If you use baseline 10.2.3 or later, use the native AAR method.
The component-based connection type (Portal & Bundle) requires Android Studio Flamingo (2022.2.1) or an earlier version.
The component-based framework is an mPaaS framework based on Open Service Gateway Initiative (OSGi) technology. It divides an app into one or more business-independent Bundle projects and one Portal project. mPaaS manages the lifecycle and dependencies of each Bundle project, and the Portal project merges all Bundle project packages into a runnable .apk package.
The mPaaS framework is ideal for team-based app development. It includes features such as component initialization and instrumentation to help you easily integrate mPaaS components.
Bundle projects
A traditional native project consists of a main module and, optionally, several sub-modules. An mPaaS Bundle project typically consists of a main module named app and several sub-modules.
For example, in Alipay, a Bundle typically consists of a main module named app and the following three sub-modules:
api: Contains only interface definitions.
biz: Contains implementations of the interfaces.
ui: Contains activities, custom views, and other UI-related components.
A Bundle must have at least one sub-module named api. Without this sub-module, the Bundle's interface package cannot be created, which prevents other Bundles from depending on it.
This topic describes Bundle projects from the following aspects:
Differences between Bundle and traditional projects
A Bundle is essentially a native project. The main difference is that the mPaaS Apply plugin is added to the build.gradle files of the project, main module, and sub-modules. The differences are found in the following files:
The
build.gradlefile in the project root directoryThe
build.gradlefile of the main moduleThe
build.gradlefile of a sub-module
build.gradle in the project root directory
In the build.gradle file in the project's root directory, a dependency on the mPaaS plugin is added:
The plugin version may increase as features are added in new iterations.
classpath 'com.alipay.android:android-gradle-plugin:3.0.0.9.13'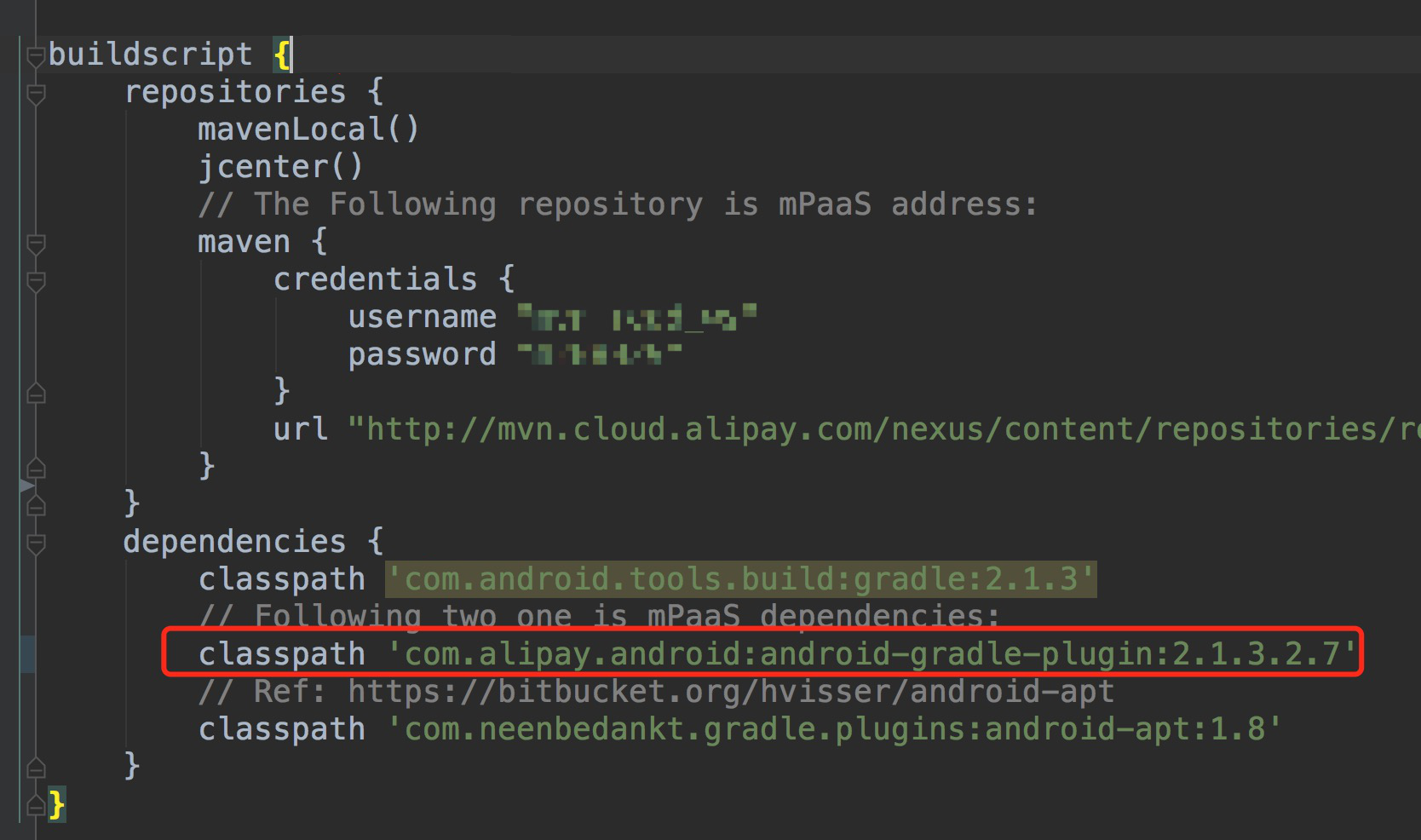
build.gradle of the main module
In the build.gradle file of the main module, a declaration for the mPaaS Bundle Apply plugin is added. This indicates that the project is a Bundle project. The Bundle configuration is as follows:
apply plugin: 'com.alipay.bundle'The following configuration is also added to the build.gradle file of the main module:
Where:
