleted.
- File size: not more than 100 MB by default When the file size exceeds 100 MB, earlier logs of a half size are deleted. For example, if the file size is 120 MB, 60 MB logs are deleted.
Obtain online user diagnosis logs
After your App is released and goes online, if you need to obtain the local diagnosis logs on the client for troubleshooting, you can deliver a command in the mPaaS console to obtain related diagnosis logs. For detailed operations, see Mobile Analysis > Extract logs.