Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) supports a combined topic-and-queue pattern that delivers each published message to multiple consumer queues. Consumers pull messages from their own queues, so their endpoints stay private. This tutorial walks through this fan-out architecture with the SMQ Java SDK.
This tutorial uses the SDK for Java. For SDKs in other languages, see Reference for New Version SDKs (Recommended).
Messaging model comparison
SMQ provides two base messaging models. The right choice depends on how consumers receive messages and whether their endpoints can be exposed.
| Model | How it works | Consumer visibility | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Queue-based | One client sends messages to a queue. Multiple consumers pull messages, but each message goes to only one consumer. | Endpoints stay private | Point-to-point task distribution |
| Topic-based | One client publishes messages to a topic. The SMQ server pushes messages to all subscribed consumers. | Endpoints must be exposed | Real-time push notifications |
| Combined (this tutorial) | One client publishes to a topic. The topic pushes messages into multiple queues. Each consumer pulls from its own queue. | Endpoints stay private | Fan-out with private consumers |
The combined pattern suits scenarios where a message must reach multiple consumers whose endpoints cannot be exposed -- for example, consumers running inside a private network.
Example scenario: An order processing system publishes each new order to a topic. Separate queues feed into fulfillment, analytics, and notification services. Each service pulls orders from its own queue independently, without exposing an inbound endpoint.
How it works
The combined pattern chains a topic with multiple queues through subscriptions:
Create a topic and one queue per consumer.
Subscribe each queue to the topic (the queue endpoint becomes the subscription target).
The producer publishes a message to the topic.
SMQ copies the message into every subscribed queue.
Each consumer pulls its copy from its own queue.
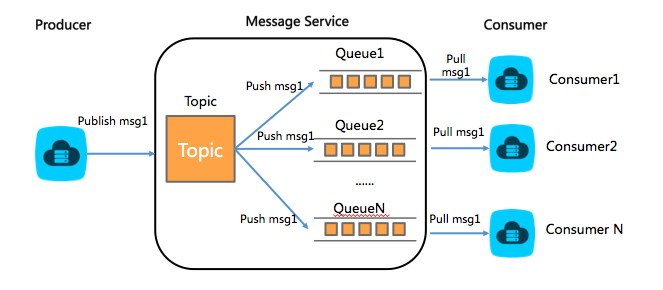
Because consumers pull from queues rather than receiving pushed messages, their endpoints are never exposed to the SMQ server or to each other.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that you have:
IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse installed (this tutorial uses IntelliJ IDEA)
JDK 1.8 or later
Apache Maven 2.5 or later
Install the Java dependency
Add the following dependency to the pom.xml file of your Java project:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.mns</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-mns</artifactId>
<version>1.1.9.2</version>
</dependency>CloudPullTopic API reference
SDK for Java 1.1.8 introduced the CloudPullTopic class that encapsulates the combined topic-and-queue pattern. Create a CloudPullTopic object through MNSClient:
// Full form: create queues automatically with a queue metadata template
public CloudPullTopic createPullTopic(
TopicMeta topicMeta,
Vector<String> queueNameList,
boolean needCreateQueue,
QueueMeta queueMetaTemplate
)
// Short form: use existing queues (no automatic creation)
public CloudPullTopic createPullTopic(
TopicMeta topicMeta,
Vector<String> queueNameList
)| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
topicMeta | Metadata of the topic (name, properties). |
queueNameList | List of queue names. Each queue receives a copy of every published message. |
needCreateQueue | Whether to create the queues listed in queueNameList. Set to true to create them automatically. |
queueMetaTemplate | Queue metadata template applied to all auto-created queues (e.g., polling wait time). |
Publish and consume messages
The following sample uses CloudPullTopic to set up the fan-out, publish a message, and consume it from three separate queues.
package doc;
import com.aliyun.mns.client.CloudAccount;
import com.aliyun.mns.client.MNSClient;
import com.aliyun.mns.client.CloudPullTopic;
import com.aliyun.mns.client.CloudQueue;
import com.aliyun.mns.model.QueueMeta;
import com.aliyun.mns.model.TopicMeta;
import com.aliyun.mns.model.TopicMessage;
import com.aliyun.mns.model.RawTopicMessage;
import com.aliyun.mns.model.Message;
import com.aliyun.mns.common.ServiceException;
import com.aliyun.mns.common.ClientException;
import java.util.Vector;
public class DemoTopicMessageBroadcast {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize the client with your AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and endpoint.