version: The version of this Bundle.group: The group ID of this Bundle.exportPackages: Specifies the package names that contain all classes of the current Bundle project. You can specify a parent package name. For Bundles that are not statically linked, you must specifyexportPackages. Otherwise, classes may fail to load. For example, if all code is undercom.alipay.demoandcom.alipay.bundle, you can specifycom.alipayinexportPackages. You can also specifycom.alipay.demoandcom.alipay.bundle. Avoid using package names that are too generic or too specific.initLevel: Specifies when the framework loads this Bundle during startup. The range is from 0 to 100. A lower value means the Bundle is loaded earlier. A value of11110000indicates lazy loading, meaning the Bundle is loaded on demand.packageId: Specifies the resource ID of the current Bundle. This ID is required for aapt packaging and must be unique for each Bundle in a multi-Bundle architecture. The packageIds currently used by mPaaS are as follows:
Bundle | packageId |
com.alipay.android.phone.thirdparty:androidsupportrecyclerview-build | 28 |
com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-build | 30 |
com.alipay.android.phone.rome:pushservice-build | 35 |
com.alipay.android.phone.sync:syncservice-build | 38 |
com.alipay.android.phone.wallet:nebulabiz-build | 41 |
com.alipay.android.phone.mobilecommon:share-build | 42 |
com.alipay.android.phone.wallet:nebulacore-build | 66 |
com.alipay.android.mpaas:scan-build | 72 |
com.alipay.android.phone.wallet:nebula-build | 76 |
com.alipay.android.phone.securitycommon:aliupgrade-build | 77 |
The following mPaaS dependencies are added in dependencies:
dependencies {
compile project(":api")
apt 'com.alipay.android.tools:androidannotations:2.7.1@jar'
//mPaaS dependencies
provided 'com.alipay.android.phone.thirdparty:fastjson-api:1.1.73@jar'
provided 'com.alipay.android.phone.thirdparty:androidsupport-api:13.23@jar'
}build.gradle of a sub-module
In the build.gradle file of a sub-module, a declaration for the mPaaS Apply plugin is added. This indicates that the project is a sub-module of a Bundle. This process ultimately creates the Bundle's interface package.
apply plugin: 'com.alipay.library'The following mPaaS dependencies are added in dependencies:
dependencies {
apt 'com.alipay.android.tools:androidannotations:2.7.1@jar'
//mPaaS dependencies
provided "com.alipay.android.phone.thirdparty:utdid-api:1.0.3@jar"
provided "com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-api:2.1.1@jar"
}Bundle properties
The design of the Bundle properties in this framework is based on OSGi Bundles, but is simpler and more lightweight.
