Learn about the use cases for API authorization. This topic describes how to enable API authorization, configure authorization rules, define authorizer interfaces, and apply these rules to your APIs.
Function Introduction
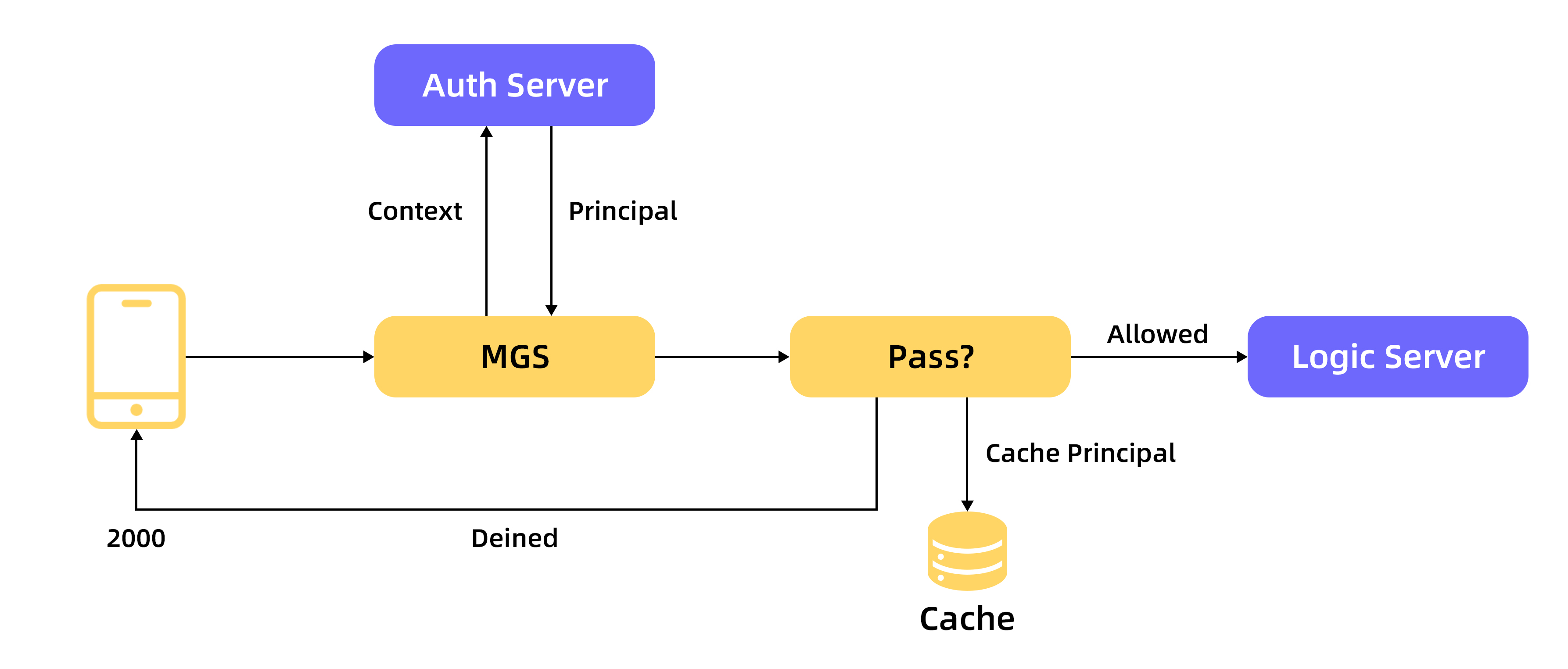
The API authorization feature lets you define general API access authorization rules on the Mobile Gateway Service (MGS):
You can create and configure an authorizer API (API A) in gateway management and then associate it with a business API (API B) in the configuration of API B.
When a client sends a request to the backend business API (API B), MGS extracts authorization parameters from the request header or cookie based on the API authorization configuration. MGS then places these parameters into the context and calls the associated authorizer API (API A). The server for API A must perform a business permission check using the parameters in the context.