CloudAccount account = new CloudAccount(
ServiceSettings.getMNSAccessKeyId(),
ServiceSettings.getMNSAccessKeySecret(),
ServiceSettings.getMNSAccountEndpoint());
MNSClient client = account.getMNSClient();
// Define three consumer queues.
Vector<String> consumerNameList = new Vector<String>();
String consumerName1 = "consumer001";
String consumerName2 = "consumer002";
String consumerName3 = "consumer003";
consumerNameList.add(consumerName1);
consumerNameList.add(consumerName2);
consumerNameList.add(consumerName3);
// Set long polling to 30 seconds for the auto-created queues.
QueueMeta queueMetaTemplate = new QueueMeta();
queueMetaTemplate.setPollingWaitSeconds(30);
try {
// --- Producer: create a topic and publish a message ---
String topicName = "demo-topic-for-pull";
TopicMeta topicMeta = new TopicMeta();
topicMeta.setTopicName(topicName);
// Create the topic and auto-create the three consumer queues.
CloudPullTopic pullTopic = client.createPullTopic(
topicMeta, consumerNameList, true, queueMetaTemplate);
// Publish a raw message to the topic.
String messageBody = "broadcast message to all the consumers:hello the world.";
TopicMessage tMessage = new RawTopicMessage();
tMessage.setBaseMessageBody(messageBody);
pullTopic.publishMessage(tMessage);
// --- Consumers: pull the message from each queue ---
CloudQueue queueForConsumer1 = client.getQueueRef(consumerName1);
CloudQueue queueForConsumer2 = client.getQueueRef(consumerName2);
CloudQueue queueForConsumer3 = client.getQueueRef(consumerName3);
// popMessage(30) waits up to 30 seconds for a message (long polling).
Message consumer1Msg = queueForConsumer1.popMessage(30);
if (consumer1Msg != null) {
System.out.println("consumer1 received: "
+ consumer1Msg.getMessageBodyAsRawString());
} else {
System.out.println("consumer1 queue is empty");
}
Message consumer2Msg = queueForConsumer2.popMessage(30);
if (consumer2Msg != null) {
System.out.println("consumer2 received: "
+ consumer2Msg.getMessageBodyAsRawString());
} else {
System.out.println("consumer2 queue is empty");
}
Message consumer3Msg = queueForConsumer3.popMessage(30);
if (consumer3Msg != null) {
System.out.println("consumer3 received: "
+ consumer3Msg.getMessageBodyAsRawString());
} else {
System.out.println("consumer3 queue is empty");
}
// Clean up: delete the topic, its subscriptions, and all associated queues.
pullTopic.delete();
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Network error between the client and SMQ. "
+ "Check your network and DNS settings.");
ce.printStackTrace();
} catch (ServiceException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}
client.close();
}
}Verify the result
After you run the sample code, confirm that each consumer received the message. The expected output:
consumer1 received: broadcast message to all the consumers:hello the world.
consumer2 received: broadcast message to all the consumers:hello the world.
consumer3 received: broadcast message to all the consumers:hello the world.If a queue shows "queue is empty", the message may not yet be delivered. Increase the popMessage timeout or check whether the topic and subscriptions were created correctly.
Code walkthrough
| Step | What happens |
|---|---|
Initialize CloudAccount | Authenticates with your AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and SMQ endpoint. |
Call createPullTopic | Creates the topic, creates the three consumer queues, and subscribes each queue to the topic. |
Call publishMessage | Publishes a raw message (RawTopicMessage) to the topic. SMQ copies it into all subscribed queues. |
Call popMessage(30) | Each consumer pulls its copy with a 30-second long-polling timeout. |
Call pullTopic.delete() | Deletes the topic, its subscriptions, and all associated queues. |
The sample publishes a raw message (RawTopicMessage). Parse raw messages withgetMessageBodyAsRawString(). If you useBase64TopicMessageinstead, parse withgetMessageBodyAsString().
Next steps
Explore other SMQ messaging patterns in Reference for New Version SDKs (Recommended).