The following table lists the Bundle properties and their descriptions.
Property | Description |
Bundle-Name | The Bundle name. It is derived from the |
Bundle-Version | The Bundle version. It comes from the |
Init-Level | The loading time of the Bundle. It comes from the |
Package-Id | The package ID of the Bundle's resources. It comes from the properties defined in the |
Contains-Dex | Indicates whether the Bundle contains a DEX file. The compile plugin determines this automatically. |
Contains-Res | Indicates whether the Bundle contains resources. The compile plugin determines this automatically. |
Native-Library | The |
Component-Name | Comes from the |
exportPackages | The package names that contain all classes of this Bundle. For more information, see the |
Bundle interface packages
A Bundle can contain multiple sub-modules, such as biz, api, and ui. When you compile and package a Bundle, each sub-module generates an interface package in .jar format. Other Bundles can use the api interface package.
During packaging, a Bundle project package is also generated. This project package contains all sub-modules and can be used by the Portal project. The project package is compiled in the Portal to generate the final .apk package.
The interface package created from a Bundle's sub-module contains only the defined Java or Kotlin interface classes. It does not include other resources, such as resources in the res directory. Only sub-modules named api can generate these interface packages.
Bundle projects depend on each other through their interface packages. To create a dependency, you must configure it in the
dependencysection of the bundle'sbuild.gradlefile. For example, if Bundle A depends on thebapisub-module in Bundle B, configure the dependency onbapiin thedependencysection of the corresponding sub-module'sbuild.gradlefile in Bundle A.provided "com.alipay.android.phone:bundleB:1.0.1:bapi@jar"The
groupId:artifactid:version:classifierin the dependency corresponds to the group, name, version, and sub-module name declared in the Bundle.By default, the Bundle's name is the folder name of the main module. You can change it in
settings.gradle, as shown in the following code. In this example, app is the project name of the main module:include ':api', ':xxxx-build' project(':xxxx-build').projectDir = new File('app')
Bundle project packages
The
.jarpackage created from the entire Bundle project is actually a file in.apkformat, but it has a.jarextension, such asframework-build.jar.To depend on a Bundle in a Portal, declare the dependency on the Bundle package in the
dependencysection of the Portal's main module'sbuild.gradlefile, as shown below:dependencies { bundle "com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-build:version@jar" manifest "com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-build:version:AndroidManifest@xml" }There are two types of Bundle packages: debug and release. When a Portal depends on a Bundle's debug package, you must add
:rawto the dependency.When the Portal depends on the Bundle's debug package:
bundle "com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-build:version:raw@jar"When the Portal depends on the Bundle's release package:
bundle "com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:framework-build:version@jar"
When packaging a Portal, you need to determine the following:
Which Bundles to package into the app's main DEX file. Bundles that are statically linked and contain a
ContentProvidermust be included.Which Bundles to load dynamically. For small apps, you can package all Bundles in the main DEX file.
To package a Bundle's code into the main DEX file, configure the Bundle in the Portal's
slinksfile. The configuration format isgroupId-artifactId. If the artifactId ends with-build, remove it. For example, if the groupId iscom.mpaas.groupand the artifactId istestBundle-build, add the linecom.mpaas.group-testBundleto theslinksfile.Static linking packages the Bundle's code into the
APK'sclasses.dex,classes1.dex,classes2.dex, and other DEX files. This allows the classes in the Bundle to be loaded at project startup.
Portal projects
A Portal project merges all Bundle project packages into a runnable .apk package.
Differences between Portal and traditional projects
The difference between a Portal project and a traditional project lies in the build.gradle file:
build.gradlein the project root directorybuild.gradlein the main module directory
build.gradle in the project root directory
As shown in the following figure, the com.alipay.android:android-gradle-plugin:2.1.3.2.7 plugin is added to the classpath:
The plugin version may increase as features are added in new iterations.