If the check is successful, MGS adds the result, called the principal, to the request header and forwards the request to the backend business API (API B). If caching is enabled, MGS caches the principal to improve authorization performance.
Scenarios
Scenario one
A customer has a distributed session. After a user logs on, a session ID is generated. The authorization process is as follows:
User A requests to log on. After a successful logon, a session ID and session information are generated and saved to a distributed cache, such as
sessionId: {username:A, age:18, ...}. The session ID is then sent to the client.User A requests an API that requires logon authorization. The gateway retrieves the session ID from the request header and sends it to the authorization system. The authorization system uses the session ID to retrieve the user information from the distributed cache and returns
{username:A, age:18,...}to the gateway.The gateway confirms that the logon was successful, adds
{username:A, age:18,...}to the request header, and forwards the request to the backend business server.
Scenario two
This scenario describes a client-side authorization scheme based on a Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC). The process is as follows:
After User A logs on successfully, a token is sent to the client, such as
token=hmac(username+password).User A requests an API that requires logon authorization. The gateway retrieves the token from the header and sends it to the authorization system. The authorization system recalculates the HMAC. If the tokens match, the system returns the user information, such as
{username:A, age:18,...}, to the gateway.The gateway confirms that the logon was successful, adds
{username:A, age:18,...}to the request header, and forwards the request to the backend business server.
Procedure
Configure authorization rules
Log on to the mPaaS console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Background connection > Mobile Gateway Service.
Select the Gateway Management tab. Under API Authorization, click Create authorization API. Alternatively, in the list of existing authorization rules, find the rule that you want to modify and click Details in the Actions column. The authorization rule configuration page opens:
Authorization API name: Required. The name of the authorization rule.
Authorization API: Required. The API is used to verify the authorization of the request.
Cache authorization result: Indicates whether to cache the verification result of authorization.
Cache TTL: the cache lifetime of the verification result.
Identity source: If you click Add source field, enter the request parameters that is used for authorization and the request identity, which consists of the following fields:
Location: the location,
headerorcookie, of the parameter.Field: the name of the parameter.
NoteIf the identity source field is missing from the API request, the authorization validation fails.
Define the authorizer interface
If the authorization interface provided by the backend system is of the HTTP type, you must configure the authorization API to use the POST method.
Before you add an authorization relationship, you must develop an Auth API in your business system. When an API requires authorization validation, it calls the Auth API to perform the check. The Auth API request and response must follow these standards:
AuthRequest
public class AuthRequest {
private Map<String,String> context;
}AuthResponse
public class AuthResponse {
private boolean success;
private Map<String,String> principal;
}Interface example
@PostMapping("/testAuth")
public AuthResponse testAuth(@RequestBody AuthRequest authRequest) {
String sid = authRequest.getContext().get("sid");
Map<String, String> principal = new HashMap<>();
principal.put("uid", sid + "_uid");
AuthResponse authResponse = new AuthResponse();
authResponse.setSuccess(true);
authResponse.setPrincipal(principal);
return authResponse;
}If the
successfield in the authorization response istrue, the gateway caches theprincipalinformation based on the cache policy. The gateway then adds theprincipalinformation to the request header and passes it to the backend business system. If there is no principal, you must still pass an empty Map.If the
successfield in the authorization response isfalse, the gateway returns error code 2000. The client must then perform a corresponding action, such as displaying a logon dialog box.
Use authorization rules
After you configure an authorization rule, go to the API configuration page. Under Advanced Settings > API Authorization, select the rule to enable authorization for the API.
To use API authorization, make sure that the API Authorization feature is enabled on the Manage gateway page. To enable the feature:
Log on to the mPaaS console. In the left navigation pane, click the Mobile Gateway Service menu.
On the Manage gateway tab, ensure that the API Authorization button is turned on.
Before the API sends a request to the backend system, it performs an authorization check. If the check passes, the gateway accepts the request and routes it to the backend system. Otherwise, the gateway rejects the request, and the caller receives an authorization failed error response.