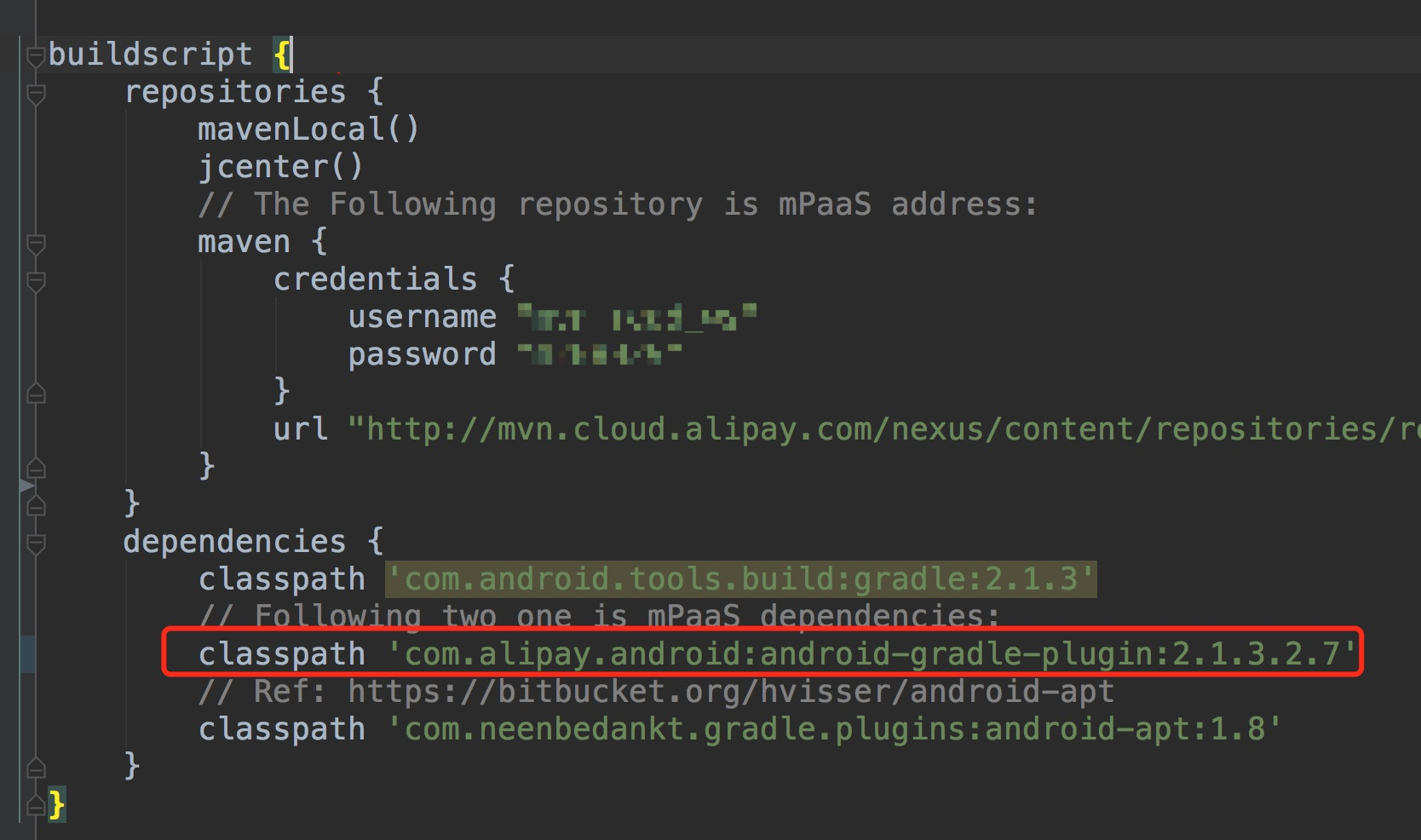
This plugin contains the Portal plugin, which merges Bundles during the packaging process.
Merged
.jarbundleMerging the bundle's
AndroidManifest
build.gradle in the main module directory
A declaration for the mPaaS Apply Portal plugin is added. This indicates that the project is a Portal project. The Portal configuration is as follows:
apply plugin: 'com.alipay.portal'You also need to add the corresponding Bundle dependencies to the dependencies block. The statements in dependencies declare the bundles and manifests that the Portal depends on:

Typically, you do not write code in a Portal project.
The following types of resources from a Bundle project, such as styles, drawables, and strings, must be placed in the Portal project. Otherwise, the resources cannot be found during compilation or at runtime:
Resources used in
AndroidManifest.xml.Resources passed to NotificationManager.
Resources used through the
getResources().getIdentifier()method.If a referenced third-party
AARpackage contains any of the three preceding resource types, you must also decompress theAARand copy the corresponding resources to the Portal project.
Project dependencies
An app based on the mPaaS framework includes one or more Bundles and one Portal. An app can have only one Portal project but can have multiple Bundle projects.
The mPaaS plugin merges all Bundle project packages in the Portal project into a runnable .apk package. After the merge, the plugin deploys the Bundle project to a specified repository. This repository address is defined in the build.gradle file of the Bundle's main module, as shown in the following code:
uploadArchives {
repositories {
mavenLocal()
}
}By default, this address points to the local ~/.m2 repository for uploads. You can also add a custom repository address, as shown below:
mavenDeployer {
mavenLocal()
repository(url: "${repository_url}") {
authentication(userName: 'userName', password: 'userName_pwd')
}
snapshotRepository(url: "${repository_url}") {
authentication(userName: 'userName', password: 'userName_pwd')
}
}After the upload, the Bundle is available in the specified repository in the format groupid:artifactid:version:classifier@type. Therefore, you can specify dependencies for each Bundle by declaring them in the dependency section of the Portal's main module's build.gradle file, as shown below:
dependencies {
bundle 'com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:quinox-build:2.2.1.161221190158:nolog@jar'
manifest 'com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:quinox-build:2.2.1.161221190158:AndroidManifest@xml'
}Similarly, for dependencies between Bundle projects, you must declare the repository address in the root build.gradle file of the dependent Bundle.
The username and password in the following configuration are not your console logon credentials. To obtain these values, search for and join the DingTalk group with the ID 145930007362. The parameters are described as follows:
mavenLocal()specifies the local repository address for dependencies.maven{}declares the remote repository address for dependencies.
allprojects {
repositories {
mavenLocal()
mavenCentral()
maven {
credentials {
username "{username}"
password "{password}"
}
url "http://mvn.cloud.alipay.com/nexus/content/repositories/releases/"
}
}
}Bundle compilation and packaging results
After you compile and package a Bundle using the mPaaS plugin, a project package (a .jar package) is generated. For more information, see Bundle project packages and Bundle interface packages.
The project package is published to the specified repository in the groupid:artifactid:version:classifier@type format. The publishing repository address is defined in the build.gradle file of the Bundle's main module, as shown in the following example:
uploadArchives {
repositories {
mavenLocal()
}
}The preceding configuration specifies the local Maven repository (mavenLocal) as the publishing repository. To change the local Maven repository address (default: ~/.m2) or add a publishing repository, see Configure a publishing repository.
Add Bundle dependencies
You can add a dependency on a Bundle from within a Portal, or add a dependency on one Bundle from another. To do so, follow these steps:
Declare the dependency repository address in the root
build.gradlefile of the Portal or Bundle. The dependency repository must correspond to the Bundle's publishing repository. For more information about how to configure a dependency repository, see Configure a dependency repository.You can declare the
dependenciesin thebuild.gradlefile of the main module of the Portal or Bundle. The following example shows how to add a dependency on thequinoxBundle:
dependencies {
bundle 'com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:quinox-build:2.2.1.161221190158:nolog@jar'
manifest 'com.alipay.android.phone.mobilesdk:quinox-build:2.2.1.161221190158:AndroidManifest@xml'
}